Updated May 15, 2023

Introduction to Oracle COALESCE Function
An Oracle COALESCE is nothing but a function that is used to get the first, not null value in the given argument in the COALESCE function. This function accepts multiple arguments and evaluates it until unless finds the first, not null value. If it does not find any not null value then return NULL.
Points of Concentration:
- The COALESCE function can accept multiple arguments.
- This function introduced by ANSI and a part of SQL ANSI – 92 standards.
- Oracle version 9i or later supports the COALESCE function.
- The COALESCE function works on the IF THEN ELSE mechanism.
- The COALESCE function is data type sensitive.
- The COALESCE function evaluates the given argument and returns the first not null value.
- The COALESCE function stops the evaluation of the argument when it finds the first not null value.
Syntax
COALESCE(expr1, expr2, ... expr_n)
Explanation: expr1, expr2, …expr_n: Expression can be a column name, any value, any default value etc. It can have any number of expressions.
Examples to Implement COALESCE Function
In this section we’ll see the implementation of COALESCE Function and its behavior.
1. COALESCE function with multiple arguments
Code:
SQL>SELECT Bonus, Manager_ID, COALESCE (Bonus, Manager_ID, 90) FROM Employee;
Output:
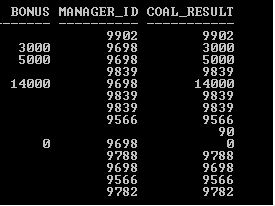
Explanation: In the above SELECT statement, there are three arguments two are column names from the table and one is a value. Now, here COALESCE function evaluates Bonus column data first if it finds a not null value then stops evaluating and returns the value else it evaluates the next argument ID column and returns the value if it’s a not null else returns the specified value “90”. In this example function will return 90 if function finds NULL values in the first two arguments. So that’s how COALESCE function works and returns the result.
In case of COALESCE function find NULL value in all arguments then it returns NULL only. Example below.
Code:
SQL>SELECT Manager_ID, Bonus, COALESCE (Bonus, Manager_ID) COAL_RESULT FROM Employee;
Output:
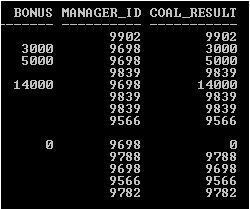
Explanation: In the above example, there is a NULL value in the COAL_RESULT column because both arguments have NULL and there are no default values being passed in COALESCE function as an argument. So function returns NULL in that cell.
2. Different Data Type Argument
Code:
SQL>SELECT Bonus, Manager_ID, COALESCE (Salary, Name) COAL_RESULT FROM Employee;
Output:
![]()
Explanation: The above SELECT statement throws an error because there are two arguments in the COALESCE function and both are different data types. Salary is the NUMBER data type and Name is VARCHAR data type in that scenario COALESCE function tries to convert all arguments to the data type of the first not-null argument if the conversion fails then Oracle returns an error.
3. Argument Evaluation
Code:
SQL >SELECT COALESCE (1, 1/0) FROM DUAL;
Output:
![]()
Explanation: The above example proves that COALESCE function stops evaluation once it finds the first not null value. Here the first expression returns not null value so the function did not evaluate second (1/0) expression. If the function had done so, Oracle would have returned “divisor is equal to zero” error.
Code:
SQL >SELECT COALESCE (NULL, 1/0) FROM DUAL;
Output:
![]()
4. COALESCE Function and CASE Expression
CASE expression can also return the same result as the COALESCE function. Examples below
CASE Expression:
Code:
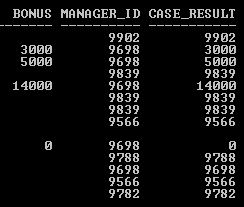
SQL>SELECT Bonus, Manager_ID, CASE WHEN Bonus IS NOT NULL THEN Bonus ELSE Manager_IDEND CASE_RESULT FROM Employee;
Output:
COALESCE Function:
Code:
SQL>SELECT Manager_ID, Bonus, COALESCE (Bonus, Manager_ID) COAL_RESULT FROM Employee;
Output:
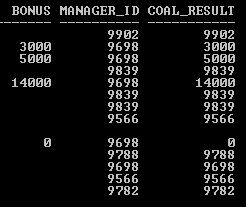
Explanation: The above two SELECT statement examples (CASE and COALESCE) return the same result set. So CASE expression can be used instead of COALESCE function to get the not null value.
Tip: As COALESCE and CASE expression returns the same result but the COALESCE function is more concise and efficient than CASE expression.
The function can be used with CASE expression. It can also be used to substitute user define value instead of NULL.
5. COALESCE Function and NVLFunction
The NVL function is introduced by Oracle while COALESCE function is introduced by ANSI and its part of ANSI-92. But both functions seem to be similar but implementations are different. Examples below.
Code: NVL Function
SQL>SELECT Bonus, Manager_ID, NVL (Bonus, Manager_ID) NVL_RESULT FROM Employee;
Output:
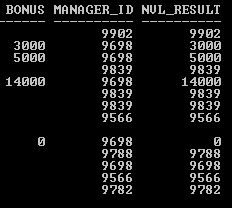
Code: COALESCE Function
SQL>SELECT Manager_ID, Bonus, COALESCE (Bonus, Manager_ID) COAL_RESULT FROM Employee;
Output:
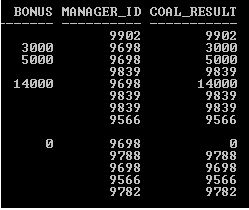
Explanation: The above two SELECT statement examples (NVL and COALESCE) return same result set. So NVL function can also be used instead of COALESCE function but there are two drawbacks of NVL function as compare to COALESCE function
NVL accepts only two arguments while COALESCE accepts more than two arguments. As we have seen above COALESCE function stops evaluating argument when it finds the not null value, But NVL evaluates both arguments. Example below
Code:
SQL>SELECT NVL (1, 1/0) FROM DUAL;
Output:
![]()
Explanation: So NVL function returns an error because NVL evaluates both the arguments that’s why it returns an error.
Conclusion
Oracle COALESCE function is used to get the first not null in the given multiple arguments. This function is more concise and efficient as compare to NVL or CASE expression. The COALESCE function is the best option to get the first, not null value from multiple columns or arguments.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Oracle COALESCE. Here we discuss an introduction Oracle COALESCE, with appropriate syntax and respective examples for better understanding. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –


