Updated May 22, 2023

Introduction to PostgreSQL ALTER TABLE
PostgreSQL alter table statement is used to change the table structure, we can change the table name, and column name, add or drop the table column, add or drop the constraint from the table, set a new schema to the table. To use alter table statement in PostgreSQL, we need to have the owner of table privileges or superuser privileges to execute the alter table statement. Alter table statement is used to delete, add, and modify the structure of the existing table in PostgreSQL.
Syntax of PostgreSQL ALTER TABLE
Below is the syntax :
1. Alter table to change the name of the table
Alter table name_of_table RENAME TO new_name_of_table;2. Alter table to add a column
Alter table name_of_table ADD name_of_column data_type_of_column;3. Alter table to drop column
Alter table name_of_table DROP name_of_column;4. Alter table to change the data type of the column
Alter table name_of_tableALTER COLUMN name_of_column type data_type_of_column;5. Alter table to set a new schema
Alter table name_of_table SET SCHEMA new_schema_name;6. Alter table to rename the column
Alter table name_of_table rename column old_column_name to new_column_name;7. Alter column to add a not-null constraint
Alter table name_of_table modify name_of_column data_type not null;8. Alter table to drop constraint
Alter table name_of_table drop constraint name_of_constraint;9. Alter table to change the tablespace
Alter table name_of_table set tablespace name_of_tablespace;Parameters
Below is the parameter description syntax of the alter table statement in PostgreSQL.
- Alter table –This statement is used to change the table structure in PostgreSQL.
- Name of the table –This is defined as the table name we used to change the table structure.
- Rename to – We use the RENAME TO keyword to change the name of a table. We can use the rename keyword to change the table name.
- The new name of the table –This is the newly created name of the table which was we have modified with alter table statement.
- Add column –We can add a column of the table by using add column keyword with alter table statement.
- Column name – The column name is the name of the column that we have changed using the ALTER TABLE statement.
- The data type of the column –This is defined as the data type which was we have allocated to the column.
- Modify – We use the MODIFY keyword to modify a column and add a NOT NULL constraint in PostgreSQL.
- Set tablespace – We use the SET TABLESPACE command in the ALTER TABLE statement to assign a new tablespace to a table.
- Set schema – The SET SCHEMA command, used with the ALTER TABLE statement, sets a new schema for a table.
- Drop constraint – The DROP CONSTRAINT command is used in conjunction with the ALTER TABLE statement to remove a constraint from a table.
How to ALTER TABLE statement work in PostgreSQL?
Below is the working of the alter table statement in PostgreSQL. The ALTER TABLE command in PostgreSQL modifies the structure of a table.
The below example shows that we need to have privileges of the owner of the table or superuser privileges.
psql -U db_test -d testing
ALTER TABLE student DROP stud_id;
psql -U Postgres
\c testing
ALTER TABLE student DROP stud_id;
\d+ student;
In the above first example, we have used the user as db_test, this user doesn’t have the privileges of table owner or superuser, so it will issue an error while executing the alter table statement.
In the second example, we have altered the table using the username as Postgres, after using this user, we have to drop the column name of stud_id from the student table.
Alter table is used to do the following action on the table are as follows.
- Change the name of the table.
- Add column.
- Drop column.
- Change the schema of the table.
- Change the tablespace of the table.
- Add a constraint to the table.
- Drop constraint from the table.
- Rename column.
- Add not null constraint.
Examples
Below is an example of the alter table statement in PostgreSQL are as follows. We have using stud1 and stud2 tables to describe examples of the alter table statement.
Below is the table description of stud1 and stud2 table.
\d+ stud1;
\d+ stud2;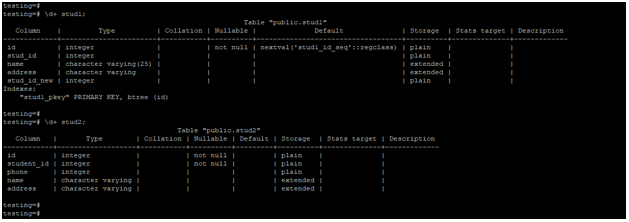
Example #1 – Alter table to change the name of the table
Below example shows that alter a table to change the name of the table. We have to change the stud1 table name to student1.
Alter table stud1 RENAME TO student1;
\d+ student1;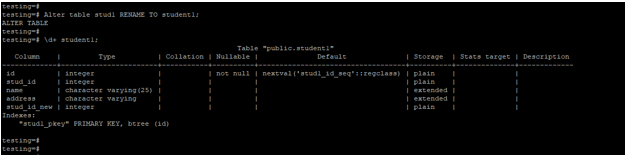
Example #2 – Alter table to add a new column
Below example shows that alter the table to add the new column. We have added the test_stud column to the student1 table.
Alter table student1 ADD test_stud varchar;
\d+ student1;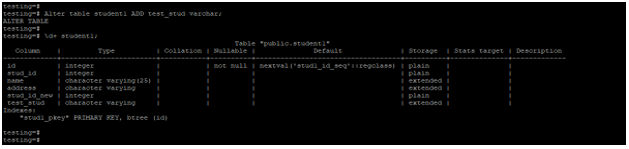
Example #3 – Alter table to drop column
Below example shows that alter the table to drop the column. We have dropped the test_stud column from the student1 table.
Alter table student1 DROP COLUMN test_stud;
\d+ student1;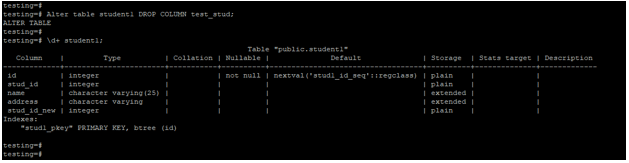
Example #4 – Alter table to change the schema of the table
The below example shows that change in the schema of the stud2 table. We have changed the schema public to my_schema.
Alter table stud2 SET SCHEMA my_schema;
\d+ my_schema.stud2;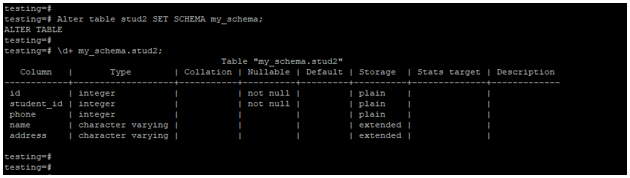
Example #5 – Alter the table to change the tablespace of a table
The below example shows that change in the tablespace of the stud2 table. We have changed tablespace from default to my_test.
Alter table my_schema.stud2 set tablespace my_test;
\d+ my_schema.stud2;
Example #6 – Alter the table to rename the column
Below example shows that alter the table to rename the column. We have to change the id column to the id1 column.
Alter table my_schema.stud2 rename column id to id1;
\d+ my_schema.stud2;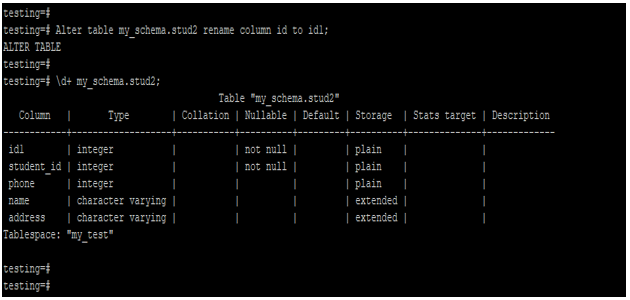
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL ALTER TABLE” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

