Updated May 26, 2023

Definition of MySQL Hour() Function
MySQL Hour() Function is MySQL DateTime function which is responsible to fetch the hour part from the datetime value specified in the query. The Hour() function in the server provides the hour portion extracted from the given date and time data type value from 0 to 838. Usually, MySQL supports the format ‘HH:MM:SS’ to query and show the time value, which displays the time of any particular day within 24 hours. But for signifying a time interval concerning two events, the server applies the format as ‘HHH:MM:SS’, which is greater than 24 hours. Generally, in MySQL, the data type Time lies between -838:59:59 to 838:59:59.
Syntax
The basic code for writing the syntax of MySQL Hour() function for querying the hour fragment from the given time value is defined as follows:
SELECT HOUR(Datetime);Here, the command includes the SELECT keyword to display the value and the function parameter as Datetime data type for getting the hour value.
Also, you can consider the following syntax for the Hour () function in MySQL using the Time type:
SELECT HOUR(Time);Again, we can additionally apply other date and time-related data types as parameters for the Hour () function. Some of them are mentioned below:
SELECT HOUR(CURTIME());
SELECT HOUR(NOW());
SELECT HOUR(CURRENT_TIME());
SELECT HOUR(CURRENT_TIMESTAMP());Hence, the MySQL Hour() function outputs the hour value with a range of 0 to 838 from the specified datetime value, and the time value can also be higher than 23, which is more than the daytime value(0 to 23).
How does Hour Function work in MySQL?
The MySQL HOUR() function extracts the hour portion from a datetime value in the server. This kind of MySQL time function queries the Hour from the standard time format as HH:MM:SS or HHH:MM:SS. The datetime format will have the syntax as YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS.
This type of temporal function is used to effectively manipulate the date-time value in the MySQL database server when executed for any table column with datetime data type.
Let us write the syntax for stating a TIME column in the table as:
ColumnName TIME;For example, while applying a query for a specific column name of a table supposing as Join_at name, we will edit the column name in the above syntax as:
Join_at TIME;Also, we can evaluate some other temporal time functions to extract the hour value, such as the current time function denoted as CURRENT_TIME() function, NOW() function, and CURRENT_TIMESTAMP in MySQL. The CURRENT_TIME() function provides the present time value. As a result, the NOW() function also returns the server’s current date and time value, and CURRENT_TIMESTAMP also does the identical work providing the date and time values existing in the present.
Therefore, we can include the parameter values using any of these time functions in MySQL for the HOUR() and get the particular hour value as,
SELECT HOUR(datetime);Take a demonstration to show the working of this hour function in the server where we will enter the datetime value manually as below:
SELECT HOUR('2020-09-12 15:30:25');Here, the output as hour value will be fragmented from the time format hour value, which will be 15.
Also, when the time parameter holds the following value, then also the hour function determines the hour value from it as,
SELECT HOUR('838:59:59');As you know, the MySQL Hour() function will return the value of 838.
