Updated May 26, 2023
Introduction to MySQL NOW
Dealing with the date and time storage in MySQL is very important as we often assign the wrong datatype to the columns without considering the usage and purpose of that column. When we have to store just the date, then the DATE type should be used; in case of time, just TIIME should be used, and when both date and time need to be stored, the DATETIME datatype can be used. Other than this, there is a provision to store the complete timestamp, and also, the zonal timezones can be considered by using data types such as timestamp and timestamps.
When we use the DATETIME datatype, we can use the NOW() function to initialize the column to the default value with the current date and time when the record insertion will be made. Besides this, the NOW() function can also generally fetch the current date and time. In this article, we will learn about the NOW() function, its syntax, and its usage with the help of some examples.
Syntax
Below is the syntax for MySQL NOW:
string/numeric NOW();Explanation: The syntax considers the call to the function NOW(), and the function’s return type is either string or numeric. The format of the DateTime depends on how we call the function within a specific context. For example, when string context is used, then the format of the retrieved date is in ‘YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM: DD’ format, while in the case of numeric context, the format of the fetched date changes to ‘YYYYMMDDHHMMSS’ format.
How does MySQL NOW work?
Let us retrieve the value of the NOW() function using the simple SELECT statement as follows:
Code:
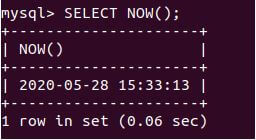
SELECT NOW();Output:
That is today’s date and the current time the article is written in the ‘YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM: DD’ format. As we can see, the default format used is the ‘YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM: DD’, and the return type is a string.
Let us convert the retrieved value in the numeric context value by adding 0 or 1 value or some other number to convert the returned value implicitly to the numeric value. We will use the following query statements:
Code:
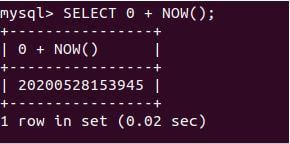
SELECT 0 + NOW();Output:
Execution of the above query statement gives the following output with today’s date and current time value in ‘YYYYMMDDHHMMSS’ format as shown in the below image:
Code:
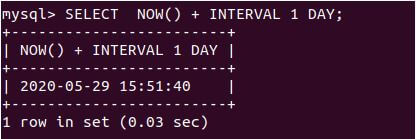
SELECT NOW() + INTERVAL 1 DAY;Output:
Execution of the above query statement gives the following output with tomorrow’s date and current time value as it is equivalent to today’s date plus one day in the ‘YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM: DD’ format. We can see that the NOW function can be used in the string and numeric context. And we can get the date-time relative to it by adding and subtracting the required interval of the period like DAY, HOUR, etc.
Examples to Implement MySQL NOW
Here are the examples:
Example #1
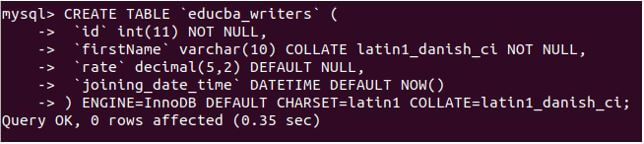
Let’s see what we can do with it in the table to assign the default value of the current date and time the value is being inserted in the column. We will create a table named educba_writers with joining_date|_time column with DATETIME data type with the help of the following query statement:
Code:
CREATE TABLE 'educba_writers' (
'id' int(11) NOT NULL,
