Updated May 25, 2023
Introduction to Postgres Switch Database
Whenever you use the database to store the data of your application or program or for some other reason, you often feel the need to create and maintain more than one database. In such cases, while working on Postgres databases and executing various queries, we must first connect with the database we wish to use. Then if you have to switch to some other database, PostgreSQL provides the metacommand \c that can be used to switch from one database to another in PostgreSQL. In this article Postgres Switch Database, we will see about \c metacommand’s syntax and try to use it in one of the examples to understand its usage.
Syntax:
\c targetdb;Or
\connect targetdb;Where,
targetdb: It is the name of the database you wish to connect to while connected to another database.
Metacommands are provided in psql for easy manipulation and working of the database related queries and making the job of database administrators easy by providing the shortcut queries that are compact and easy to use. Metacommands mostly begin with \ and are further appended with a letter of word related to the query task and then are followed by the parameters required for that query execution.\c, and \connect two metacommands provided for database switching purposes. Whenever you execute the \c or \connect command, your current connection with the current database will be closed, and a new connection with the targeted database will be established.
Example of Postgres Switch Database
Given below is the example of the Postgres Switch Database:
Upon logging in to the PostgreSQL database server, you establish an automatic connection to the default database, which is the Postgres database. This database is typically present by default after installing PostgreSQL on your system. You can even change the default database that you wish to connect to.
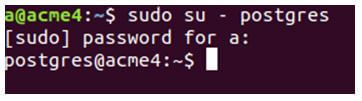
Firstly, let us login to Postgres by using the following command.
Code:
sudo su – postgresAnd enter the password that you have set.
Output:
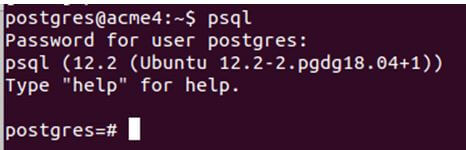
Now, you will have to enter into the psql command prompt.
Code:
psqlAnd then, enter the password if prompted. The output will be as follows with a psql command prompt shell where you can run your Postgres queries such as meta-commands.
Output:
By default, you can see you are connected to the Postgres database. The database name you are connected to can be seen from the command prompt shell; for example, postgres=# represents the same in our case.
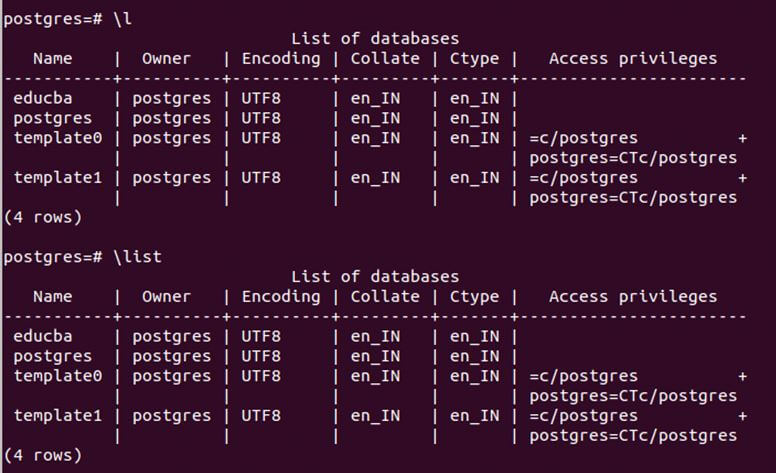
Now, we will list all the databases in our Postgres database server using the metacommand \l or \list that lists the names of all the databases in the current database server. Firing \l and \list gives the following output on my server.
Code:
\lOutput:
template0, template1, and Postgres are the default databases created whenever you install Postgres. We have created one more database named educba, which we want to switch. You can create a new database if you’re going to by using the CREATE DATABASE query.
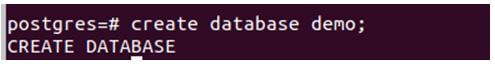
For example, we will fire the following command for creating a database named demo.
Code:
create database demo;Output:
Further, using the \l or \list command, you can verify whether your database is created successfully.
Now, we want to switch to the educba database from the current database Postgres.
For this, we can either use:
Code:
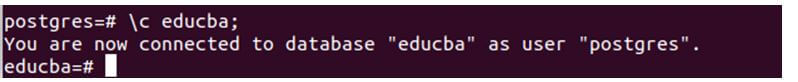
\c educba;Or
\connect educba;Output:
A message appears, indicating a successful connection to the “educba” database, along with the name of the currently connected user, which, in this case, is Postgres. Also, we can see the command prompt shell changing from postgres=# to educba=#, which ensures that we successfully switched out the database to educba. Executing the \c or \connect command closes the initially created database connection used to connect to the Postgres database. The user who logs into Postgres at that specific time creates a new database connection with “educba”.
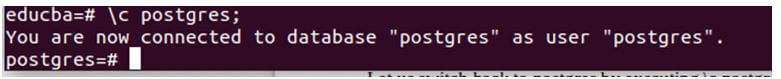
Let us switch back to Postgres by executing the \c postgres command that gives the following output.
Code:
\c postgres;Output:
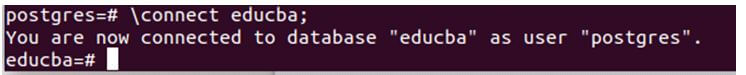
Instead of \c, let us execute \connect educba; command and check whether we can switch to the educba database.
Code:
\connect educba;Output:
That is the same as \c educba; command execution result.
Alternatively, you can connect to the “educba” database right at the beginning when opening the psql command prompt shell. This eliminates the need for any switching later on, as long as you are aware of the database’s name and it exists within your current database server.
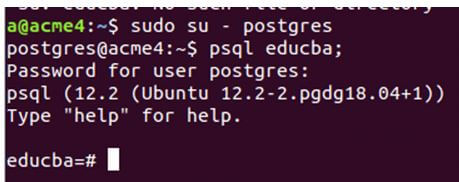
First, enter the following command to login using Postgres user and enter the password.
Code:
sudo su - postgresThen enter the command.
Code:
psql dbname;Where dbname is the database name you wish to connect to.
Code:
psql educba;Output:
As you can see, the command prompt shell opens to educba=#; hence, we are connected to the educba database with a new connection instead of the default one. In this case, when psql attempts to create a new database connection, it searches for the presence of the database named “dbname” and then establishes a connection with it. If you supply the wrong dbname, it won’t allow connecting to.
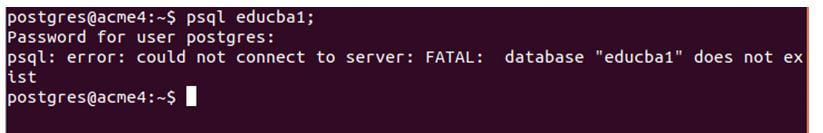
Let us try connecting to the educba1 database that is not present on my database server of Postgres using the psql educba1; command that results in the following output.
Code:
psql educba1;Saying that database doesn’t exist.
Output:
Conclusion
We can switch between the databases in PostgreSQL using \c or \connect metacommand, which creates a new connection and closes the current one. You can log in and connect to the database you want to other than the default one while opening the psql command shell itself by specifying the name of the database in the parameter of psql command, as shown above.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Postgres Switch Database” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.