Updated May 16, 2023
Introduction to MySQL NULLIF() Function
MySQL NULLIF() function is a part of the flow control MySQL function, which is responsible for comparing two expressions, which it accepts as arguments to execute the query. Generally, NULLIF() is helpful to avoid the division by zero faults that may occur in MySQL statements during implementation. The MySQL NULLIF() function takes two expressional parameters and performs the comparison similar to the CASE statement. If both the expressions passed are equal on execution, then the result will be NULL. Otherwise, if the condition fails, the function returns the initial expression as the output value. The NULLIF() accepts the expressions as arguments and compares them to return NULLIF. They are equivalent logically.
Syntax
Here is the elementary syntax code to apply the NULLIF() function in MySQL:
NULLIF(Expr_1, Expr_2)The arguments provided above for the function NULLIF() are required terminologies command code to be matched where Expr_1 denotes the first expression, and Expr_2 is the second expression for the NULLIF() function in MySQL.
The return value of the NULLIF() function is NULL when both terms are equivalent. Else, it will display the first parameter specified in the function.
Also, NULLIF() can be explained as identical to the CASE statement, which generates the following expression query:
CASE WHEN Expr_1 = Expr_2
THEN NULL
ELSE EXPR_1
END;Explanation: We should be aware not to get confused with the MySQL NULLIF() function is the same as the IFNULL() function because both functions are slightly different. We use the SELECT statement and NULLIF() function while writing the query command in MySQL.
How does MySQL NULLIF() Function work?
To understand how the MySQL NULLIF() function works:
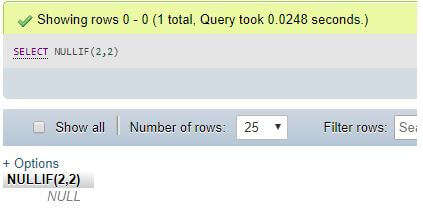
Step 1:
SELECT NULLIF(2,2);Explanation: NULLIF(2,2) results NULL as 2 = 2
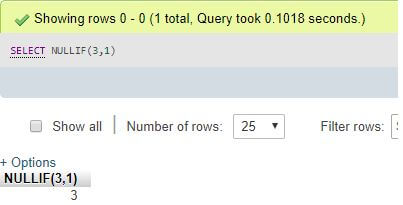
Step 2:
SELECT NULLIF(3,1);Explanation: NULLIF(3,1) results in 3, which is the first argument, as three is not equal to 1
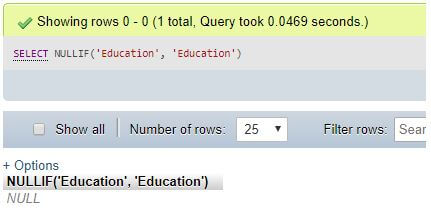
Step 3:
SELECT NULLIF('Education', 'Education');Explanation: NULLIF(‘Education’, ‘Education’) results in NULL as both the expressional string values are the same
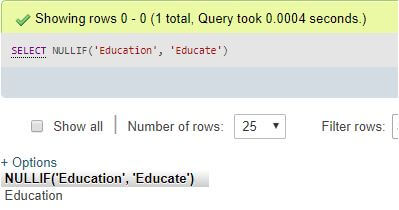
Step 4:
SELECT NULLIF('Education', 'Educate');Explanation: NULLIF(‘Education’, ‘Educate’) results in Education as the expressional string values are not identical
Step 5:
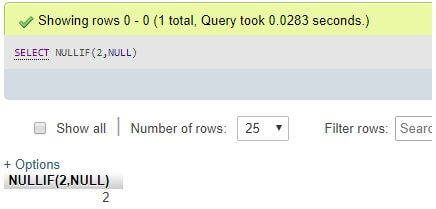
SELECT NULLIF(2,NULL);Explanation: NULLIF(2, NULL) results in 2 as both the expressions are not similar
Step 6:
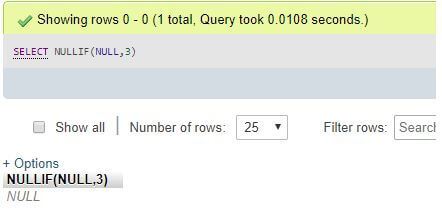
SELECT NULLIF(NULL,3);Explanation: NULLIF(NULL,3) results NULL as it is the first expressional term, and as NULL and three are not equal
Examples to Implement NULLIF() function in MySQL
Below are some examples of the NULLIF() function:
1. Using NULLIF() function with Table Column values in the database
Let us suppose a table by the name ‘Employees to be created to implement some examples using the table records with NULLIF() function in MYSQL. For this, we will write code and then execute it on the database having field names and data types:
CREATE TABLE Employees (EmpID INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, EmpNameVarchar(255) NOT NULL, EmpProfileVarchar(255) NOT NULL, EmpSalary INT NOT NULL, EmpPF INT);Also, we need to input some records in the table to perform the NULLIF() query command completion within the field data. Let us query the following statements to process some entries into the Employees table:
