Updated May 16, 2023
Definition of MySQL TRUNCATE()
MySQL TRUNCATE() function is specified to return a literal number after trimming it to a certain number of decimal places mentioned in the query. The number to be truncated and the number of decimal places are signified as the arguments or parameters of this TRUNCATE() function. This function involves the use of two components. The first component of the function is a numeric expression that undergoes truncation based on the value specified by the second parameter in the TRUNCATE() function. The second component is a number that determines the decimal positions up to which the first number should be trimmed. For the execution of the TRUNCATE() function-based SQL statement, we need to add both parameters.
Syntax:
The following syntax is specified in MySQL to determine the resultant number from the TRUNCATE() function.
TRUNCATE(Any_Number,Decimal_Value)The parameters used in the above function syntax are described briefly below:
- Any_Number: Denotes the number to be used for the truncate function.
- Decimal_Value: Indicates a number of decimal places required to truncate the Any_Number parameter.
When the second argument of the function, Decimal_Value, is negative, the process sets the digits to the left of the decimal point in Any_Number to zero. Therefore, once the Decimal_Value is zero, the resultant value has no fractional part in it.
How does the TRUNCATE() Function Work in MySQL?
Supposing that we have an SQL statement for a description of the TRUNCATE() function as follows:
SELECT TRUNCATE(543.145,0);Output:
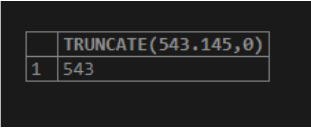
The returned value represents a numeric expression that has undergone truncation to 0 decimal places. MySQL supports this MySQL TRUNCATE() function responsible for trimming a number to a particular number of decimal positions.
While for Oracle and PostgreSQL, we have to use TRUNC() function, which provides identical functionality to the TRUNCATE() function. However, for SQL Server, the ROUND() function is used along with the third argument in the function that defines the truncation process. The syntax is denoted as ROUND(Num, Dec, f). If the f parameter is not zero, then the ROUND() function performs the Dec number of decimal points and rounds the Num number to return the required value when executed.
Examples to Implement TRUNCATE() in MySQL
Let us consider the following examples by using the function TRUNCATE() in MySQL:
1. MySQL TRUNCATE() Function with Positive Decimal Places Number
Suppose we take the below query statement to perform the TRUNCATE() function execution:
SELECT TRUNCATE(2.444, 1);Output:
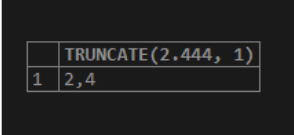
Here, we see that since the second argument, i.e., a number of decimal places, is 1, the TRUNCATE() function generates the value with only one decimal point.
2. MySQL TRUNCATE() function with Negative Decimal Places Number
The SQL statement below shows how to add the TRUNCATE() function with a negative number of decimal positions.
The SQL query is:
SELECT TRUNCATE(233.33, -2);Output:
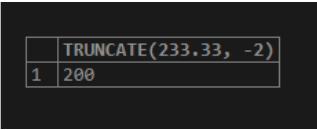
From the above statement, we can see that the TRUNCATE() function causes the negative number digits left of the decimal point of the literal number 233.33 and makes to become zero. So, as the (-2) part is 0, the resultant value has no fractional section.
3. MySQL TRUNCATE() Function and ROUND() Function Comparison
We have selected the two SQL statements to apply the TRUNCATE() & ROUND() MySQL functions and display the difference between the functional resultant.
Let us consider the examples as follows:
SELECT TRUNCATE(288.88,2);Output:
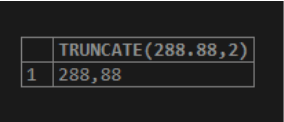
SELECT ROUND(288.88,2);Output:
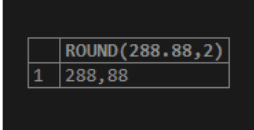
We can now consider that the ROUND() function indicates the return value rounded off, and the TRUNCATE() function signifies the value returned trimmed up to the decimal places, as mentioned in the above SQL query.
