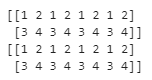Updated June 6, 2023
Introduction to NumPy Tile
Python provides different functions to the users. To work with arrays, the Python library provides a numpy tile. The numpy tile allows the creation of a new array by repeating several times per repetition. After execution of the tile function, we get a new array with dimension max(A, ND, R) where R is the repetition length if A.ND > R is promoted to A.ND by prepending 1’s to it. Suppose A.ND<R is promoted to A.ND prepending a new axis. Arrays play a significant role in data science, where speed matters. Numpy is an acronym for numerical PPython. Numpy is an open-source project.
Syntax
numpy.tile(A,R)Explanation
In the above syntax, where numpy.tile is the function, where A is the input of the array, and this element must be required. R represents the number of repetitions with array (A) along each axis; this element must be necessary.
How does the tile function work in NumPy?
- We must install Python on your system.
- You must install numpy using the pip command.
- It required basic knowledge of Python.
- It required basic knowledge about tile.
- Can perform different operations using a numpy.tile function.
Examples of NumPy Tile
Let’s see a different example of a numpy tile.
Example #1 – D Array
Code:
import numpy as np
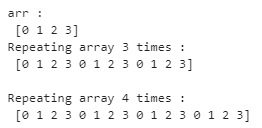
array = np.arange(4)
print("arr : \n", array)
repetitions = 3
print("Repeating array 3 times : \n", np.tile(array, repetitions))
repetitions = 4
print("\nRepeating array 4 times : \n", np.tile(array, repetitions))Explanation:
In the above example, we implement numpy.tile function with a 1D array. In this example, we first import the numpy function and assign it as np. Then we declare a variable array and assign array values 4 with arange function. After that, we try to print array values. Then we declare two repetition values that are 3 and 4, with the help of the np.tile function, and finally, we try to print the given array with repetitions. Illustrate the result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Example #2 – Normal Example of numpy tile
Code:
import numpy as np
A = np.array([0, 1, 2])
print(A)
x=np.tile(A, reps=3)
print(x)Explanation:
In the above example, we import the numpy function and assign it as np. Then we have an array with an axis value of 0 and repeat thrice. Illustrate the result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Example #3 – A.ND is less than R
Code:
import numpy as np
A = np.array([1, 2, 3])
print(A)
print("repeated array....")
x=np.tile(A, reps=(3, 3))
print(x)Explanation:
In the above example, we try to implement the first case that the array dimension is less than repetition. First, we import the numpy function and assign it as np. Then we declare an array with values and assign repetition values. Finally, the result has been printed. Illustrate the result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Example #4 – A.ND is greater than R
Code:
import numpy as np
A = np.array([[2, 3], [4, 5]])
print(A)
print("repeated array....")
x=np.tile(A, reps=3)
print(x)Explanation:
In the above example, we have implemented another special case that is A.ND is > than R. First, we import numpy functions and use them as np. Then we declare an array with values and assign repetition values. Finally, we tried to print the result. Illustrate the result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Example #5 – for (A.ND==R) == 0
Code:
import numpy as np
A = np.arange(4).reshape(2, 2)
print("Array : \n", A)
x = 2
y = 1
repetitions = (x, y)
print("\n Repeated array : \n", np.tile(A, repetitions))
print("Array Shape : \n", np.tile(A, repetitions).shape)
x = 3
y = 2
repetitions = (x, y)
print("\n Repeated array : \n", np.tile(A, repetitions))
print("Array Shape : \n", np.tile(A, repetitions).shape)
x = 2
y = 3
repetitions = (x, y)
print("\n Repeated array : \n", np.tile(A, repetitions))
print("Array Shape : \n", np.tile(A, repetitions).shape)Explanation:
In the above example, we implement a special case (A.ND==R)== 0 condition in which we first import numpy functions and use them as np. Then we declared an array with values and assigned different repetition values in the program. Finally, we tried to print the array with shape. Illustrate the result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Example #6 – for different methods to write tile function
Code:
import numpy as np
matrix= np.array([[1,2],[3,4]])
x = np.tile(matrix,4)
y = np.tile(matrix,(1,4))
print(x)
print(y)Explanation:
We implement a tile function in the above example using two different methods. The resultant array is the same after the execution of both methods. Illustrate the result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Example #7 – For Horizontal +Vertical implementation of tile function
Code:
import numpy as np
matrix= np.array([[2,3],[4,5]])
x = np.tile(matrix,(3,4))
print(x)Explanation:
In the above example, we implement a horizontal and vertical matrix tile function. Illustrate the result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Example #8
Code:
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(3)
print("array : \n", a)
x = 3
y = 23
rep = (x, y)
print("\n Repeated array : \n", np.tile(a, rep))
print("Array Shape : \n", np.tile(a, rep).shape)
x = 3
y = 2
rep = (x, y)
print("\n Repeated array : \n", np.tile(a, rep))
print("Array Shape : \n", np.tile(a, rep).shape)
x = 2
y = 3
rep = (x, y)
print("\n Repeating array : \n", np.tile(a, rep))
print("Array Shape : \n", np.tile(a, rep).shape)Explanation:
In the above example, we import a numpy function and assign it as np. Then we created an array by arange function. After that, we assigned repetition values to the array by using numpy.tile function, then we tried to print an array with the shape of the array. The same process we follow repeatedly for different repetition values. Illustrate the result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Conclusion
We hope you understand the numpy tile function from this article. The above article taught us the basic syntax numpy tile function. We also know how to implement them in Python with different examples of each type. From this article, we have learned how we can handle numpy tile in Python.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “NumPy Tile” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.