Updated June 2, 2023
Introduction to PHP 7 MySQL
PHP is a server-side pre-arranging language used to assemble dynamic programming or a powerful web application. A few variants are accessible in PHP, for example, PHP 5 and PHP 7, and each has different usefulness and administration. We should associate with an information base like MySQL when we want to make dynamic programming around them. We the association between PHP 7 and MySQL we can accomplish through coding. MySQL is an open association; however, it was censored from PHP 5.5 and eliminated from PHP 7.
What is PHP 7 MySQL?
Accessing and adding data to a MySQL information base, you should initially layout an association between the data set and a PHP script.mysql_connect() spreads out a relationship with a MySQL server. The going with defaults are acknowledged for missing optional limits: server = ‘localhost: 8080’, username = name of the client that guarantees the server cycle, and mystery key = void mystery word. The server limit can, in like manner, consolidate a port number. The mysql_connect() work opens a non-resolute MySQL affiliation. This limit returns the relationship of progress, or FALSE, and a slip-up of frustration. You can hide the excellent yield by adding an ‘@’ before the limit name.
If you have XAMPP (not the web server) in your structure, you must name it localhost. MySQL client name and mystery key are “root” and clear (“”) independently. Permit us to make one essential endeavor and relate our PHP code to MySQL. If you use Windows, there is a “htdocs” envelope in “C: /xampp/htdocs/” (at whatever point presented in the default region). If you are on Linux (probably Ubuntu), it is arranged on “/pick/lampp/htdocs” (you should change to attach client before making a coordinator in it.).
How to Create PHP 7 MySQL?
Now let’s see how we can create MySQL in PHP 7.
First, we want to introduce any server we need, and it depends upon the engineer whether we can introduce Tomcat, XAMPP, or others according to our necessity. From that point onward, we want to roll out the improvements on the server according to the application necessities. We can also introduce a MySQL server and any programming apparatus to do the coding. For better agreement, consider the linguistic structure.
Resource mysql_connect ( [string server [, string determined username [, string user_password [, bool new_link [, int banners value]]]]])Returns a MySQL interface identifier on progress or FALSE on frustration.
mysql_connect() spreads out a relationship with a MySQL server. Going with defaults is normal for missing optional limits: server = ‘localhost: 8080’, username = name of the client that asserts the server cycle, and mystery express = void mystery state.
The server limit can, moreover, fuse a port number. For instance, “hostname: port.”
After that, I need to create the database using the following command.
create database specified database name;The above command specified database name means the actual database name we want to create.
Example
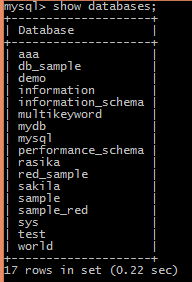
First, let’s see the available database by using the following command.
show databases;After running the above command, we see a list of all databases, as seen in the screenshot below.
We need to create a sample_php database by using the following command.
create database sample_php;The output of the above command is as follows.
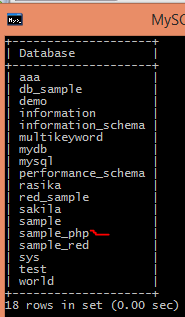
Now check in the database by using the following command as follows.
show databases;The output of the above command is as follows.
Now create a .php file and write the following code.
<?php
$server = "localhost";
$db_user = "root";
$db_password = "specified password of database";
$db_name = "Specified database name";PHP 7 MySQL Drivers
Now let’s see what drivers are available in PHP 7 as follows.
A driver is a programming component designed to communicate with a specific type of database server.
PHP MySQL extensions
MySQL extensions are lightweight and mostly used; in PHP, there are three types.
- exy/mysql
- exy/mysqli
- PDO_MySQL
Mysqlnd:
The mysqlnd library integrates tightly and efficiently into PHP, providing exceptional performance. Unfortunately, the MySQL Client Library can’t offer similar advancements since it is a broadly helpful client library.
The mysqlnd library involves PHP inside the foundation for consistent joining into PHP. Moreover, it utilizes PHP memory, the executives, PHP Streams (I/O deliberation), and PHP string for schedules. Using PHP memory by the executives by mysqlnd permits, for instance, memory investment funds by utilizing readjust factors (duplicate on composing) and makes mysqlnd apply to PHP memory limits.
Conclusion
We try to learn about PHP 7 MySQL using the information in the above article. From this article, we learn basic things about PHP 7 MySQL, and as well as we also see the syntax and examples of PHP 7 MySQL.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PHP 7 MySQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.