Updated May 15, 2023

Introduction to Postgres List Schemas
The database administrator and manager need to be aware of the database server’s environment. In the case of PostgreSQL, the server can handle data from multiple databases at a single time. The database administrator needs to know about all the databases and the tables, and schema related data about the database server. This article will learn how to check and view the information in Postgres List Schemas.
We will begin by knowing what schema is in the database. The schema in any database is a collection of views that stores all information about the managed objects. The information schema is stable and portable because it is defined inside the SQL standards. However, the system catalogs are variable as they contain specific information and are modelled after PostgreSQL implementation. The schema is accessible to the first user of the database and has all the privileges to handle and operate on the schema, including dropping it.
Datatypes – Postgres List Schemas
The views in the information schema use a special type of data types, which are simple domains created over the built-in data types. We should not use these data types in our external work with databases, as the information schema view exclusively uses them. However, when the information is fetched from the information schema, you need to handle them in your application. All columns in information schema views can belong to one of the following datatypes.
| Data type | Description |
| cardinal_number | It is a non-negative, i.e., positive integer |
| character_data | It specifies the string of characters with no maximum length specified, which is used for fields containing data other than SQL identifiers. |
| sql_identifier | It specifies the string of characters with no maximum length specified, used for SQL identifiers. |
| time_stamp | It is the domain defined over timestamp, which also considers time zones. |
| yes_or_no | The string of characters can either have YES or NO value in it. It is kept for backward compatibility of information schema as it was created and used even before the boolean data type was added in the SQL standards, which had either true/false value. |
MetaCommands
Instead of using raw SQL queries to list the data from the database, we can use short and precise metacommands that can be used with psql. Psql evaluates these metacommands and, if issued in the server’s system tables, translates them to SQL raw commands. A backslash recognizes metacommands and the command keyword followed by the parameters, if any if you want to pass to the query.
When you create a PostgreSQL server, it comes with three default databases: template0, template1, and Postgres. The CREATE DATABASE command uses the basic databases, template, and template1 for its operations. We refer to these two databases as skeleton databases. The default database that is selected and displayed is the Postgres database. After that, you can create databases of your choice and switch to them to create and manipulate tables in your databases. All databases can be retrieved and listed using the metacommand \list or \l and switched from one to another using \connect or \c. We can list out all the tables using the metacommand \dt command.
How to Use Postgres List Schemas?
Now, we will see how to list databases using the psql command.\list, or \l can be used.
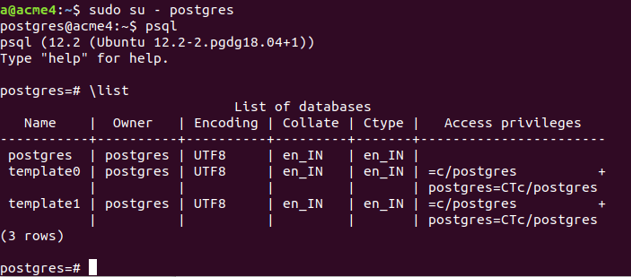
Open your PostgreSQL command prompt and then type SQL to get its command prompt. No type \list and press enter. You will see these output “Three default databases of PostgreSQL”.
Code:
sudo su - postgres
psqlOutput:
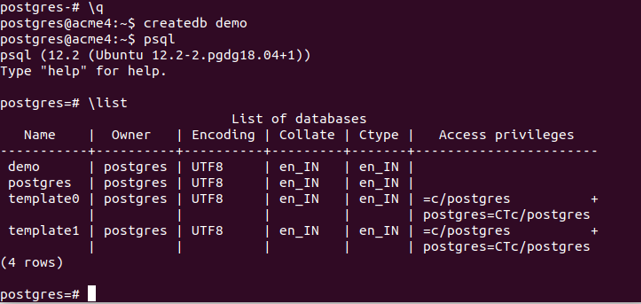
Let us create one new database named demo by using the createdb command. Exit the psql by typing \q, type createdb demo and press enter. Then again, enter \list and press enter to list out all the databases after typing psql to get the command prompt of psql. The output will be as follows –
Code:
\q
createdb demo
psql
\listOutput:
Schemas
Three types of schemas are present in any PostgreSQL database: information schemas, temporary schemas, and default pg_* schemas. Besides the user-defined and public schemas, one more type of schema in PostgreSQL is the pg_catalog schema. This schema contains information about the current database’s system tables, operators, data types, and functions. We will create a query to retrieve from the pg_catalog schema to list out all the user-related schemas.
Code:
SELECT * FROM pg_catalog.pg_namespace;Output:
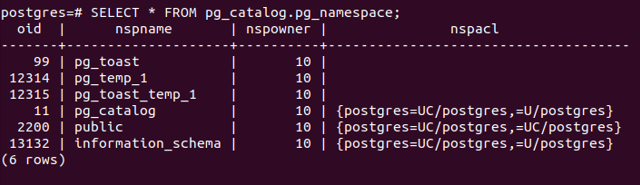
The field nspname displays the names of the schemas. These are all the schemas present in our database right now. The npsowner field stores the user id which owns that schema. We can see that the user with id 10 owns all schemas. To get the information about the user with id 10, we can query the pg_user table.
Code:
SELECT * FROM pg_catalog.pg_user where usesysid = 10;Output:
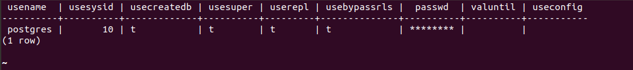
We can say that the user with usesysid =10 is postgres which owns all the above-retrieved schemas. If we want to retrieve the name os the schema and the person owning it in a single output, we can create a join on pg_namespace and pg_user, as shown below.
Code:
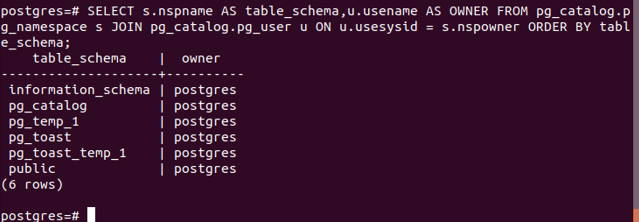
SELECT s.nspname AS table_schema, u.usename AS OWNER FROM pg_catalog.pg_namespace s JOIN pg_catalog.pg_user u ON u.usesysid = s.nspowner ORDER BY table_schema;Output:
Conclusion
PostgreSQL databases provide us with compact and immensely useful metacommands for database administrators and managers to check the database environments and structure related information faster and more effectively during their daily routines. Schemas can be retrieved from the system tables of pg_catalog schema, which is present in PostgreSQL databases. pg_namespace and pg_user are two main tables that convey schema related information to us.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Postgres List Schemas” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

