Updated May 18, 2023
Introduction to Postgres Change Password
In this article, we will learn how we can change the Postgres Change Password of the user if present and, if not, assign a password to the user for further authenticated usage by him in the PostgreSQL database server. There are two methods to do so. The first method involves using the ALTER query statement to change the password, and the second method is to use the meta-command \password in PostgreSQL’s psql utility.
To proceed with the password change process, it is crucial to have a clear understanding of how the password mechanism operates in PostgreSQL and the password policy that is applied to the default superuser, commonly known as “postgres.”
In any Unix distribution system of PostgreSQL, there are two types of authentication methods, namely ident, and peer. The default authentication method in PostgreSQL depends on the version of PostgreSQL being used and the installation configuration on the machine.
Ident Authentication method: In this method, a TCP port with 113 as the port number authenticates the user’s credentials where the identification server of the operating system is running.
Peer Authentication Method: In the peer authentication method, the PostgreSQL system matches the password of the current user with the password of the corresponding operating system user.
Syntax
Format 1:
ALTER USER name [ [ WITH ] option [ ... ] ] where option can be:
CREATEDB | NOCREATEDB
| CREATEUSER | NOCREATEUSER
| [ ENCRYPTED | UNENCRYPTED ] PASSWORD 'newPassword'
| VALID UNTIL 'expirytime'Explanation: Using the above alter command, the password of the user can be changed, and along with that, other options can also be reassigned.
Name: It is the name of the user or role whose properties or password you want to change.
Option: We can change multiple parameters and privileges associated with the user using this format.
CREATEDB: This can be specified if you want to give the privilege to the user to create a new database
NOCREATEDB: This can be mentioned if you want to restrict the user from creating any new database.
CREATEUSER: This property can be specified to allow the user to create new users.
NOCREATEUSER: When this property is mentioned in the query in the above format, the user won’t be able to create new users.
ENCRYPTED: The “ENCRYPTED” property determines whether the password stored in the pg_catalog’s pg_shadow table is stored in the form of an MD5 encrypted format.
UNENCRYPTED: The password is not stored in encrypted format in pg_catalog. If neither ENCRYPTED or UNENCRYPTED property is specified and neither this is done while user creation, then the default password storing mechanism is decided based on the password_encryption configuration variable.
PASSWORD: The new password is the string that you want to set as the password for the user. If the password field is not specified and the user has no previously set password, the user will be able to log in to the system without providing a password, as no authentication will be required. But in case if you switch to a password authentication system, then the user won’t be able to log in.
You can utilize the “VALID UNTIL” field to set an expiry time for the password, making it valid only until a specific period. This field if the timestamp up to which you want to permit the assigned password to work.
Examples to Implement Postgres Change Password
Below are examples mentioned:
Example #1
We will firstly login to the system by Postgres default user. Here we have assigned a password to the Postgres role already. So, we will enter the password.
Code:
sudo su - postgresOutput:
Example #2
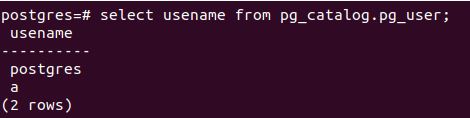
Further, let us check all the users which are present in the database server by firing the command using psql promo:
Code:
select username from pg_catalog.pg_user;Output:
Example #3
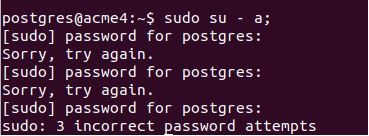
Let us try to login using a user:
Code:
sudo su – a;Output:
Example #4
As we have forgotten the password associated to that user assigned to it while its creation, we will reset it to pay by using the format 1 ALTER USER query in the following way:
Code:
ALTER USER a WITH ENCRYPTED PASSWORD 'payal';Output:
As the output is ALTER ROLE. The password reset operation has been completed successfully.
Format 2:
ALTER USER name RENAME TO alteredName
This format specifically changes the name of the user to a different name, such as “alteredName”.
Example #5
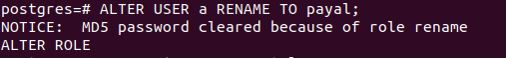
Code:
ALTER USER a RENAME TO payal;Output:
Example #6
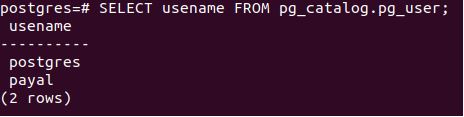
Let us verify the available users in our database server now.
Code:
SELECT usename FROM pg_catalog.pg_user;Output:
Example #7
Code:
ALTER USER name SET parameter { TO | = } { targetValue | DEFAULT }the parameter can be any configuration property of PostgreSQL. You can see all the configuration properties by firing the command
SHOW ALL;Output:
Example #8
ALTER USER name RESET parameterYou can use this command to reset the value of any field related to the user. Example –
Now, in case if we want to reset the password of the payal user. we can do so by using the query statement :
Code:
ALTER USER payal RESET password;Output:
That gives the output “ALTER ROLE,” which means that the password for the payal user has been reset successfully.
Example #9
MetaCommand to change password: In PostgreSQL, we have this amazing functionality called meta-commands that can be used with the help of psql utility. MetaCommands are short commands that facilitate easy and efficient database administration. These metacommands internally fire the SQL commands, which are basic, like ALTER, CREATE, SELECT, etc. One such meta-command for changing the password of the user is available and named \password. It asks to enter the password and then reenter the password for confirmation and then sets the entered password for that user.
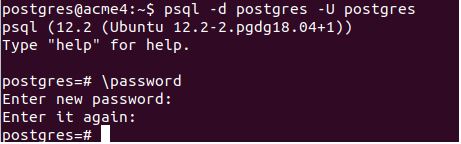
\passwordLet us check the working of metacommand with the help of an example. Suppose we want to change the password of a Postgres user after login to the Postgres database. Then we will query for the same in the following steps:
Code:
psql -d postgres -U postgres
\passwordOutput:
Conclusion
We can change the password of the user either by using the ALTER command or the metacommand \password in PostgreSQL.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Postgres Change Password” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.