Examples
Let us illustrate the MySQL HOUR() function with a few examples, including simple and table columns with the date and time data type as follows:
Example #1 – Using the Hour() Function
- For Time value as parameter:
SELECT HOUR('16:30:45');Output:
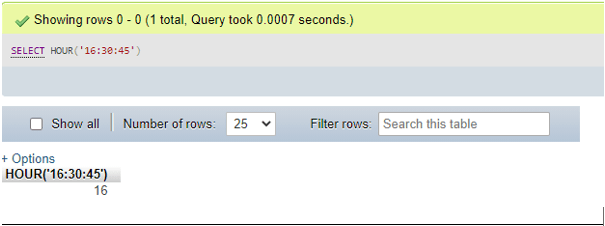
- For DateTime value as parameter:
SELECT HOUR('2020-09-10 16:30:45');Output:
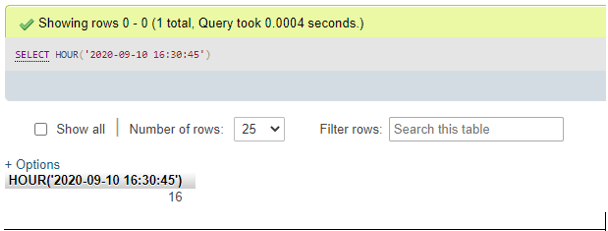
- For CURRENT_TIME() function value as parameter:
SELECT HOUR(CURRENT_TIME());- For CURTIME() function value as parameter:
SELECT HOUR(CURTIME());Output:
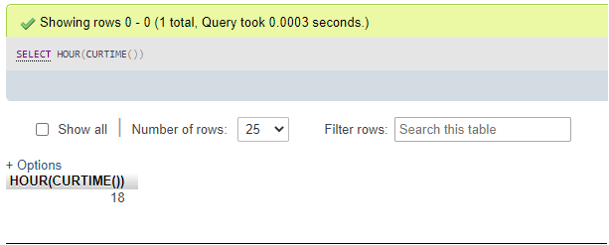
- For CURRENT_TIMESTAMP value as parameter:
SELECT HOUR(CURRENT_TIMESTAMP);Output:
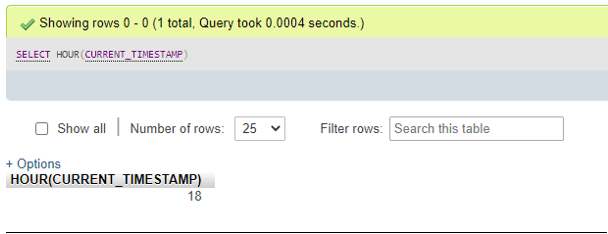
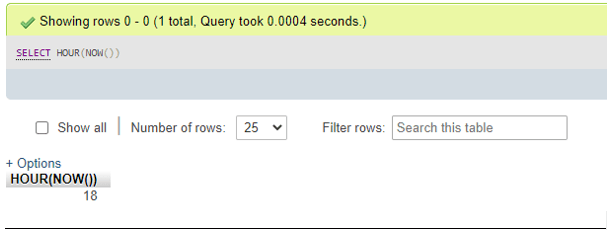
- For NOW() function value as parameter:
SELECT HOUR(NOW());Output:
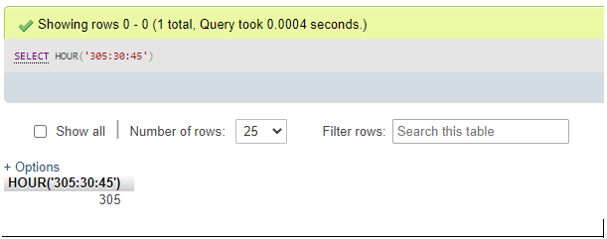
- For Time value larger than 24 hours as parameter:
SELECT HOUR('305:30:45');Output:
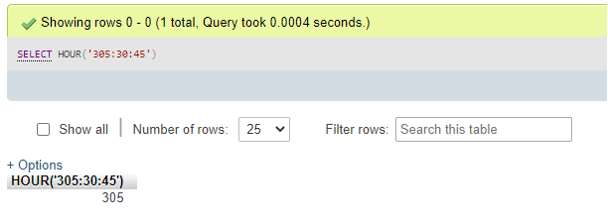
- For negative Time value as a parameter:
SELECT HOUR('-305:30:45');Output:
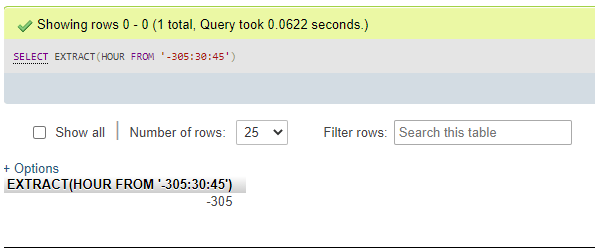
Here, suppose there is any problem like if you need the resultant hour value to be negative, then you can use the MySQL EXTRACT() function to find the output as we are looking for it:
SELECT EXTRACT(HOUR FROM '-305:30:45');Output:
- For Date value and Time value with additional microseconds value as parameter:
SELECT HOUR('2020-09-10 05:30:45.000008');Output:
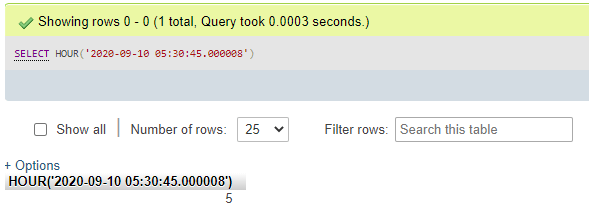
Here, the part of the time value after the decimal, i.e., .000008, denotes the microseconds value.
