Updated May 29, 2023
Introduction to MySQL Data Type
When dealing with any relational database, you must use tables to store the data. These tables can contain multiple columns to store the number of fields for each record. A single row corresponds to a single record of that table. When you define the fields to be stored in the table while creating it, you need to specify the column’s name, the corresponding data type, and other constraints and properties, if any. Data types play a crucial role while designing the tables and their columns. You need to consider the column’s purpose, what type of values it will store, the range of the values stored, and the format in which the data needs to be stored for each column. The data type used for each table column defines all these aspects. In this article, we will learn about the data types available in MySQL, their range, and other details, and also discuss their usage and purpose.
Characteristics of datatypes in MySQL
MySQL provides many datatypes other than numeric and string types to store the values in the columns. These datatypes can specify the behavior of the columns and the type of values that will be allowed to store in it. Datatypes in MySQL are associated with multiple characteristics that are as defined below:
The type of values that will be stored and represented in the declared columns.
The memory space requirement of that datatype is used for storage and to determine whether the values in that column will be of variable or fixed length.
Whether the column values for that data type can be used for indexing.
Comparison of the values of that datatype with other values in MySQL.
MySQL Data Type
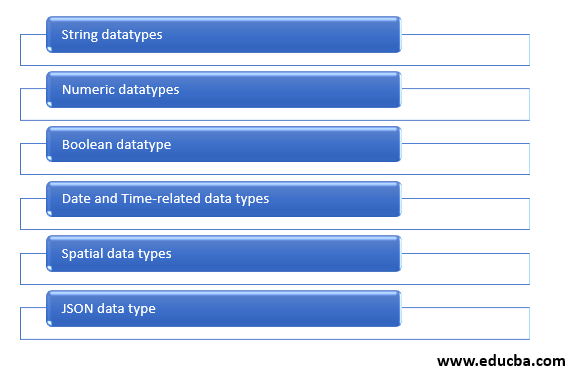
Mysql provides various data types that are further grouped based on the kind of values stored in that datatype columns. The datatypes can be broadly classified into the following groups:
We will discuss and have a look at the datatypes under each group in the list manner that will contain the name of all data types. Before that, let us briefly overlook some of the most used data types, along with the range of the values and kind of content that will be stored in them.
|
Name of datatype |
Range |
Kind of data stored |
| VARCHAR | (0 – 255) | String |
| CHAR | (0 – 255) | String |
| INT | (-2147483648 to 214748- 3647) | Integer |
| TINYINT | (-128 to 127) | Integer |
| MEDIUMINT | (-8388608 to 8388607) | Integer |
| BIGINT | (-9223372036854775808 to 9223372036854775807) | Integer |
| SMALLINT | (-32768 to 32767) | Integer |
| TEXT | 0 – 65535 | String |
| DOUBLE | (24 to 53 digits) | Decimal |
| BLOB | (0 – 65535) | String |
| DECIMAL | (24 to 53 digits) | Double value but stored in string format |
| BOOLEAN | 1 | TINYINT |
| DATETIME | YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM: SS | |
| TIME | HH:MM: SS | |
| DATE | YYYY-MM-DD | |
| ENUM | Can store one of the defined options of values | |
| SET | Can store selected values of the defined options of values |
1. String Data Types
We can store binary data like images of other media files and even plain tests in MySQL’s string data type values. Further, MySQL provides different functionalities for searching the string values using regular expressions, like operator or full-text search, that help us to use and manipulate string values.
The following list contains all the available data types that help to store string values:
- TEXT
- LONGTEXT
- MEDIUMTEXT
- TINYTEXT
- BLOB
- MEDIUMBLOB
- TINYBLOB
- LONGBLOB
- CHAR
- VARCHAR
- ENUM
- SET
- BINARY
- VARBINARY
2. Numeric Data type
We can store numeric values of different ranges and formats in MySQL. Exact and approximate numeric values can be stored using MySQL numeric datatypes. Besides that, MySQL also provides the functionality to store the bit values using the BIT data type.
The following list contains all the numeric data types available in MySQL.
- INT
- SMALLINT
- BIGINT
- MEDIUMINT
- TINYINT
- FLOAT
- DECIMAL
- DOUBLE
- BIT
3. Boolean Data Type
Mysql does not provide a dedicated data type for storing boolean values. However, whenever a BOOLEAN or BOOL named datatype is created in MySQL, it is internally interpreted as TINYINT(1) datatype by MySQL.
4. Date and Time Data Types
We can store dates and times individually as well as togetherly in MySQL. The timestamp can also be used to store and track the changes to the rows of the table. Besides that, if you want to store just a year, then you can use the YEAR data type.
The following list contains all MySQL’s date and time-related data types.
- DATETIME
- DATE
- TIME
- YEAR
- TIMESTAMP
5. Spatial Data Type
MySQL provides us with the facility to store the geometrical and geographical values in various data types.
The following list contains all the spatial data types available in MySQL.
- GEOMETRY
- MULTIPOINT
- POINT
- MULTIPOLYGON
- LINESTRING
- GEOMETRY COLLECTION
- MULTILINESTRING
- POLYGON
6. JSON Data Type
Mysql version 5.7.8 and further comes with the support of storing the JSON data type for storing and manipulating documents of JSON easily and efficiently. The JSON documents are validated automatically when the column is declared to be JSON data type in MySQL. This datatype provides optimal storage of JJSON documents that can be handled and stored effectively.
Conclusion
MySQL comes with multiple data types that can be used to declare the value type, format, nature, storage space required, and comparison basis. Different data types are grouped in MySQL depending on the kind of values stored in those columns. Which data type should be used to store the values in your table’s columns depends on all the above factors. It would be best to consider the value type and the range up to which the value can extend while determining the datatype to be assigned to the column.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL Data Type” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.