Updated May 29, 2023

Introduction to Oracle Function-based Index
Oracle Function-based Index is a schema object which contains an entry for each value that appears in the indexed column(s) of the Table or Cluster. Function-based indexes are based on expressions and enable queries to evaluate the value returned by a word. It provides direct and fast access to rows.
Syntax
Creating an Index:
CREATE INDEX IndexName ON Table (Function);
Dropping an Index:
DROP INDEX IndexName;
Explanation:
IndexName: It can be any name of that Index object according to the Oracle naming convention.
Function: It can be an Oracle function or a User-defined function.
Specification of an Index
An index is a schema object. Indexes are independent of the table they Indexes, both logically and physically. When someone drops a table, they also drop the corresponding indexes automatically. Although it is possible to create more than one index on a table, it does not necessarily mean that having more indexes results in faster performance. Each DML operation committed on a table with an index requires updating the index. Index reduces the disk I/O by using a rapid path access method to locate the data quickly.
Points of Concentration
- The OWN schema must contain the table or cluster that needs to be indexed.
- Create Index system privilege must be available for users who create Index and query rewrite privileges.
- Unlimited tablespace system privilege or space quota on space quota on tablespaces must be available.
- Function-based indexes based on expressions in SELECT statements.
- Function-Based Indexes defined with the UPPER (ColumnName) OR LOWER (ColumnName) allow case-sensitive searches.
- Users should have to to Execute object privilege on the functions used in the Function-based indexes.
- To ensure that Oracle uses the Index rather than performing a full table scan, users should be sure that the value of the Function is NOT NULL in the subsequent queries.
- Oracle treats Indexes with columns marked DESC as Function-Based Indexes.
Examples to Implement Oracle Function-based Index
Implementations of FUNCTION Based Index with Examples:
In this section, we’ll see the implementation of the Oracle Function-based Index and its behavior. For that, we will use the below sample table (Employee) with 14 records to understand the Oracle Function-based Index behavior.
Code:
SELECT * FROM Employee;
Output:
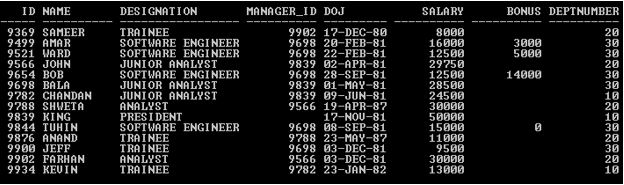
Example #1: Without FUNCTION Based Index
Code:
SELECT Name, Deptnumber, Salary, Bonus, Salary + NVL (Bonus, 0) Total FROM Employee where Salary + NVL(Bonus, 0) > 20000;
Output:
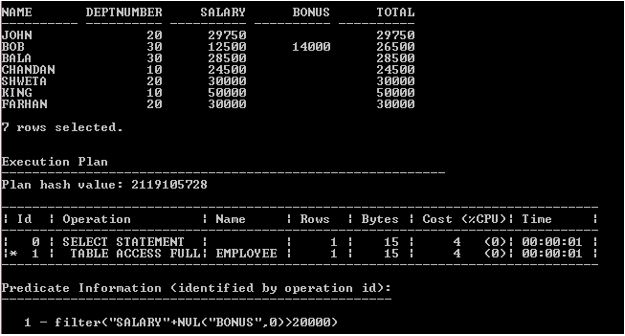
Explanation: The above execution plan of the above SELECT statement scanned the full Employee table. The Employee table does not have an index, so the data is being retrieved using an Oracle function-based expression in the SELECT statement above.
Example #2: FUNCTION Based Index
Now we’ll create a Function-Based Index for the above expression to prevent the full scan of the table and reduce the I/O cycle.
Code:
CREATE INDEX Emptotal ON Employee (Salary + NVL (Bonus, 0));
Output:
![]()
Now we’ll execute the above query to fetch the rows.
Code:
SELECT Name, Deptnumber, Salary, Bonus, Salary + NVL (Bonus, 0) Total FROM Employee where Salary + NVL (Bonus, 0) > 20000;
Output:
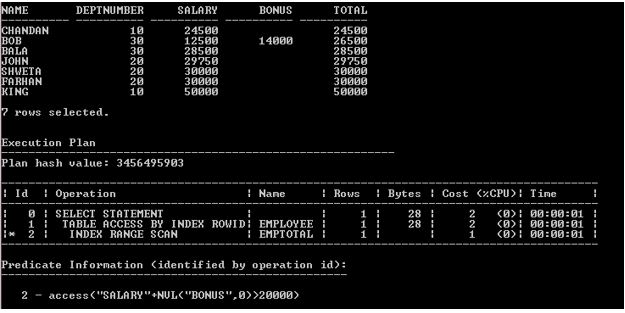
Explanation: The above execution plan of the above SELECT statement shows that the table accessed by Index ROWID is not the full Employee table. And Execution plan clearly shows the difference in Cost.
Example #3: How to check Indexes
The index can be checked from the USER_INDEXES data dictionary.
Code:
SELECT Table_Name,Index_Name FROM USER_INDEXES WHERE TABLE_NAME='EMPLOYEE';
Output:

Example #4: Dropping Function-Based Index
The index can be dropped at any time, but User needs to have drop privilege.
Code:
DROP INDEX Emptotal;
Output:
![]()
So now the Employee table does not have an “Emptotal” Index.
Code:
SELECT Table_Name,Index_Name FROM USER_INDEXES WHERE TABLE_NAME='EMPLOYEE';
Output:
![]()
When to Create Function-Based Index
The Function-Based expression is used frequently in the WHERE clause or in a join condition. The table is large and most queries are expected to retrieve less than 2 to 4 % of the rows.
TIP:
1. Should not create a Function-Based Index when the table is too small.
2. Should not create a Function-Based Index when the table is updated frequently.
Conclusion
Oracle Function Based Index reduces computation for the database. If any query consists of a function-based expression and executes on a regular basis or multiple times, then the database has to compute in everyone runs. To avoid this computation on the database every time, the Function-Based Index is a better option.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Oracle Function-based Index. Here we discuss an introduction to Oracle Function-based Index, the appropriate syntax when to create it along with sample code. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –

