Updated May 30, 2023
Introduction to MySQL LOWERCASE
The following article provides an outline for MySQL LOWERCASE. To convert the string to lowercase, we can do it by using the LOWERCASE function. The LOWERCASE has one argument which will accept the string and convert it into the lower case. The function used for the above functionality is LOWER() or LCASE(). Binary, BLOB, and Varbinary are binary string data; these are ineffective when applied to the LOWER() function. To pass such data, we first convert the string to a non-binary string.
Syntax:
The syntax for the LOWERCASE function is as below:
LOWER( <string> / <column_name> )Or
LCASE (<string> / <column_name>)How does MySQL LOWERCASE work?
Now let’s see how the LOWER() function works individually and in the table:
Code:
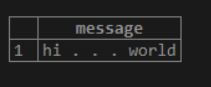
SELECT LOWER ( 'HI . . . WORLD' ) AS MESSAGE;Here we can see that the <string> is mentioned as “HI . . . WORLD”. Above, we use the LOWER function to convert the ‘upper string’ to the ‘lower string’.
Output:
Code:
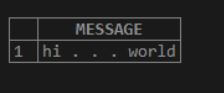
SELECT LCASE( 'HI . . . WORLD' ) AS MESSAGE;Here we can see that the <string> is mentioned as “HI . . . WORLD”. Above, we use the LCASE function to convert the ‘upper string’ to the ‘lower string’.
Output:
Now let us create a table and apply the LOWER () function:
Code:
CREATE TABLE LOWERCASE_DEMO (
ID INT,
UPPERCASE_VALUE VARCHAR(15)
);Now let us insert data into the table:
Code:
INSERT INTO LOWERCASE_DEMO VALUES ( 1, 'BE INDEPENDENT');
INSERT INTO LOWERCASE_DEMO VALUES ( 2, 'BE CONFIDENT');
INSERT INTO LOWERCASE_DEMO VALUES ( 3, 'BE YOU');
INSERT INTO LOWERCASE_DEMO VALUES ( 4, 'BE POSITIVE');
INSERT INTO LOWERCASE_DEMO VALUES ( 5, 'BE REAL');
INSERT INTO LOWERCASE_DEMO VALUES ( 6, 'BE KIND');
INSERT INTO LOWERCASE_DEMO VALUES ( 7, 'BE GENEROUS');
INSERT INTO LOWERCASE_DEMO VALUES ( 8, 'BE FAMOUS');
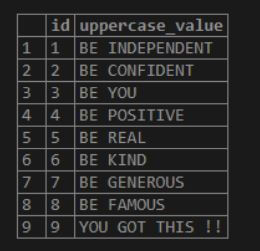
INSERT INTO LOWERCASE_DEMO VALUES ( 9, 'YOU GOT THIS !!');Now let us select the data from the table without applying the LOWER function. The output would be as below—screenshot for the same. Here we can see that the column ‘UPPERCASE_VALUE’ data is in upper case. We use the LOWER and LCASE functions to convert the characters into the LOWER cases.
Code:
select * from LOWERCASE_DEMO;Output:
Now let us see the LOWER function and LCASE function:
Code:
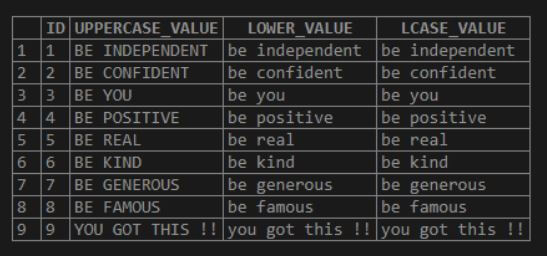
SELECT *, LOWER ( UPPERCASE_VALUE) AS LOWER_VALUE,
LCASE ( UPPERCASE_VALUE) AS LCASE_VALUE FROM LOWERCASE_DEMO;In the above select statement, we could see that instead of ‘string expression’, we have specified the ‘column name.’ Which will convert the column values from upper case to lower case as below. The LOWER function or LCASE function achieves this.
Output:
Examples of MySQL LOWERCASE
Given below are the examples of MySQL LOWERCASE:
Example #1
Now let us see how the LOWER () function works individually and in the table.
Multiple cases in one string output also give lower case using the LOWER function.
Code:
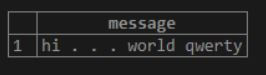
SELECT LOWER( 'Hi . . . world QwErTy' ) AS MESSAGE;Here we can see that the <string> is mentioned as ‘Hi . . . world QwErTy’, which is a combination of upper case and lower case. Once we use the LOWER function to convert the ‘upper string’ to ‘lower string’. The lower characters will convert to upper case, while the upper case characters will remain as they are.
Output:
Code:
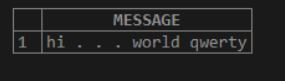
SELECT LCASE ( 'Hi . . . world QwErTy' ) AS MESSAGE;Here we can see that the <string> is mentioned as ‘Hi . . . world QwErTy’, which is a combination of upper case and lower case. Once we use the LCASE function to convert the ‘upper string’ to ‘lower string,’. The lower characters will be converted to upper, and the upper case remains upper.
Output:
Example #2
Let us see another example for the LOWER and LCASE functions below.
Code:
CREATE TABLE COLLEGEDATA
(
COLLEGE_ID INT,
COLLEGE_NAME VARCHAR(50),
NO_OF_STUDENTS INT,
LOCATION VARCHAR(20)
);The below data is inserted into the above table:
Code:
INSERT INTO COLLEGEDATA VALUES (1890, 'Narayana pvt college', 700000, 'Hyderabad');
INSERT INTO COLLEGEDATA VALUES (2890, 'St.Josephpvt college', 560000, 'Kerala');
INSERT INTO COLLEGEDATA VALUES (3890, 'Private Plan pvt college', 230000, 'Hyderabad');
INSERT INTO COLLEGEDATA VALUES (4890, 'Chorniclepvt college', 60000, 'Maharastra');
INSERT INTO COLLEGEDATA VALUES (5890, 'Number one pvt college', 780000, 'Hyderabad');
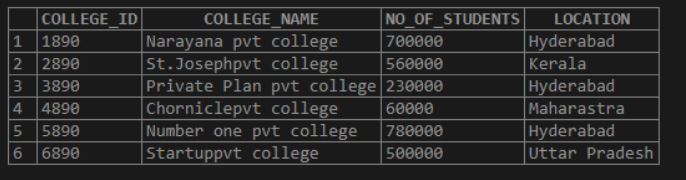
INSERT INTO COLLEGEDATA VALUES (6890, 'Startuppvt college', 500000, 'Uttar Pradesh');Select the data from the above table, and the rows look as below:
Code:
SELECT * FROM COLLEGEDATA;Now let us select the data from the table without applying the LOWER function.
Output:
Let us apply the LOWER and LCASE functions:
Code:
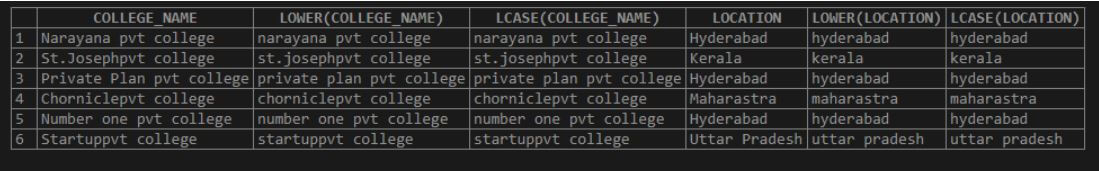
SELECT COLLEGE_NAME,LOWER(COLLEGE_NAME),LCASE(COLLEGE_NAME)
,LOCATION , LOWER(LOCATION) , LCASE(LOCATION) FROM COLLEGEDATA;Here we can see that the column ‘COLUMN_NAME’ data is in upper case. We use the LOWER and LCASE functions to convert the characters into the LOWER issues.
Output:
Conclusion
To convert the string to lowercase, we can do it by using the LOWER CASE function. The LOWERCASE has one argument which will accept the string and convert it into the lower case. The function used for the above functionality is LOWER () or LCASE (). Binary, BLOB, and VARBINARY are types of binary string data. However, applying the LOWER() function to these data types is ineffective. To pass such data, we first convert the string to a non-binary string.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL LOWERCASE” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.