Updated February 27, 2023
Introduction to Oracle REPLACE()
An Oracle REPLACE Function is used to replace the string with a given string as the name suggests. It accepts a search string and replaces it with another given string but pattern-wise.
- It returns CHAR with every replaced with replacement string for the search string.
- If the first argument is not LOB, it returns VARCHAR2.
- If the first argument is LOB, it returns CLOB.
- It returns every occurrence of the search string replaced by the replacement string.
- If the replacement string is omitted or NULL, all occurrences of the search string will be removed.
- It substitutes one string for another as well as removes character strings.
Syntax
REPLACE(CHAR, Search_str, Replace_str)
Explanation:
- CHAR: It can be a column name or string to replace a sequence of characters with another set of characters.
- Search_str: It is a string that will be searched for in CHAR.
- Replace_str: It is a string that will replace the Search_str in CHAR. It is optional. If Replace_str has omitted or NULL all occurrences of Search_str will be removed.
| Parameter | Data Type |
| CHAR | CHAR, VARCHAR2, NCHAR, NVARCHAR2, CLOB, or NCLOB |
| Search_str | CHAR, VARCHAR2, NCHAR, NVARCHAR2, CLOB, or NCLOB |
| Replace_str | CHAR, VARCHAR2, NCHAR, NVARCHAR2, CLOB, or NCLOB |
How REPLACE() function works in Oracle?
As REPLACE function syntax shows it accepts a maximum of three arguments. They are CHAR, Search_str, and Replace_str. So the function takes the Search_str and searches it in CHAR if it finds any match or occurrences then it replaces it with Replace_str and returns the updated CHAR values. If it does not find any match then return the existing CHAR values. Here Replace_str is an optional parameter. It can be omitted or NULL in that case it removes the matching string. But the Search_str cannot be omitted else it returns “missing expression” error.
Examples to Implement REPLACE( ) Function
Below are some examples mentioned:
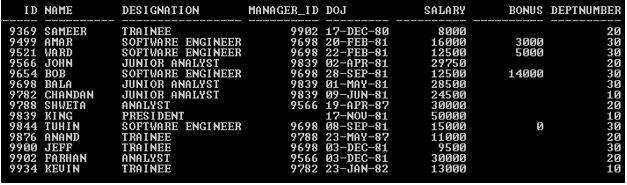
In this section we’ll see the implementation of Oracle REPLACE Function and its behavior. For that, we will use the below sample table (Employee) with 14 records to understand the Oracle REPLACE( ) function behavior.
SELECT * Employee;
Output:
Example #1
REPLACE( ) Function with all three parameter
Code:
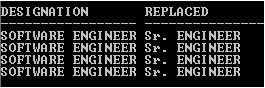
SELECT Designation, REPLACE(Designation,'SOFTWARE','Sr.') Replaced FROM Employee WHERE Designation='SOFTWARE ENGINEER';
Output:
Explanation: In the above example, REPLACE function replacing ‘SOFTWARE ENGINEER’ with ‘Sr. ENGINEER’. Because Search_str (‘‘SOFTWARE’) searching for the occurrence in the Designation column and where ever it finds, replaced it with the given Replace_str (‘Sr.’) and returns the updated result.
Code:
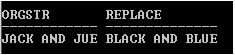
SELECT 'JACK AND JUE' OrgStr, REPLACE('JACK AND JUE','J','BL') Replace FROM DUAL;
Output:
Explanation: In the above example ‘J’ is being replaced by ‘BL’. Here ‘J’ is a single character but ‘BL’ is double because REPLACE function operates as a string not a character. That’s why ‘J’ is being replaced by ‘BL’.
Example #2
REPLACE( ) Function without Replace_str
Code:
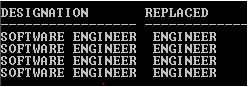
SELECT Designation, REPLACE(Designation,'SOFTWARE') Replaced FROM Employee WHERE Designation='SOFTWARE ENGINEER';
Output:
Explanation: In the above example, REPLACE function replacing ‘SOFTWARE ENGINEER’ with ‘ENGINEER’. Because Search_str (‘‘SOFTWARE’) searching for the occurrence in the Designation column and where ever it finds, it gets removed because Replace_str is omitted.
Example #3
REPLACE( ) Function without Search_str
Code:
SELECT Designation, REPLACE(Designation, ,'Sr.') Replaced FROM Employee WHERE Designation='SOFTWARE ENGINEER';
Output:
Explanation: In the above example, the Search_str parameter of the REPLACE function is omitted. And because it is a mandatory parameter, it returns a “missing expression” error.
Example #4
REPLACE( ) function for finding number of Search_str occurrences
Code:
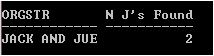
SELECT 'JACK AND JUE' OrgStr, LENGTH('JACK AND JUE')-LENGTH(REPLACE('JACK AND JUE', 'J')) "N J's Found" FROM DUAL;
Output:
Explanation: In the above example, REPLACE function playing a vital role with LENGTH function to find out the number of occurrences of Search_str.
LENGTH(REPLACE(‘JACK AND JUE’, ‘J’)) : In this part REPLACE function removes ‘J’ because Replace_str is omitted and then LENGTH function calculates the length of the CHAR parameter (‘JACK AND JUE’) that becomes 10.
LENGTH(‘JACK AND JUE’): In this part LENGTH function calculate the length of the CHAR parameter (‘JACK AND JUE’) that is 12. And then Subtract function (-) subtracts it 12-10 and returns the number of Search_str occurrences.
Tips:
- The functionality of the REPLACE function is similar to the TRANSLATE function. Translate single character, one to one substitution while REPLACE provides string
- REPLACE function can be used as a nested REPLACE function.
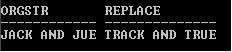
Code:
SELECT 'JACK AND JUE' OrgStr, REPLACE(REPLACE('JACK AND JUE','J', 'BL'), ’BL’, ’TR’) Replace FROM DUAL;
Output:
Example #3
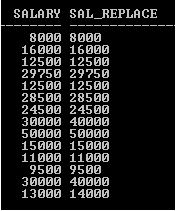
REPLACE function can be applied on the NUMBER data type column.
Code:
SELECT Salary, REPLACE(Salary, 30, 40) Sal_Replace FROM Employee;
Output:
Conclusion
Oracle REPLACE( ) function is very useful function for string substitution. This function can be used to calculate the number of Search_str occurrences. This is the simplest way to replace or substitute the string.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Oracle REPLACE(). Here we discuss introduction to Oracle REPLACE() along with syntax, how does it work and examples for better understanding. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –