Updated May 29, 2023
Introduction to MySQL BLOB
Blob is the data type in MySQL that helps us store the object in binary format. It is typically used to store files, images, etc., media files for security or other purposes in MySQL. It can keep and hold a variable amount of data, and four blob types can be used in MySQL: LONGBLOB, MEDIUMBLOB, BLOB, and TINYBLOB. All these types differ in the storage space required and the maximum length that can e stored. These data type values are primarily handled as byte strings or binary strings.
The BLOB values contain the binary character set and collation. The bytes stored in such column values hold numeric values for sorting and comparison operations in MySQL. In this article, we will learn about the BLOB datatype and how we can declare the columns of the table as BLOB; further, we will discuss the behavior of the BLOB values for different settings of strict mode and see the examples related to BLOB values.
BLOB Datatype
The maximum row size of the table in MySQL is 65535, which represents the internal capability of the row even though the storage engine has larger capability support for rows. This maximum row size does not include the BLOB or TEXT data type column. Different storage engines distribute the storage of BLOB-valued data across various memory areas, and the allocation of memory for this type of value varies among them. Each storage engine uses a different method to handle the data of such datatype.
The storage requirement for all the blob datatypes is as given below –
- TINYBLOB – length+ 1 byte, where length< 2^8
- BLOB – length+ 2 bytes, where length< 2^16
- MEDIUMBLOB – length+ 3 bytes, where length< 2^24
- LONGBLOB – length+ 4 bytes, where length< 2^32
where the length stands for the original length of the character string that the blob data typed column contains.
Below are some important points to know about the BLOB datatype:
- The BLOB data type is a variable-length column; hence, it is regarded as the VARBINARY column. However, it differs from the VARBINARY in specific ways. When using a BLOB column for indexing in MySQL, it is necessary to specify the length of the prefix used for indexing. Assigning a default value to the BLOB column is not allowed.
- If you disable strict mode in MySQL and try to insert a value in a BLOB column that exceeds the maximum length, the system will truncate the value to fit the column’s maximum length. MySQL will insert only the truncated portion of the value that exceeds the column’s maximum length. It will generate a warning to indicate the truncation.
- Enabling strict mode in MySQL prevents the truncation of values exceeding a column’s maximum length. Instead, it raises an error indicating that the inserted value exceeds the defined column length.
- Whenever we sort on the BLOB column, only the first max_sort_length bytes are considered for sorting. max_sort_length variable has the default value of 1024. However, we can further change the value of max_sort_length and increase it to consider many bytes of the value while sorting and grouping the data based on the BLOB column.
- The type of the BLOB determines the maximum size the column can have. However, the largest possible value size transmitted between the client and server depends on the size of the buffers used in communication and the available memory. You can change the maximum capacity of the buffer size by simply modifying the value of the max_allowed_packet variable. To ensure proper functionality, you need to change the value of this variable on both the server and client sides.
