Updated May 20, 2023
Introduction of MySQL InnoDB
Mysql supports many storage engines for the table, which define the internal working and support for different features of the tables. Some of the storage engines supported by MySQL include InnoDB, MyISAM, Memory, CSV, Merge, Archive, Federated, Blackhole, and Example. The Innodb storage engine is the most widely utilized among them, while MyISAM is one of the original storage engines used in internal tables for manipulating MySQL databases belonging to information_schema and MySQL databases.
MyISAM engine is non-transactional and has table-level locking, while InnoDB is a transactional storage engine with a row-level locking feature. InnoDB storage engine provides excellent performance and reliability balance and is one of the most preferred and suggested storage engines by Oracle. In this article, we will learn about the InnoDB storage engine of MySQL, its supported features, and a working example of creating a table with an InnoDB storage engine by explicitly specifying the same.
Advantages of InnoDB Storage Engine
The InnoDB storage engine offers numerous advantages, including:
- All the data manipulation language statements and operations support the ACID(Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability) transaction properties and other transactional features of rollback, commit, and crash-recovery support for securing the user data.
- The InnoDB storage engine achieves concurrent access by multiple users with high performance and consistent reads in Oracle style through its row-level locking feature.
- Arranging the data in such a way on the disk will lead to optimizing data retrieval when using primary keys in your query. The clustered index defined on the primary key of InnoDB tables leads to the organization of the data to minimize the input/output operation for lookups of the primary key.
- To avoid inconsistency in the tables that are related and dependent on each other, the InnoDB storage engine supports the usage of the foreign keys that help in the consistent update, insert and delete operations and helps in maintaining integrity and consistency in the contents of tables of the database.
Features of MySQL InnoDB
Features of InnoDB include B-tree indexes, Backup/point-in-time recovery, Clustered indexes, Compressed data, Data caches, Encrypted data, Foreign key support, Full-text search indexes for MySQL 5.6 and later versions, Geospatial data type support, Geospatial indexing support for MySQL 5.7 and later versions, Index caches, Locking granularity at the Row level, MVCC, Replication support, Storage limits up to 64TB, Transactions, Update statistics for the data dictionary. InnoDB uses hash indexes internally for the Adaptive Hash Index feature, but it does not support the use of hash indexes directly for manipulating InnoDB tables.
Examples of MySQL InnoDB
Whenever we create a table using create table statement in MySQL 5.5 and above versions, the default storage engine of the created table is always Innodb. In contrast, for the versions before MySQL 5.5, MyISAM is the default storage engine for the table. We can mention the table’s storage engine while creating it by using the ENGINE= clause if we want to create a table of any other storage engine or in case we want to specify the engine type as InnoDB explicitly.
Firstly, we will see how we can use the ENGINE= clause to specify the storage engine with the help of an example. We will create a table named educba_innodb using the following create table statement –
CREATE TABLE educba_innodb (id INTEGER, description VARCHAR(20), PRIMARY KEY (id)) ENGINE=InnoDB;Output:
While making the table with the InnoDB storage engine, it is necessary to use a primary key column that has the following properties –
- Most of the crucial queries should utilize and reference this column.
- Ensure that the column always has a value and is never left blank.
- Duplicate values should never exist in this column.
- The value in this column should remain unchanged once it is inserted into the table.
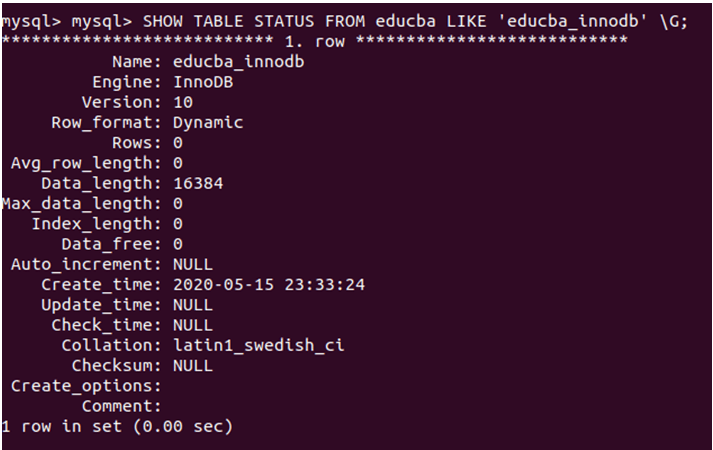
We can check the status of the table and all the related information by using the SHOW TABLE STATUS statement in MySQL. For example, if we want to check the status of the table we created earlier named educba_innodb, then we will use the following query statement –
SHOW TABLE STATUS FROM educba LIKE 'educba_innodb' \G;that gives the following output displaying all the details related to the educba_innodb table –
In our case, we can even see the table’s engine in this status, which is InnoDB.
