Updated May 15, 2023
What is MySQL ROW_NUMBER() Function?
Mysql ROW_NUMBER() function is a type of function that returns a number for each row in sequence or serial, beginning from 1 for the first record of the result set to the end in ascending order. It assigns a number value to each row or record in the table from 1 given to the first row to n to the nth row.
Row_number() feature was included in MySQL version 8.0.
Luckily, MySQL provides us with session variables by which we can find the row_number() function.
More precisely, It returns the serial number of a row within a partition of a result set or table, beginning with 1 for the first row in each partition till n for the nth row.
Syntax of MySQL ROW_NUMBER()
row_number() over (<partition><order by>)1. Partition Definition
Syntax:
partition by <expression1>,<expression2>,….<expression n>The Partition by clause is used to break the rows or records into smaller chunks of data. The expression followed by the partition clause is a valid condition that can be used in the group by syntax. The expression can be a single expression or multiple expressions separated by commas depending upon the requirement of the query.
We can use it as an optional statement. If the partition by clause is neglected in the row_number() function query, the entire output is treated as a single partition.
2. Order Definition
Syntax:
order by<expression> [acending|decending],[{,<expression>}..]The order by clause is mainly used to set the orders or sequence of rows or records.
Examples to Implement MySQL ROW_NUMBER()
Below is the Illustration of MySql row_number(). For the illustration purpose, we have taken the product table from our database:
Adding a row number or sequence number for each row of data, we have to use session Variables in the query to estimate the row number(): function.
Example #1
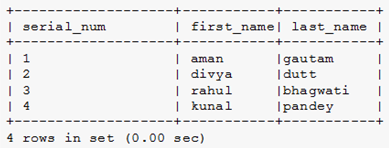
Explain adding a row number for each row: The following statements return four students from the STUDENT table and add a row number for each row, starting from 1.
Query:
set @row_num=0;
select
(@row_num:=@row_num+1) AS serial_num,
first_name,last_name
from
STUDENT
order by first_name,last_name
limit 4;Output:
Explanation:
- First, define a variable with the name @row_num and set it with an initial value of 0. The @row_num is a session variable incrementing each row’s value by 1. The @ prefix follows it.
- Then, using the select clause, we select data from the table STUDENT and increment each row value by 1 using the variable @row_num as row_num.
- The ORDER BY clause sorts or arranges the records in the result set in either ascending (ASC) or descending (DESC) order. By default, it sorts in ascending order.
- In the last line of the query, we have used the limit clause to constrain or restrict the number of returned rows or records to seven.
Another practice for using a session variable is as a derived table and cross-joining it with the main table. Below is the query to use the session variable as a derived table.
Example #2
Query:
select
(@row_num:=@row_num +1) AS num1,first_name,last_name
from
STUDENT
(select @row_num:=0) AS s
orderby first _name,last_name
limit 4;- In the above query, define a variable named @row_num and set it with an initial value of 0. The session variable @row_num increments the value of each row by 1. The @ prefix follows it.
- We have used the concept of subquery, a query within a query. One select clause represents the outer query, while the other represents the inner query, declared with the variable row_num initialized to 0. The outer query increments the row value of the result set.
- Then, using the select clause, we select data from the table STUDENT and increment each row value by 1 using the variable @row_num as row_num.
- The ORDER BY clause is responsible for sorting or arranging the records in the result set in ascending (ASC) or descending (DESC) order. By default, it sorts in ascending order.
- In the last line of the query, we have used the limit clause to constrain or restrict the number of returned rows or records to seven.
Example #3
Giving a row number to each data group; if we want to add a row number, we have taken a bank table from my database to explain this.
Query:
select
Cust_num,
Amt
from
Bank
orderby
Cust_num;We want to add a row number or sequence number to each customer, and we also want to reset the row number when the customer number changes.
For this purpose, we have to take two session variables, one for the row number increment and another for storing the old customer number to compare it with the current customer number.
Example #4
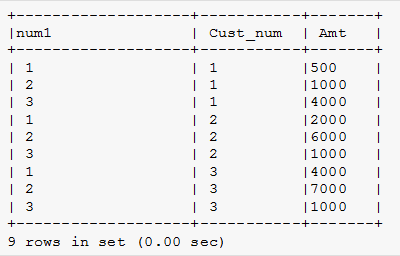
The below query is the illustration for adding a row number to the group of customers.
Query:
set @row_num:=0;
select @row_num:=CASE
when @cust_no=Cust_num
then @row_number+1
else 1
end AS num,
@cust_no:=Cust_num cust_num,Amt
from bank
order by Cust_num;Output:
Explanation: In the above query, we have used the CASE expression in the query. The @row_num variable increments if the customer number remains the same; otherwise, it resets to 1. The above query uses a derived table and the cross-join to give the same outcome.
Example #5
Query:
select
@row_num:=CASE
When @cust_no=Cust_num
then
@row_num+1
else 1
end AS num1,
@cust_no:=cust_numcust_num,Amt
from
Bank,
(select @cust_no:=0,@row_num:=0) as b
order by Cust_num;Conclusion
In this article on the row_number function, we have learned how to use the MySQL row_number() function to generate a serial number for each row or record in a result set of data. This article taught us how to use a select statement, order by clause, and cross-join.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL ROW_NUMBER()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.