'firstName' varchar(10) COLLATE latin1_danish_ci NOT NULL,
'rate' decimal(5,2) DEFAULT NULL,
'joining_date_time' DATETIME DEFAULT NOW()
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1 COLLATE=latin1_danish_ci;Output:
Example #2
Let us first insert the record with a null value as the joining_date_time column value using the following statement:
Code:
INSERT INTO 'educba_writers' ('id', 'firstName', 'rate') VALUES (1, 'Payal', 750);Output:
Example #3
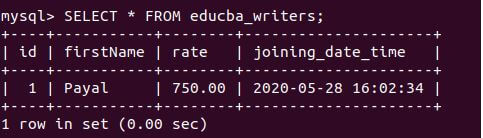
Let us retrieve the record and view the inserted value in the educba_writers table using the following query statement:
Code:
SELECT * FROM educba_writers;Output:
Example #4
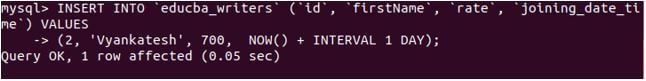
We will insert the values in the educba_writers table with tomorrow’s date and current time as joining_date_time values using the NOW() function along with the interval. For this, we will use the following insert query statements. Let us insert some more rows with non-null rate and joining date value:
Code:
INSERT INTO 'educba_writers' ('id', 'firstName', 'rate', 'joining_date_time') VALUES
(2, 'Vyankatesh', 700, NOW() + INTERVAL 1 DAY);Output:
Example #5
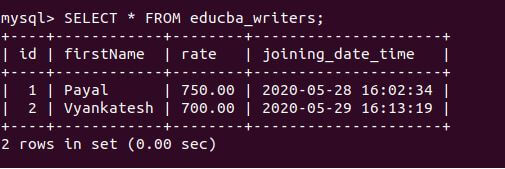
Let us retrieve the record and view the inserted value in the educba_writers table using the following query statement:
Code:
SELECT * FROM educba_writers;Output:
Explanation: We can see that the value of tomorrow’s date, 2020-05-27, and the current time in the ‘YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM: DD’ format is inserted in the joining_date_time column. We can even insert the DateTime concerning today’s date and current time using the NOW() function. Like for example, we can add the joining date as two days prior or three days later than today by reducing that many days from the NOW() function. We can even change the time by using the INTERVAL HOUR to set any number of hours later or prior to the current date-time.
Example #6
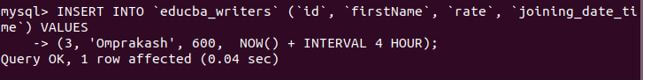
Let us consider one more example of setting the joining_date_time 4 hours later to the current time and date using the following query statement:
Code:
INSERT INTO 'educba_writers' ('id', 'firstName', 'rate', 'joining_date_time') VALUES
(3, 'Omprakash', 600, NOW() + INTERVAL 4 HOUR);Output:
Example #7
Let us retrieve the record and view the inserted value in the educba_writers table using the following query statement:
Code:
SELECT * FROM educba_writers;Output:
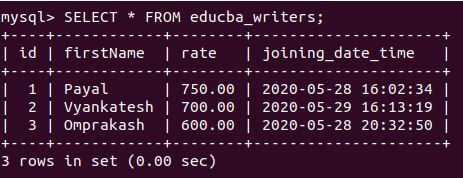
Example #8
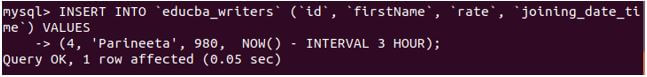
Consider one more example of setting the joining_date_time 3 hours before the current time and date using the following query statement:
Code:
INSERT INTO 'educba_writers' ('id', 'firstName', 'rate', 'joining_date_ti') VALUES
(4, 'Parineeta', 980, NOW() - INTERVAL 3 HOUR);Output:
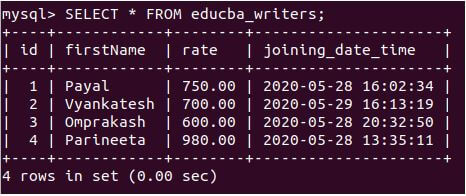
Example #9
Let us retrieve the record and view the inserted value in the educba_writers table using the following query statement:
Code:
SELECT * FROM educba_writers;Output:
Conclusion
We can utilize the NOW() function to set the default value of the DATETIME column as the current date and time during insertion. Furthermore, we can manipulate the retrieved value from the NOW() function by adding and subtracting intervals.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL NOW” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.