Let us try creating a table with different storage engines, say MyISAM, with the name educba_myisam. For this, we will mention the ENGINE= MyISAM clause to create a query as shown below –
CREATE TABLE educba_myisam (id INTEGER, description VARCHAR(20), PRIMARY KEY (id)) ENGINE=MyISAM;that gives the following output –
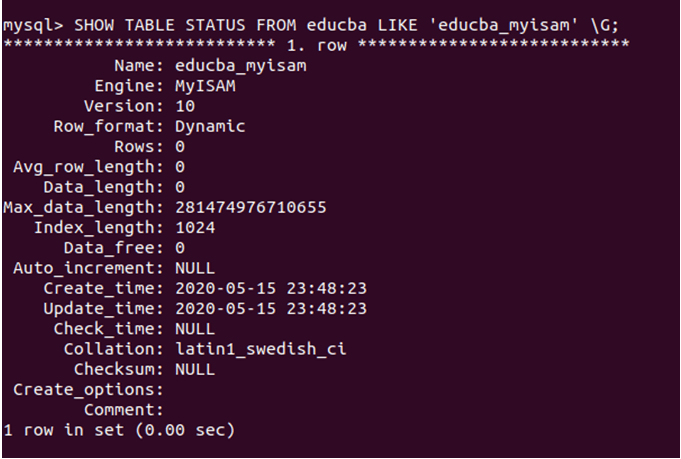
After checking the status using the following query for the educba_myisam table –
SHOW TABLE STATUS FROM educba LIKE 'educba_myisam' \G;gives the following output saying the Engine of the table is MyISAM –
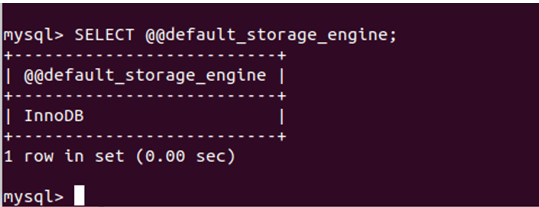
To determine the default storage engine installed on your database server, you can execute the following command:
SELECT @@default_storage_engine;Running the above command gives the following output:
Let us try creating a table without specifying the ENGINE= clause in CREATE TABLE statement. We will create a table named educba_default using the following query –
CREATE TABLE educba_default (id INTEGER, description VARCHAR(20), PRIMARY KEY (id));that gives the output as follows after execution –
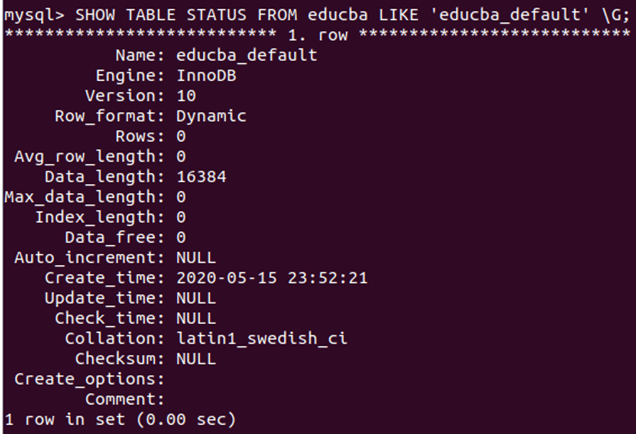
Let’s check the table’s status to determine which storage engine was used by default when creating the table. Earlier, we queried and found that the default storage engine for MySQL installed on your machine is InnoDB. Hence, the educba_default should have an InnoDB engine. Here’s the output –
SHOW TABLE STATUS FROM educba LIKE 'educba_default' \G;Running the above command gives the following output:
Conclusion
The InnoDB storage engine is the default engine assigned to the table while creating in Mysql 5.5 and above versions. To explicitly mention the table’s storage engine while creating, you can use the ENGINE= clause. The Innodb engine performs well due to many features, such as row-level locking, transaction support, and indexing on primary keys. InnoDB storage engine also provides the feature to use foreign keys that help maintain the consistency and integrity of MySQL databases. Concurrent access by multiple users and each of them retrieving consistent data is possible using the InnoDB storage engine.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL InnoDB” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.