Introduction to PostgreSQL ALTER DATABASE
PostgreSQL alter database statement is used to alter the database features like changing the ownership, change the name of the database, set the new tablespace of the database, and set the configuration parameter for the database. Alter database command is essential and useful in PostgreSQL to change the feature of the database. To change the database settings, we need to privilege of database owner or admin user of the database. If we want to change the name of the database, we have used alter database command in PostgreSQL; also, if we want to change the database’s ownership, we have used the same command.
Syntax
Below is the syntax of the alter database statement in PostgreSQL.
1. Change the name
Alter database name_of_database rename to new_database_name;2. Change ownership
Alter database name_of_database owner to new_owner_of_the_database;3. Change the tablespace
Alter database name_of_database set tablespace new_tablespace_name;4. Change the defaults runtime parameter
Alter database name_of_database set configuration_parameter = value (New value of database which we have setting.)Parameters
Below is the parameter description syntax of alter database statement in PostgreSQL.
- Alter database: The “ALTER DATABASE” statement is used in PostgreSQL to change the features of a database.
- Database name: We changed the features of the database, and the name of the database from which we made these changes is referred to as the database name.
- Owner: This keyword is defined as changing the ownership of the database. We have to change the database ownership by using alter database statements. We have to change the database owner after the database creating.
- Rename: This keyword is defined as changing the name of the database. We have to change the name of the database by using the alter database statement. We have to change the database name after database creation.
- Tablespace: This keyword is defined as changing the tablespace of the database. We have to change the tablespace of the database by using the alter database statement. We have to change the database tablespace after database creation.
- New tablespace name: We have defined a new tablespace name for the database.
- Configuration parameter: Changing the configuration parameter of the database is the definition of a configuration parameter. We have to change the database configuration parameter by using the alter database statement.
- New database name: We have defined a new database name for the database.
- New owner: The new owner, which we have defined in the database, is the name assigned to the ownership of the database.
How to ALTER DATABASE statement work in PostgreSQL?
Below is the working of the alter database statement.
- If we have to use alter database statements in PostgreSQL, we need to have privileges of the owner of the database or need to have admin privileges.
- The below example shows we need to have privileges of admin or owner of the database to use the alter database statement in PostgreSQL.
psql -U db_test -d db_testing
alter database db_testing rename to db_testing_new;
psql -U postgres
alter database db_testing rename to db_testing_new;
\l+Output:
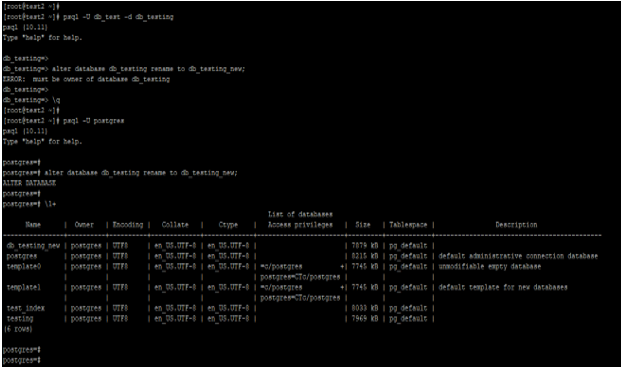
- The above first example shows that we have to alter the database using the username as db_test, but it will not work; it shows the error as “ERROR: must be the owner of database db_testing”.
- In the second example, we have altered the database using the username as Postgres; after using this user, we have changed the database’s name to db_testing_new.
- We can also set the concurrent connection limit to the database using the alter database statement in PostgreSQL.
- We can set the session default setting by using the given configuration parameter. When you set the value to the default, new sessions inherit the system-wide settings, and they remove any database-specific settings.
- We can also disable an index scan of the database using the alter database statement in PostgreSQL.
- PostgreSQL uses the “ALTER DATABASE” command as an extension for modifying databases. We can change the attribute of the database by using an alter statement.
Examples
Below are the examples mentioned:
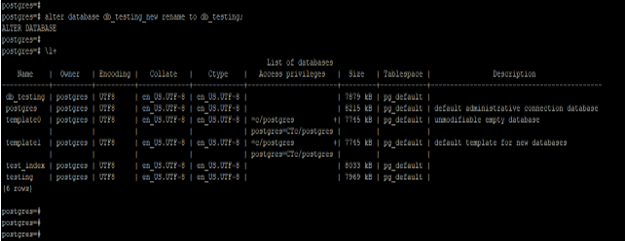
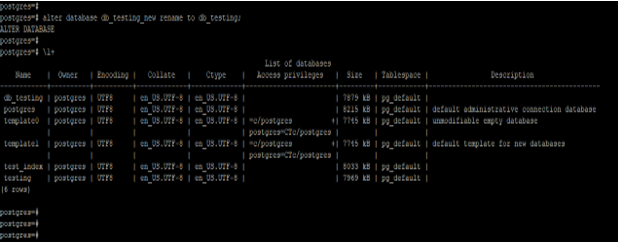
1. Change the Name
Below example shows that alter the database to change the database name. We are changing the database name of db_testing_new to db_testing using alter database statement. We have used Postgres user to change the name of the database in PostgreSQL.
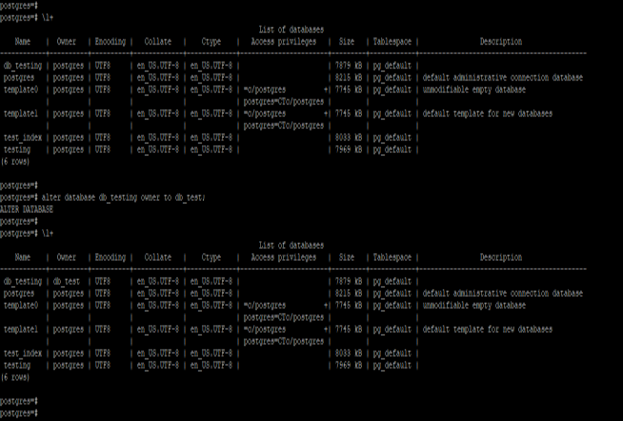
2. Change the Ownership
Below example shows that alter the database to change the database ownership. We are changing the db_testing database ownership from Postgres user to db_test user using alter database statement. We have used Postgres user to change the ownership of the db_testing database in PostgreSQL.
Code:
\l+
alter database db_testing owner to db_test;
\l+Output:
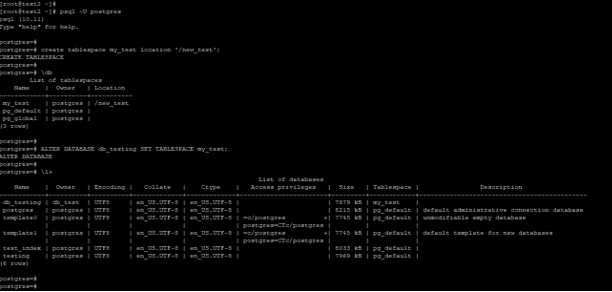
3. Change the Tablespace
Below example shows that alter the database to change the database tablespace. Using the alter database statement, we are changing the db_testing database tablespace from the default tablespace to the my_test tablespace. We have used Postgres users to change the tablespace of the db_testing database in PostgreSQL.
Code:
create tablespace my_test location '/new_test';
\db
ALTER DATABASE db_testing SET TABLESPACE my_test;
\l+Output:
4. Configuration Parameter
Below example shows that alter the database to change the database configuration parameter. We have to change the database configuration parameter to disable the index scan of db_testing using alter database statement. We have used Postgres users to change the configuration parameter of the db_testing database in PostgreSQL.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL ALTER DATABASE” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

