Updated May 15, 2023
What is an Oracle PIVOT Clause?
An Oracle PIVOTclauseis used to get a result in a matrix form. It allows us to write a query in cross-tabulation form. It also enables us to transpose rows into columns. It is introduced in Oracle 11g version and it supports 11g or later version. This is a very useful function for transposing rows into columns and aggregating data in the process. It is also called a CROSSTAB query. Multiple columns can be used in the PIVOT clause. If rows need to be converted into columns to split out a specific set of data points then the PIVOT clause can be used.
Syntax and Parameters
The syntax of the pivot in oracle:
Syntax:
SELECT Columns FROM Table_Name
PIVOT [XML]
(
Pivot_Clause
Pivot_For_Clause
Pivot_In_Clause
) WHERE Conditions
Parameter:
- Columns: Columns that needs to be displayed or fetched.
- Table_Name: Table that can be used for data.
- XML: It is used to convert pivoted data into xml. It is an optional keyword.
- Pivot_Clause: It uses Oracle aggregate function on the column’s data to fill the pivoted column accordingly. Oracle aggregate functions are SUM,COUNT,MIN,MAX or AVG.
- Pivot_For_Clause: In this clause, specify column will be grouped or pivoted.
- Pivot_In_Clause: It is used to define a filter for the specified column in Pivot_For_Clause.
- WHERE: This clause is used to filter the data. It’s optional.
How does PIVOT Clause Work in Oracle?
ThePIVOTclause is a key technique in many data warehouse applications. Its main functionality is to transpose rows into the column. It transforms multiple input rows into columns, aggregating data as part of the rotation process.
Implementing EXTRACT( ) Function
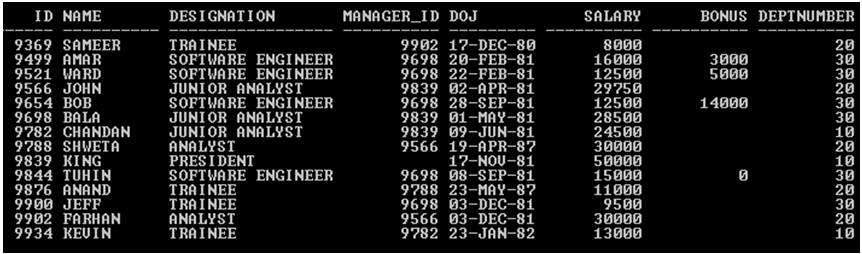
In this section we’ll see the implementation of Oracle PIVOT Clause and its behavior. For that, we will use the below sample table (Employee) with 14records to understand the Oracle PIVOT Clause behavior.
SELECT * FROM Employee;
Output:
1. Oracle PIVOT Clause
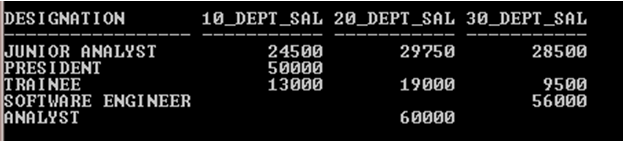
SELECT * FROM (SELECT Name, Designation, Deptnumber, Salary FROM Employee) PIVOT (SUM (Salary) FORDeptnumber IN (10,20,30));
Output:
In the above example, In the PIVOTclause SUM () function performs a summation of salary forDeptnumbrwhich is declared using Pivot FOR clause. In Pivot IN clause, department numbers have been declared which is pointing to the FOR clause Deptnumbr column and converts Deptnumbr column values into column names and displays the sum of salary Deptnumber wise.
2. PIVOT Column Aliasing or Alias Name
Pivot column aliasing is nothing but to provide a temporary name to the column or values.
- In the Pivot_Clause, one or more columns can have an alias name.
- In the Pivot_In_Clause, one or more values can have an alias name.
- The final column name (after aliasing) will be:
Pivot_In_Clause Alias || ‘_’ || Pivot_Clause Alias
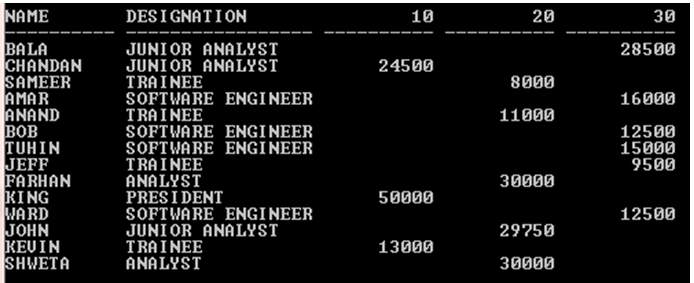
SELECT * FROM (SELECT Designation, Deptnumber, Salary FROM Employee) PIVOT (SUM (Salary) Dept_Sal FOR Deptnumber IN (10, 20, 30));
Output:
In the above example, Dept_Sal is an Alias name of Pivot_Clause (SUM (Salary)). The alias name gets concatenated or added with Pivot_In_Clause using underscore ‘_’.
3. Multiple Columns in PIVOT Clause
In PIVOT clause, multiple columns can be used in Pivot_Clause.
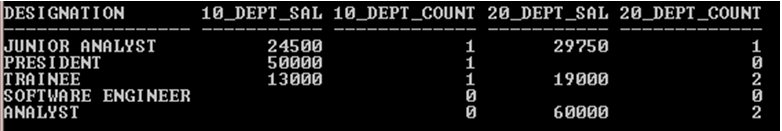
SELECT * FROM (SELECT Designation, Deptnumber, Salary FROM Employee) PIVOT (SUM (Salary) Dept_Sal, COUNT(DeptNumber) Dept_Count FOR Deptnumber IN (10, 20));
Output:
In the above PIVOTClause, there are two columns (Salary & DeptNumber) are being used for aggregation in Pivot_Clause. The output showing summation of salary department wise and count of the employee Deptnumber wise who falls in the same department with the same designation and returns the result
4. Sub Query in Oracle PIVOT
SELECT * FROM (SELECT Designation, Deptnumber, Salary FROM Employee) PIVOT (SUM(Salary) Dept_Sal, COUNT(DeptNumber) Dept_Count FOR Deptnumber IN (select Deptnumber from employee));
Output:
The above PIVOT Clause example returns an error “missing expression”.WHY?
Because that subquery return all department value means duplicate values that’s why in Pivot_In_Clause subquery is not allowed or not acceptable. If you declare, it will return an error.
But Sub Query can be used in Pivot_In_Clause, see the example below.
SELECT * FROM (SELECT Designation, Deptnumber, Salary FROM Employee) PIVOT (SUM(Salary) Dept_SalFOR Deptnumber IN (select Deptno FROMEmp));
Output:
In the above Pivot clause, used a subquery to populate department number in Pivot_In_Clause and it returns an output without any error. Because in the above example XML keyword is used which converts subquery returns values in a single XML string column.
Conclusion
Oracle PIVOTclause is a very useful clause that adds more practical functionality in the field of data analysis or crosstab reporting. Pivot clause reduced writing of convoluted non-intuitive or lengthy code. It is a very efficient way to transpose the data.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PIVOT in Oracle. Here we also discuss the introduction and how does pivot clause work in oracle? along with different examples and its code implementation. you may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –