Updated April 7, 2023
Introduction to PL/SQL Date Functions
PL/SQL provides a lot of date functions in order to perform the date and time tasks according to the specific requirements. PL/SQL provides the various data types related to datetime and interval. These date functions make the task quite easy as the user does not need to write the length codes in order to perform the operations like calculating days in between, getting the first day. Last day of the month, rounding off the date, calculating time of the different timezone, etc. These tasks can be easily done using the simple function provided by PL/SQL by passing the required arguments.
Various PL/SQL Date Functions
Given below are the various date functions provided by PL/SQL in order to perform various operations:
1. ADD_MONTHS(date, x): PL/SQL allows to perform the arithmetic operations on the date values. This is one of the most useful functions of date in PL/SQL which is used to add or subtract the number of the months from the given date. Here ‘x’ in the argument list is the number of months that would be added or subtracted from the given ‘date’ argument. So ‘x’ can be both negative as well as positive.
2. EXTRACT(): EXTRACT() is a very simple function used to perform the operation in PL/SQL. It basically extracts separate Year, Month, Day values from the date value.
3. LAST_DAY(date): As the name indicates, this function is used to retrieve the last date of the month for the specified ‘date’ argument. Since in a year, the number of days varies from month to month, this function is quite useful for this purpose as it helps to get the last date instantly.
4. NEXT_DAY(date, weekday): This function returns the date of the first day which will fall for the specified ‘weekday’ argument after the specified date. It takes 2 arguments and both are mandatory. For example, there is some date (‘19- JUN- 2021’, ‘SUNDAY’), so passing this argument in the above function will return the date at which the next SUNDAY will fall.
5. MONTHS_BETWEEN(date1, date2): This function is used to retrieve the months between the two dates specified by the user in the argument as ‘date1’ and ‘date2’.
There are some important points regarding the MONTHS_BETWEEN(date1, date2) functions:
- If date1 comes after date2, then the value returned is a positive value.
- If date1 comes before date2, then the value returned is a negative value.
- If date1 and date2 fall in the same month, the function will return a fraction value (between -1 and +1).
- Function returns the whole number if both the date1 and date2 falls on the last day of their respective months.
6. SYSDATE(): This function is used widely to get the system’s current date and time stored in the database. It takes no arguments. Its time component is used to extract the current time.
7. NEW_TIME (date, zone1, zone2): This function of PL/SQL is used to convert the date and it’s time components from one timezone to another timezone. The specifications of the time zones provided in the above function are not case- sensitive. This function is quite useful because one can know the exact date and time of another region providing the date and time components of its own region.
8. ROUND(x [, format_mask]): The round function of date in PL/SQL works similar to the one works in normal mathematics. It simply rounds the date values to the nearest date according to the specified format mask. It rounds the time component of the date to 12:00 A.M. Format_mask is an Optional parameter, if not provided, this function will round the date value to the nearest day (by checking the time components). The format_mask used in the round function is quite different from the mask used in TO_CHAR and TO_DATE function. PL/SQL provides the complete set of the mask that can be used in ROUND functions like CC for century, Q for Quarter, YYYY for year, SYYY rounds for next year, and so on.
9. TRUNC(x [, format_mask]): This function is used to truncate the specified date value according to the format_mask provided. It basically rounds the beginning of minute, second, hour, year, month, etc. It is somewhat similar to the FLOOR function provided in PL/SQL. This function eliminates the time components from the date and is widely used when required to make comparisons in the date values. One can easily retrieve the first day of the month and first day of the year easily by using this function. The fomat_mask is an optional argument in this function, if not provided, TRUNC sets the time to 12:00 A.M. of the same day.
Examples of PL/SQL Date Functions
Given below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
Code:
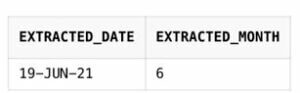
SELECT SYSDATE AS Extracted_date, EXTRACT(Month FROM SYSDATE) AS extracted_month
FROM DualOutput:
Example #2
Code:
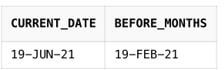
SELECT SYSDATE AS CURRENT_DATE, ADD_MONTHS(SYSDATE, -4) as BEFORE_MONTHS
FROM DualOutput:
Example #3
Code:
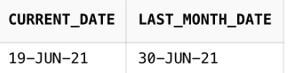
SELECT SYSDATE AS current_date, LAST_DAY(SYSDATE) AS last_month_date FROM DualOutput:
Example #4
Code:
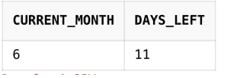
SELECT EXTRACT(Month FROM SYSDATE) AS current_month, LAST_DAY(SYSDATE)- SYSDATE AS days_left
FROM DualOutput:
Example #5
Code:
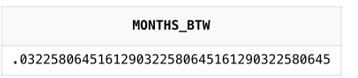
SELECT MONTHS_BETWEEN (TO_DATE ('10-03-2021', 'dd-mm-yyyy'),
TO_DATE ('09-03-2021', 'dd-mm-yyyy')) AS months_btw
FROM DualOutput:
Example #6
Code:
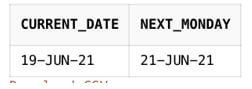
SELECT SYSDATE AS current_date, NEXT_DAY(SYSDATE, 'MONDAY') AS next_monday
FROM DualOutput:
Example #7
Code:
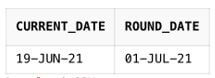
SELECT SYSDATE AS current_date, ROUND (SYSDATE, 'MONTH') AS round_date
from dual;Output:
Example #8
Code:
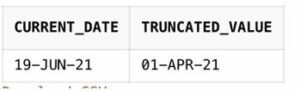
SELECT SYSDATE AS current_date, TRUNC (TO_DATE (SYSDATE), 'Q') AS truncated_value
from dual;Output:
Example #9
Code:
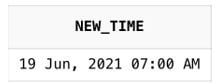
SELECT TO_CHAR (NEW_TIME (TO_DATE ('06192021 10:00 AM', 'MMDDYYYY
HH:MI AM'),'CST', 'hdt'),'DD Mon, YYYY HH:MI AM') AS new_time from dual;Output:
Conclusion
Above description clearly explains the various date functions used in PL/SQL in order to perform the different operations. Every program or query has different requirements, and date/ time are frequently used in them. So, in order to perform the operations according to the program requirement, it is mandatory for a programmer to have a clear knowledge of the various functions along with their usage.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PL/SQL Date Functions” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.