What is Payroll Management?
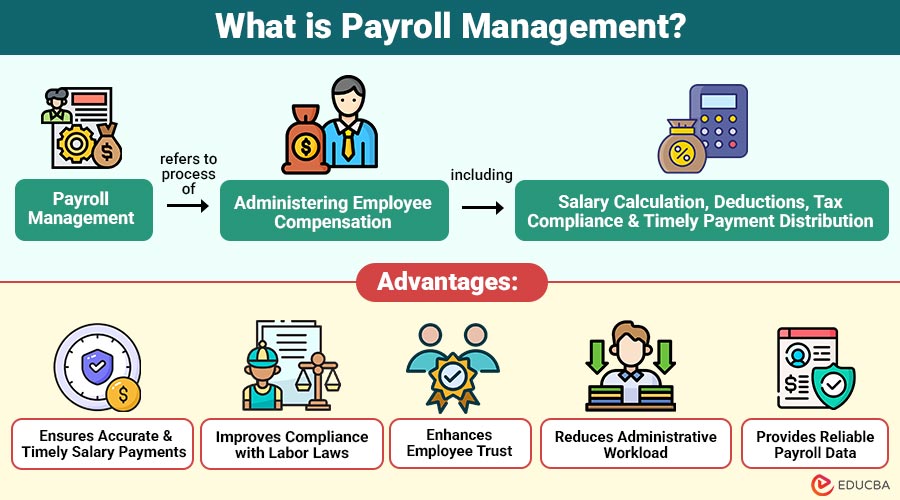
Payroll management refers to process of administering employee compensation, including salary calculation, deductions, tax compliance, and timely payment distribution.
It covers everything from collecting employee attendance data to generating payslips and filing payroll-related statutory reports with government authorities. Effective payroll management guarantees that employees are compensated correctly while organizations remain compliant with labor laws and taxation requirements.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Payroll management ensures accurate employee compensation, statutory compliance, timely payments, and organizational trust through processes.
- Effective payroll systems reduce errors, support legal compliance, improve efficiency, and enhance overall employee satisfaction.
- Automation and technology simplify payroll operations, strengthen data security, support scalability, and enable strategic decisions.
- Well-managed payroll builds credibility, supports financial planning, minimizes risks, and allows organizations to focus on growth.
Importance of Payroll Management
Effective payroll management plays a vital role in organizational success:
1. Ensures Employee Satisfaction
Timely and accurate salary payments build employee trust, boost morale, reduce dissatisfaction, and consistently improve productivity across the organization.
2. Legal and Tax Compliance
Payroll management reduces the risk of fines, penalties, audits, and legal issues by ensuring compliance with tax and labor laws.
3. Financial Accuracy
Accurate payroll calculations help organizations control costs, forecast budgets effectively, ensure correct reporting, and maintain long-term financial stability.
4. Enhances Organizational Credibility
Reliable payroll processes strengthen organizational reputation among employees, government authorities, auditors, investors, and other key stakeholders.
Key Components of Payroll Management
Payroll management consists of several interconnected components that work together to ensure smooth operations:
1. Employee Information Management
This includes maintaining accurate employee records such as:
- Personal details
- Employment type (full-time, part-time, contract)
- Salary structure
- Bank account details
- Tax declarations
Accurate data forms the foundation of error-free payroll processing.
2. Salary Structure and Compensation Planning
Organizations define salary components such as:
- Basic pay
- Allowances (HRA, conveyance, special allowance)
- Bonuses and incentives
- Overtime payments
A clearly structured salary ensures transparency for employees and simplifies payroll calculations.
3. Attendance and Leave Tracking
Payroll calculations depend heavily on:
- Working days
- Paid and unpaid leaves
- Overtime hours
- Holidays and absences
Integration with attendance or leave management systems ensures accurate salary computation.
4. Payroll Processing
This is the core function of payroll management, which includes:
- Gross salary calculation
- Deduction of taxes and statutory contributions
- Net salary computation
- Payslip generation
Payroll processing must be precise to avoid employee dissatisfaction and compliance issues.
5. Statutory Compliance
Payroll management must adhere to labor laws and tax regulations, such as:
- Income tax deduction and filing
- Provident fund (PF) contributions
- Employee state insurance (ESI)
- Professional tax
- Minimum wage laws
There may be fines, audits, and legal action for noncompliance.
6. Payroll Reporting and Record Keeping
Organizations must maintain payroll records for:
- Audits
- Tax filings
- Financial reporting
- Legal documentation
Payroll reports help management analyze labor costs and make informed decisions.
Payroll Management Process
A typical payroll management process follows these steps:
1. Collect Employee Data
Gather accurate employee salary structures, attendance records, leave details, reimbursements, and personal information required for payroll processing.