Code:
INSERT INTO Employees(EmpID, EmpName,EmpProfile,mpSalary,EmpPF)
VALUES('210', 'Radha ', 'Engineer ', '50000 ', '3600 ');
INSERT INTO Employees (EmpID, EmpName,EmpProfile,mpSalary,EmpPF)
VALUES('211', 'Mohan ', 'Manager ', '40000 ', '2000 ');
INSERT INTO Employees (EmpID, EmpName,EmpProfile,mpSalary,EmpPF)
VALUES('212', 'Dev ', 'Executive ', '32000 ', '1800 ');
INSERT INTO Employees (EmpID, EmpName,EmpProfile,mpSalary,EmpPF)
VALUES('213', 'Madhuri ', 'Blogger ', '20000 ', '');
INSERT INTO Employees (EmpID, EmpName,EmpProfile,mpSalary,EmpPF)
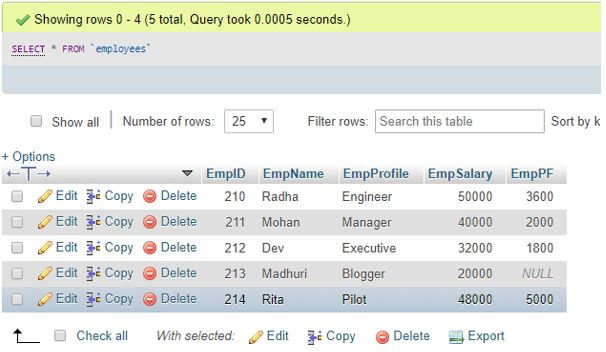
VALUES('214', 'Rita ', 'Pilot ', '48000', '5000 ');After running these queries, the values will be inserted as rows in the table Employees. We can display the records from the table Employees using the below command in MySQL:
Output:
It will provide the above details filled in the table as a view of the table.
Now, we will use the NULLIF() function on the column values to check the expressions passed as arguments to the function, compare them to provide the desired result, and explain the usage of the NULLIF() function with the database rows.
We have written the following query to represent the NULLIF() function in a query:
Code:
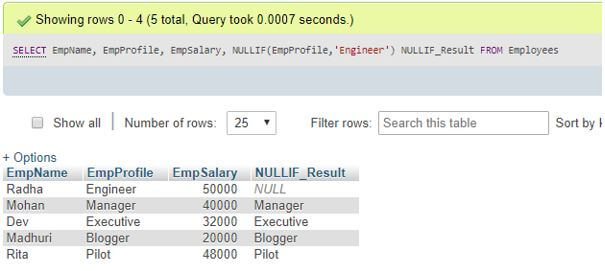
SELECT EmpName, EmpProfile, EmpSalary,
NULLIF(EmpProfile, 'Engineer') NULLIF_Result FROM Employees;Output:
Explanation: When we run the above query, it will execute successfully and return the result, as shown in the screenshot overhead. The result of the MySQL NULLIF() function checks the column value of EmpProfile as the first argument with the second argument set as Engineer. When the comparison starts on query execution, the Employee profile values are matched against the Engineer value respectively and generates the result as NULL if the values are equivalent; otherwise returns the column value if the match does not occur as the NULLIF() function returns first parameter value in the output if the function arguments are not equal. Take to be noted that MySQL will evaluate the first expression value twice with the second one if the matching of the two parameters does not show valid results or if they are not equivalent.
2. Using NULLIF() function to avoid division by zero error
In a MySQL query, we often practice using the NULLIF() function to stop the division by zero faults. If your MySQL server has enabled ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO mode, then when a division by zero happens, it will give an error at execution.
Consider the SQL statement below to show the error occurs:
SELECT 1/0;As you can see that the query produces an error. We need to use the NULLIF() function to remove this division by zero error. The updated query is as follows:
Code:
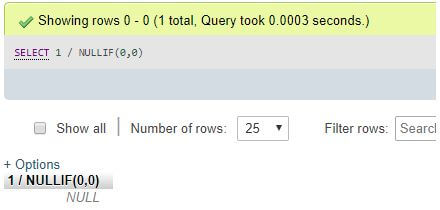
SELECT 1/NULLIF(0,0);Output:
Explanation: The NULLIF() function will return a NULL value as (0 = 0) zero is equivalent to zero provided in the arguments, resulting in NULL, and then one is divided b NULL. Therefore the result of the query above will also be NULL.
Conclusion
With NULLIF() function, we got introduced to a MySQL flow control function that is very handy in cases where we must prevent division by zero error in the respective queries executed on the server. The function takes two parameters, and after comparing the expressions, it provides the results; if the terms are equal, then NULL else shows the first term as an output on execution.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL NULLIF()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.