4. MySQL TRUNCATE() Function used in Table Columns
The TRUNCATE() function shows the trimmed value of the column values when added with the SQL statement along with SELECT, GROUP BY, ORDER BY clauses, and INNER JOIN-like SQL keywords.
Let us consider the below statements to create two tables as sample tables to proceed further:
Person Table Query:
CREATE TABLE Person(Person_ID INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY, Person_Name varchar(255)NOT NULL, Person_Address varchar(255)NOT NULL);Employee Table Query:
CREATE TABLE Employee (Person_ID INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY, Employee_Name varchar(255)NOT NULL, Salary INT NOT NULL);After this, let us insert some values in both tables with the SQL query below:
INSERT INTO Person (Person_ID, Person_Name, Person_Address) VALUES
('101', 'Aakash', 'Delhi'),
('102', 'Kajol', 'Mumbai'),
('103', 'Chetan', 'Pune'),
('104', 'Ankit', 'Goa');
INSERT INTO Employee (Person_ID, Employee_Name, Salary) VALUES
('101', 'Aakash', '1045.234'),
('102', 'Kajol', '1901.123'),
('103', 'Chetan', '2110.456'),
('104', 'Ankit', '2490.246');
select * from Employee;Output:
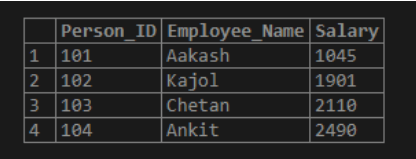
select * from Person;Output:
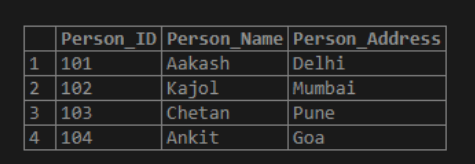
After these entries of a few records, let us move toward the queries related to the execution of the TRUNCATE() function.
Here is the SQL query:
SELECT Employee_Name, TRUNCATE(AVG (Salary),0)Avg_Salary FROM Employee a
INNER JOIN Person b ON b.Person_ID = a.Person_ID GROUP BY Person_Name ORDER BY Avg_Salary;Output:
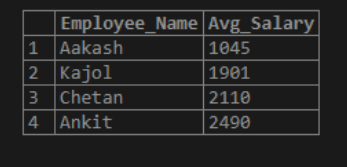
In the above illustration, we have used the TRUNCATE() function to eliminate all the numbers placed after the decimal digits from the average salary column in the table.
So, the TRUNCATE () may be helpful to produce the result set when we need to truncate the number values in a specific column of the database table to particular numeric value decimals. It provides us with the integer numbers to fetch the desired row.
5. MySQL TRUNCATE with Some Other Examples
We have more examples to explain the TRUNCATE() function and its importance in MySQL to trim the specific decimal places of a number.
SELECT TRUNCATE(251.315, -2);Output:
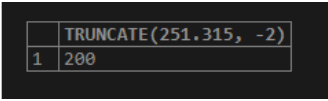
The above MySQL statement returns the value by truncating 251.315 to 1 decimal place.
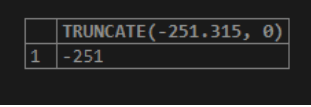
SELECT TRUNCATE(-251.315, 0);Output:
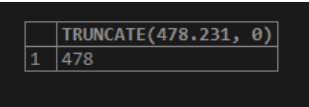
SELECT TRUNCATE(478.231, 0);Output:
Thus, the TRUNCATE() function returns the number truncated to the specified decimal places. When the decimal places value or parameter of the TRUNCATE() function is not provided, the number to be truncated is rounded down to 0 fractional points. Remember that the second argument of the TRUNCATE() function should be either a positive or negative integer.
Conclusion
If we notice, the TRUNCATE() function works similarly to the MySQL ROUND() function based on decreasing the number of decimal positions. But this function is not responsible for performing any rounding result as the ROUND() function. To clarify, we can conclude that the MySQL TRUNCATE () helps trim the decimal places, but the ROUND() function executes the rounding process.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL TRUNCATE()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

