Updated May 25, 2023
Introduction to Postgres ALTER TABLE
Whenever we perform manipulations on the table in the postgreSQL database, we often feel the necessity to perform some changes on the existing table. We can add more columns to the table, modify the existing column and its related properties, add or remove the constraints, remove columns, rename the table or assign the default value to specific columns, add or remove primary and foreign key constraints, and many more. We can perform all these operations using the ALTER TABLE command in postgreSQL. In this article, we will study the syntax and general usage of the Postgres ALTER TABLE command and view a few examples to understand its application in detail.
Syntax:
Format 1 –
ALTER TABLE [ ONLY ] tableName [ * ] actionOnTable [, ... ]- tableName – Name of the table which you want to alter or modify.
- ActionOnTable – It can be any of the following actions you wish to perform on the target table –
add, drop, and modify columns and their datatype, add or remove the constraints and rules and properties like replicas, primary and foreign constraints; enabling and disabling the triggers on the table; set OIDS and clusters; inheriting and not inheriting the parent properties, and resettable properties. The constraint which can be added should be mentioned in the following way –
[ CONSTRAINT nameOfConstraint ]
{ UNIQUE | PRIMARY KEY } USING INDEX nameOfIndex
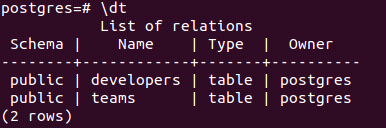
[ DEFERRABLE | NOT DEFERRABLE ] [ INITIALLY DEFERRED | INITIALLY IMMEDIATE ]Let us begin by creating a new table named educba, which will store the data related to the corporation after checking all the present tables in our current db by using \dt command –
\dtOutput:
Command:
CREATE TABLE educba
(id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
technologies VARCHAR,
workforce INTEGER,
address VARCHAR);Output:
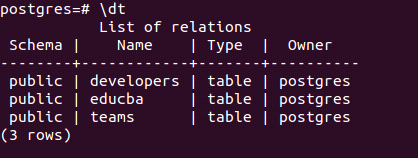
Check whether the table is created by \dt command that gives output –
\dtOutput:
Example of Postgres ALTER TABLE
Let us add one more column name clientcount of integer datatype with zero as the default value using alter command in the following way –
ALTER TABLE educba ADD COLUMN clientcount INTEGER DEFAULT 0;Output:
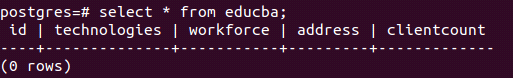
To check our change, we can see the records of the educba table that are as follows –
select * from educba;Output:
Hence, our column is added successfully.
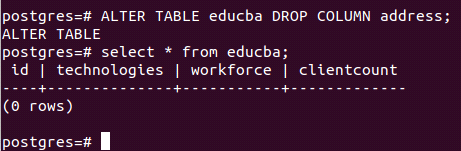
Let us similarly drop the column address as we added.
ALTER TABLE educba DROP COLUMN address;and check by selecting the records from the educba whether our column is dropped. Here is the output we get –
select * from educba;Output:
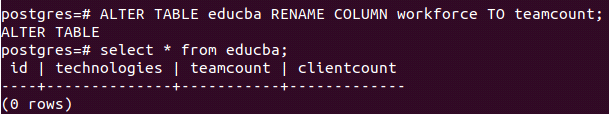
Now, if we want to change the name of the column named workforce to team count, we can do so by firing the following query –
ALTER TABLE educba RENAME COLUMN workforce TO teamcount;that gives the following output after the below query firing –
select * from educba;Output:
For setting the default value to the clientcount column, we can fire the following alter query statement –
ALTER TABLE educba ALTER COLUMN clientcount SET DEFAULT 0 ;Output:
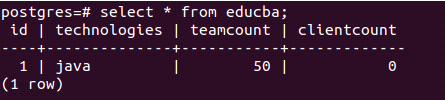
and verify by inserting a record in the educba table –
insert into educba values (1,'java',50,DEFAULT);Output:
select * from educba;Output:
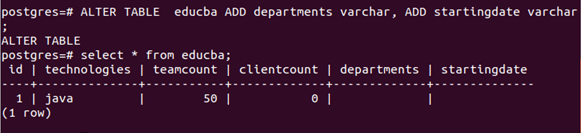
We can even add and remove multiple columns simultaneously. Let us insert two columns named departments and starting date of the varchar datatype. We can even perform column related alter queries without using the keyword COLUMN in it. For example –
ALTER TABLE educba
ADD departments varchar,
ADD startingdate varchar;and check our change using the below query that gives us the following output –
SELECT * FROM educba;To describe the table in psql, you can fire the command \d and the name of a table as the parameter in the following way –
Syntax:
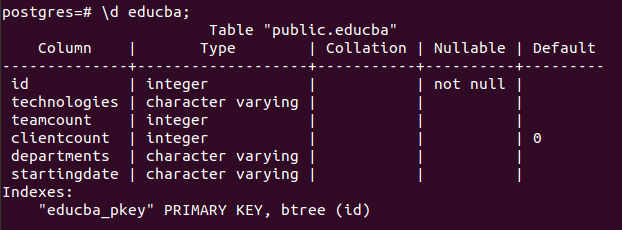
\d nameOfTableFor describing the educba table, we can use the below command:
\d educba;Output:
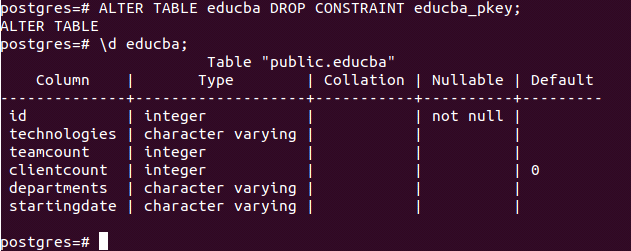
Now, to drop the primary constraint educba_pkey, we can use the alter command in the following way –
ALTER TABLE educba DROP CONSTRAINT educba_pkey;\d educba;firing, which gives the output as follows –
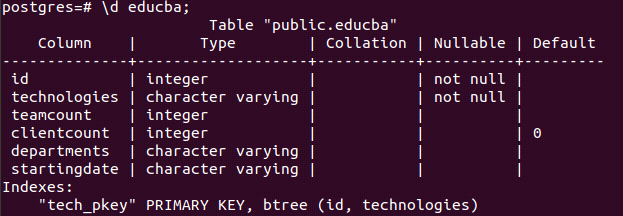
Now, we will add a new primary key constraint on the id and technologies of the table using the following alter table command –
ALTER TABLE educba ADD CONSTRAINT tech_pkey PRIMARY KEY (id, technologies);that results in the following output-
To check the keys, let’s describe the educba table using the command:
\d educba;Output:
Hence, our primary key constraint is added successfully.
Format 2
ALTER TABLE [ ONLY ] tableName [ * ]
RENAME [ COLUMN ] existingColumn TO alteredColumnNow, if we wish to change the name of the column, then we can use the format 2 queries of alter table to fulfill our purpose.\
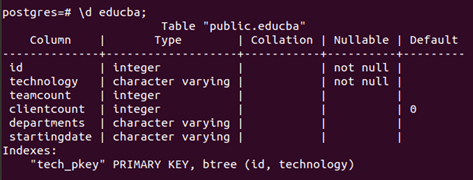
Suppose we want to change the name of the column technologies to technology. Then we can fire the following query to do so –
ALTER TABLE educba RENAME technologies TO technology;\d educba;Above query results in the following output –
Now, to check whether a column is renamed. Let us describe the educba table using \d educba; which results in the following output –
Format 3
ALTER TABLE tableName
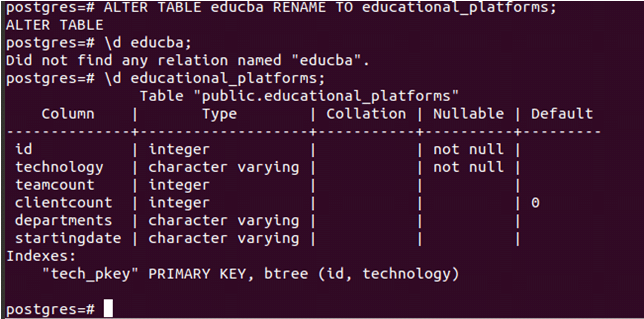
RENAME TO alteredTableNameWe can even rename the table’s name using the alter table command. To rename the name of the table educba to educational_platforms, we can use format 3 of alter table command in the following way –
ALTER TABLE educba RENAME TO educational_platforms;Let us check using the \d command after firing the above command to describe the educba and educational_platforms table.
\d educba;This gives the following output –
Format 4
ALTER TABLE tableName
SET SCHEMA alteredSchemaWe can even alter the table schema to another schema using the above format.
Conclusion
We have a versatile and variable ALTER TABLE command in the PostgreSQL database that can be used to add, remove, and modify the columns their datatypes, and constraints such as not null, default, etc. Other than this, the replica, trigger enabling, and disabling can be done using the same alter table command. The primary key and foreign key constraints can be added and removed, and indexes can be modified using the same command. We should maximize the utilization of such commands available in PostgreSQL to prepare efficient, robust, and consistent PostgreSQL databases.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Postgres ALTER TABLE” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.