Examples of MySQL BLOB
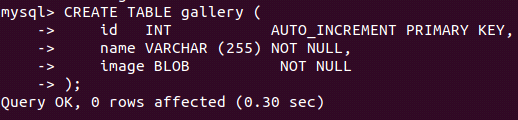
We will create a table named Gallery containing the id, name, and image columns. The image column will be of BLOB datatype. We can use the following query to create our table –
Code:
CREATE TABLE gallery (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR (255) NOT NULL,
image BLOB NOT NULL
);Output:
We can use PDO to insert the values in tables with blob datatype columns in PHP. We will see a program in PHP that will show how we can insert and retrieve the blob values to and from the database, which is as follows –
Code:
<?php
class galleryBlob {
const DB_HOST = 'localhost';
const DB_NAME = 'educba';
const DB_USER = 'username';
const DB_PASSWORD = 'password';
public function __construct() {
$conStr = sprintf("mysql:host=%s;dbname=%s;charset=utf8", self::DB_HOST, self::DB_NAME);
try {
$this->pdo = new PDO($conStr, self::DB_USER, self::DB_PASSWORD);
} catch (PDOException $e) {
echo $e->getMessage();
}
}
public function insertImage($filePath, $name) {
$blob = fopen($filePath, 'rb');
$sql = "INSERT INTO gallery(name,image) VALUES(:name,:image)";
$stmt = $this->pdo->prepare($sql);
$stmt->bindParam(':name', $name);
$stmt->bindParam(':image', $blob, PDO::PARAM_LOB);
return $stmt->execute();
}
public function selectImage($id) {
$sql = "SELECT name,
image
FROM gallery
WHERE id = :id;";
$stmt = $this->pdo->prepare($sql);
$stmt->execute(array(":id" => $id));
$stmt->bindColumn(1, $name);
$stmt->bindColumn(2, $image, PDO::PARAM_LOB);
$stmt->fetch(PDO::FETCH_BOUND);
return array("name" => $name,
"image" => $image);
}
public function __destruct() {
$this->pdo = null;
}
}
$sampleImage = new galleryBlob();
$sampleImage->insertImage('sample.jpg',"image/jpg");
$a = $sampleImage->selectImage(1);
header("Content-Type:" . $a['name']);
echo $a['image'];
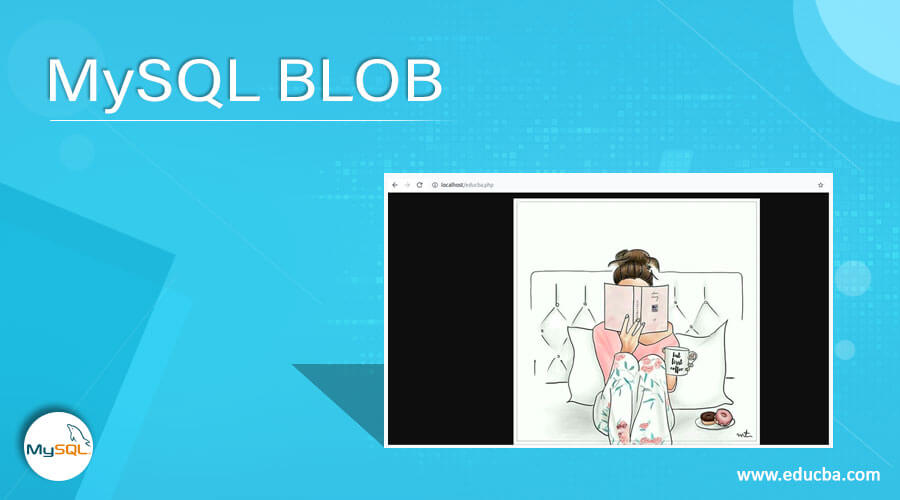
?>When you execute the above code and open it in the browser with the file saved as “educba.php,” the output will display as follows: you inserted an image with the name “sample.jpg”.
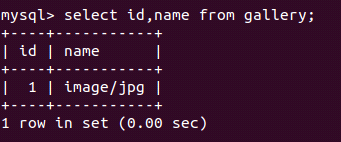
Which shows the image that we stored in the SQL table gallery. Let us retrieve the record in MySQL and check the contents of the gallery table –
select id, name from gallery;Output:
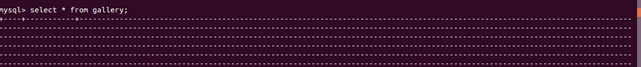
When attempting to retrieve the blob value using the following query statement, the output becomes excessively large because of the jpg file stored in the image column of the blob type. As a result, the result set becomes vast and unreadable on the terminal, as the jpg file cannot be parsed on the terminal.
select * from gallery;Output:
Conclusion
In MySQL, we use the blob type to store various media files, including images, PDF files, videos, reports, and more. Taking the precautions discussed above is essential when working with this type.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL BLOB” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.