Updated May 15, 2023

Introduction to Postgres Show Tables
Postgres show tables are defined as list tables from a specific database or specific schema; we can retrieve a table from the command as \dt and using the query to retrieving data from the pg_catalog schema. In MySQL, we can list all tables from the database using the show tables; in PostgreSQL, we can list all the database tables using the \dt command. To show tables from the database, we need to connect to the specific database from which we need to show the tables.
Syntax and Parameters
Below is the syntax of show tables in PostgreSQL.
1. Show tables from the database
\c database_name
\dtOR
\dt+ (Show descriptive output of show tables)2. Show specific schema tables
\dt shema_name.*OR
\dt+ shema_name.* (Show descriptive output of show tables)3. Show all schema tables
SELECT *(Show all rows from pg_tables) FROM pg_catalog.pg_tables;OR
\dt *.* (All schema and all tables)Below is the parameter description syntax of show tables in PostgreSQL
- Database name: This is defined as the database name used to connect to the database to show all tables from a connected database using the \dt command. We can use any database name to show all tables from the database.
- \dt: This command is used to show all tables from the connected database.
- \dt+: This command is used to show all table descriptive output from the connected database.
- Schema name: We define it to show all tables from the specified schema. We can use any schema name to show all tables from the schema.
- Select: Select operations are used when we show tables from the catalog schema using pg_tables.
- Pg_catalog: This schema uses the table name as pg_tables, a catalog schema in PostgreSQL.
- Pg_tables: This table is a system table that contains the information related to all tables. This contains information like table name, schema name, etc.
- \dt *.*: This is used when we want to show all the schema tables; first, * define as all schema and second, will define as all tables.
- *: This is defined as to show all tables from the specified schema. First is the schema name from which we have shown tables, the second * is defined as to show all tables from the specified schema.
How does Show Table work in PostgreSQL?
Below is the working of the show table in PostgreSQL.
It must be present on the database server to show a table from the specified database. The below example shows that we need to connect to the specified database to show the database’s table.
Code:
\dt
\c testing;
\dtIn the above example, we first connected to the default database, i.e., Postgres database; connecting to this database will only display the connected databases’ tables. In the first example, the Postgres database contained no tables to return an empty set. But in the second example, we have connected to the testing database; after connecting to the testing database, it will display all tables from the testing database.
Examples to Implement Postgres Show Tables
Below is an example of show tables in PostgreSQL.
Example #1
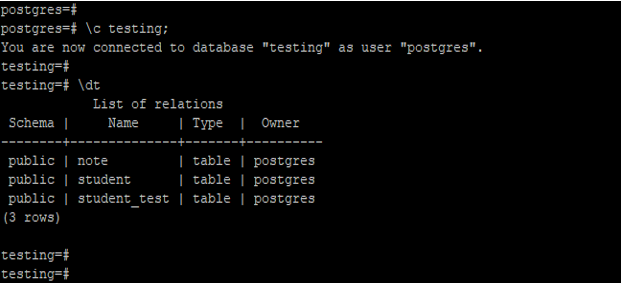
Show all tables from the specified database.
The below example shows that it display all tables from the specified database. We have to retrieve all tables from the testing database. We need first connect to the database to show tables.
Code:
\c testing;
\dtOutput:
Example #2
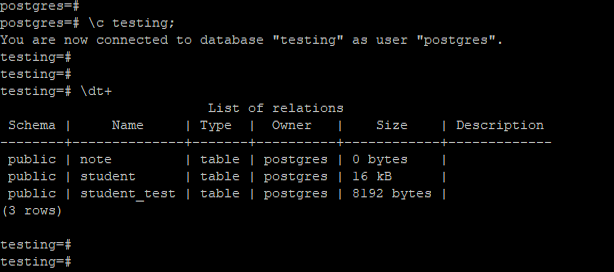
Show all tables descriptive output from the specified database.
The example below shows the descriptive output from all tables from the specified database. We have to retrieve all tables from the testing database.
Code:
\c testing;
\dt+Output:
Example #3
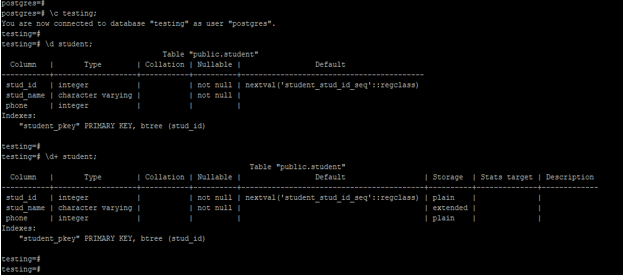
Show a description of the specified table
The below example shows the description of the specified table. We have described the student table.
Code:
\c testing;
\d student;
\d+ student;Output:
Example #4
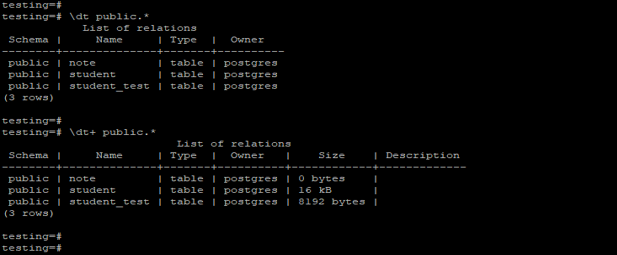
Show all tables from the specified schema.
The below example shows that show all tables from the specified schema. We have to show all tables from the public schema.
Code:
\dt public.*
\dt+ public.*Output:
Example #5
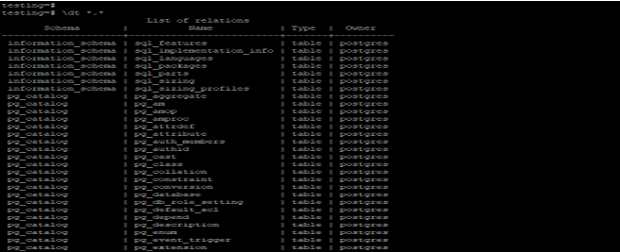
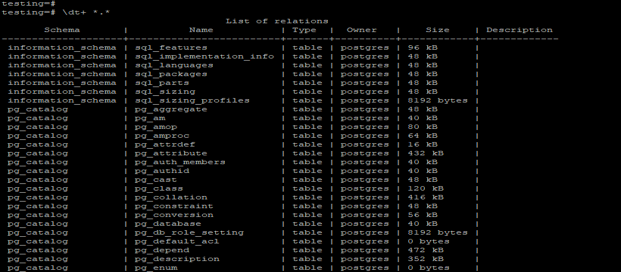
Show all tables from all schema.
The below example shows that display all tables from all schema.
Code:
\dt *.*
\dt+ *.*Output:
Example #6
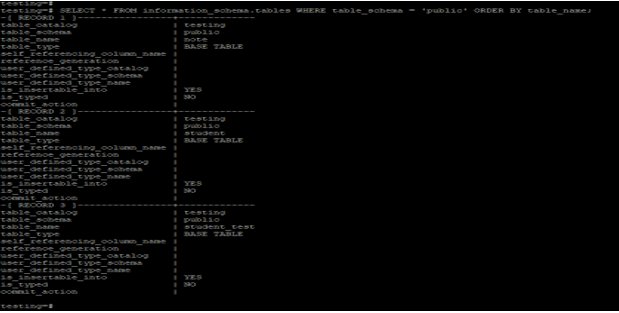
Show all tables from the specified schema using the query.
The below example shows that retrieving all tables from the specified schema using the query.
Code:
SELECT * FROM information_schema.tables WHERE table_schema = 'public' ORDER BY table_name;Output:
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Postgres Show Tables” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