2. Validate Inputs
Review and verify attendance data, salary revisions, new joiners, exits, and employee changes to avoid payroll errors.
3. Calculate Gross Pay
Compute total earnings, including basic salary, allowances, bonuses, overtime, and performance-based incentives, before deductions.
4. Apply Deductions
Deduct applicable income tax, provident fund, ESI, professional tax, loan repayments, and other statutory or voluntary deductions.
5. Compute Net Pay
Determine each employee’s final payable salary by subtracting all deductions from gross earnings.
6. Disburse Salaries
Transfer net salaries to employee bank accounts through secure electronic payment systems or approved payment methods.
7. Generate Payslips
Create detailed digital or physical payslips showing earnings, deductions, and net pay for employee reference.
8. File Statutory Returns
Submit payroll-related tax filings, compliance reports, and statutory returns to government authorities within prescribed deadlines.
Advantages of Payroll Management
Here are the key advantages of effective payroll management in organizations:
1. Ensures Accurate and Timely Salary Payments
Payroll management guarantees correct salary calculations and on-time payments, preventing errors, delays, and employee dissatisfaction.
2. Improves Compliance with Labor Laws
Structured payroll processes help organizations follow labor laws, tax regulations, and statutory requirements, reducing compliance risks.
3. Enhances Employee Trust
Consistent and transparent payroll practices build employee confidence, trust, and long-term engagement within the organization.
4. Reduces Administrative Workload
Automated payroll systems save time and increase operational efficiency by reducing manual labor, paperwork, and repetitive operations.
5. Provides Reliable Payroll Data
Accurate payroll records support financial planning, budgeting, audits, and informed strategic decision-making by management.
Challenges in Payroll Management
Despite automation, payroll management faces several challenges:
1. Regulatory Changes
Regular modifications to labor rules and tax laws necessitate ongoing system updates, payroll process modifications, and monitoring.
2. Data Accuracy
Inaccurate employee information, attendance errors, or missing records can result in incorrect salary calculations and compliance issues.
3. Scalability Issues
Organizational growth increases payroll complexity due to multiple pay structures, locations, employee categories, and regulatory requirements.
4. Confidentiality and Data Security
Payroll systems must protect sensitive employee data from unauthorized access, cyber threats, and potential data breaches.
Best Practices for Effective Payroll Management
To ensure smooth payroll operations, organizations should follow these best practices:
1. Automate Payroll Processes
Implement payroll software to streamline calculations, reduce manual effort, minimize errors, and improve overall processing efficiency.
2. Maintain Accurate Employee Records
Regularly update employee personal, salary, attendance, and tax information to prevent payroll discrepancies and delays.
3. Stay Updated with Compliance
Continuously monitor labor law changes and tax regulations to ensure payroll processes remain legally compliant.
4. Conduct Regular Payroll Audits
Perform periodic payroll audits to detect errors, improve accuracy, prevent fraud, and ensure regulatory compliance.
5. Provide Employee Transparency
Offer clear payslips and employee self-service portals to build trust and reduce payroll-related queries.
Future Trends in Payroll Management
Payroll management is rapidly evolving with technology advancements:
1. Cloud-Based Payroll Systems
Cloud payroll solutions enable remote access, real-time updates, scalability, and secure payroll processing across multiple locations.
2. AI and Automation
Artificial intelligence automates calculations, detects payroll errors, monitors compliance, and improves accuracy while reducing manual intervention.
3. Integration with HR Analytics
Payroll systems integrated with HR analytics provide insights into workforce costs, productivity trends, and strategic decision-making.
4. Employee Self-Service Platforms
Self-service payroll platforms empower employees to access payslips, tax details, and salary information, improving transparency and efficiency.
Final Thoughts
Payroll management is critical business function that ensures accurate salary processing, legal compliance, and employee satisfaction. It covers wage calculation, statutory deductions, reporting, and record-keeping. As organizations expand and regulations evolve, automated payroll systems and best practices help reduce errors, save time, improve transparency, minimize risks, and allow businesses to focus on strategic growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Can small businesses use payroll software?
Answer: Yes, payroll software is highly beneficial for small businesses to reduce errors and ensure compliance.
Q2. What happens if payroll compliance is not followed?
Answer: Non-compliance can lead to penalties, legal action, and reputational damage.
Q3. Can payroll be outsourced?
Answer: Yes, many organizations outsource payroll to reduce costs and compliance risks.
Q4. How often is payroll processed?
Answer: Payroll is usually processed monthly, but some organizations follow weekly or bi-weekly cycles.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Payroll Management” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

