Updated October 26, 2023
What is Negative Goodwill?
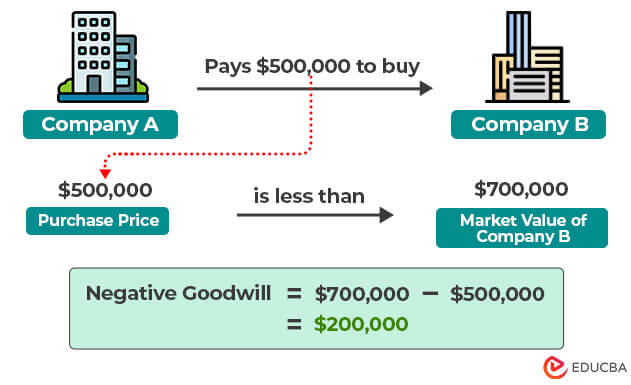
Negative goodwill (bargain purchase), common in mergers & acquisitions, is when a company acquires another company for a lower price than its actual book value (market value of its assets).
Explanation
Imagine you want to buy a company. Usually, you have to pay a certain amount as per the company’s value in the market. However, sometimes, due to economic conditions or the company’s financial situation, you may have to pay less than the company’s actual worth. When this happens, the difference between what you paid and the company’s actual value is called negative goodwill.
Now, if this is the situation, why is it important? It is mainly good for the buyer because they get a bargain. It indicates a smart financial move. It is similar to purchasing a new iPhone at a discount during the holiday sale. In this situation, you get the newest phone by paying less for it.
Real Example of Negative Goodwill
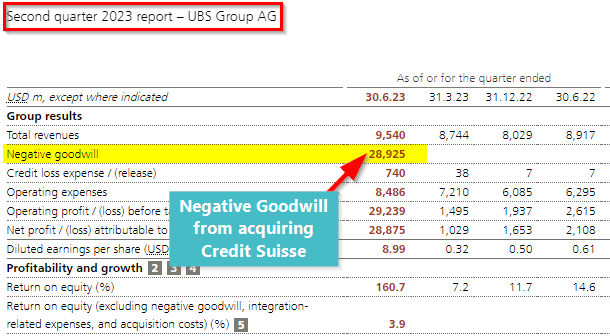
In 2023, UBS acquired Credit Suisse for $3.25 billion and gained $34.8 billion in assets. They paid less than Credit Suisse’s actual book value, so they have $28.9 billion in negative goodwill.
As reported, Credit Suisse was facing financial issues and was on the verge of bankruptcy. Thus, in order to save a global bank from failing, the Switzerland authorities offered UBS a deal to go ahead with this bargain purchase.
We can find the reported negative goodwill in UBS’s 2nd quarterly report for 2023. They will add this as an extraordinary gain in their consolidated income statement at the end of the fiscal year.
(Image Source: UBS Quarterly Report)
Accounting for Negative Goodwill
Reporting requirements vary according to different accounting standards. Here is a common stepwise guide on how to account for negative goodwill.
1. Calculating Negative Goodwill
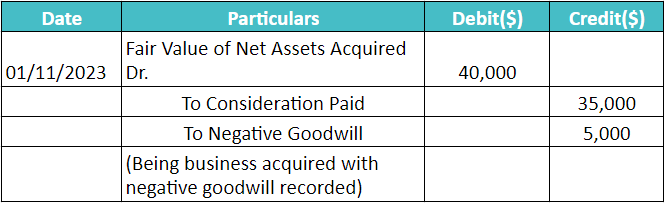
First, calculate the negative goodwill by calculating the net assets of the acquired company and subtracting the acquisition purchase price from it.
Journal Entry will be as follows:
2. Recording in Financial Statements
As per both US GAAP and IFRS, companies can report negative goodwill on the financial statements as follows:
#1: Income Statement
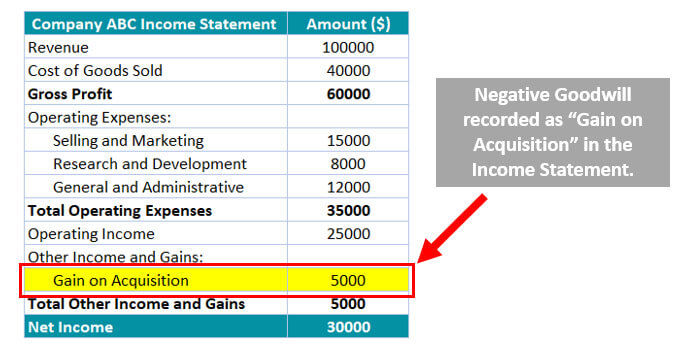
The company can directly add the negative goodwill as ‘Gain on Acquisition’ or ‘Extraordinary Gain’ in the income statement. For example, here, $5,000 is recorded as ‘Gain on Acquisition’ in the income statement.
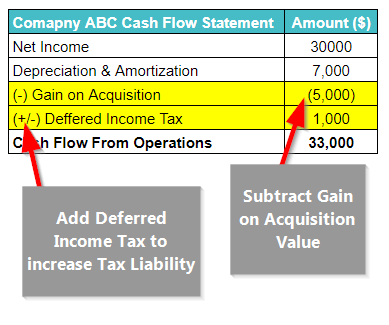
#2: Cash Flow Statement
As the extraordinary gain leads to an increase in net income, on the income statement, the tax also increases. However, as the company has not actually paid that tax amount, they decrease those taxes in the cash flow statement.
This is called the tax treatment that increases the tax liability, indicating that the company didn’t really pay the reported taxes. They also subtract the extraordinary gain from the net income in the cash flow statement, lowering the net income.
Example
A company named Adam’s Mark bought the net assets of company Johny International for $3.5 million on 25 October 2023. This deal occurred because the company Johny International urgently needed cash.
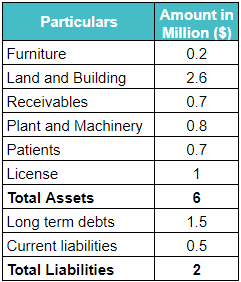
This is Johny International’s Balance sheet. Let’s see how to calculate negative goodwill and record it.
Solution:
#1: Calculate HostileGoodwill
Step 1: Let’s first calculate the Net Assets Value of Johny International using the formula given below.
Net Assets Value = Total Assets – Total External Liabilities
= $6 million – $2 million = $4 million.
Step 2: Now, we will calculate the negative goodwill.
Negative Goodwill = Net Assets Value – Purchase Price
= $4 million – $3.5 million = $0.5 million or $500,000
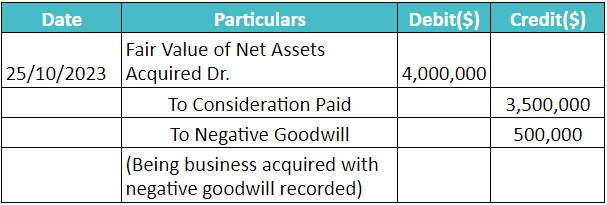
#2: Create Journal Entry
The journal entry will look like this:
Finally, when Adam’s Mark prepares the consolidated financial statements, it will record the $500,000 of negative goodwill as extraordinary gain in its income statement.
Final Thoughts
Negative goodwill is usually the most advantageous for a buyer as it allows them to buy the net assets of a business at a lower price than the market rate. It also helps in cost savings as it represents the discount availed in acquiring a running/distressed business.
Recommended Articles
We hope this article on negative goodwill has helped you. For similar articles, refer to the following recommendations.