Example #2 – Using the Table Column Datetime Value to Extract HOUR() Function
Let us take a sample table named Employee created in the database using the following query:
CREATE TABLE Employee('Person_ID INT PRIMARY KEY', 'Employee_Name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL', 'Salary INT NOT NULL', 'JoinDate DATETIME NOT NULL');Also, we will add a few records to the Employee table using the INSERT command:
INSERT INTO Employee(Peron_ID, Employee_Name, Salary, JoinDate) VALUES('101','Aakash','1045', '2020-02-10 05:00:00');And so on.
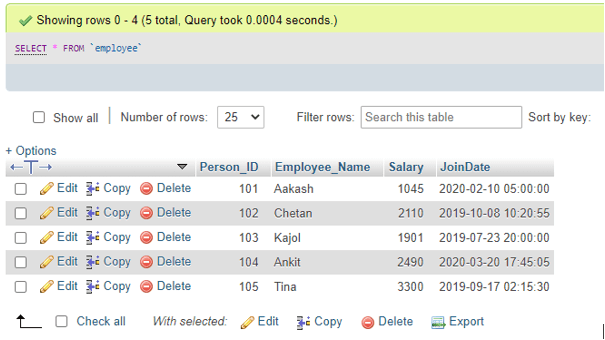
Displaying the table contents as:
SELECT * FROM Employee;Output:
Let us implement the HOUR() function with the WHERE clause with the Employee table query as follows:
SELECT * FROM Employee WHERE HOUR(JoinDate) > 05;Output:
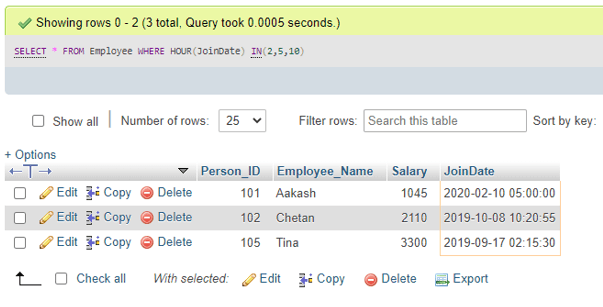
It outputs the rows from the table that joined after 5 A.M.
Also, let us query using the MySQL HOUR() function with the BETWEEN operator in the Employee table as follows:
SELECT * FROM Employee WHERE HOUR(JoinDate) BETWEEN 05 AND 10;Output:

It results in the data rows for a time duration of 5 to 10 hours.
Again, querying command using the MySQL HOUR() function with the IN operator in the Employee table as follows:
SELECT * FROM Employee WHERE HOUR(JoinDate) IN(2,5,10);Output:
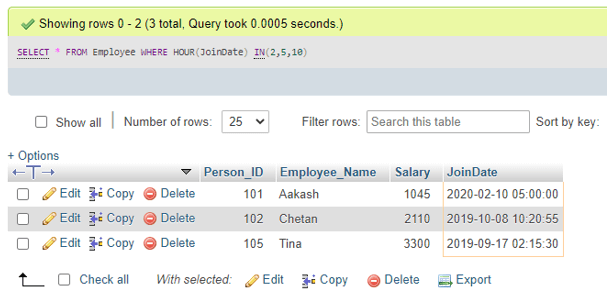
It gives information about the join Hour at 2 or 5, or 10 A.M. from the given datetime value in the JoinDate.
Conclusion
The server implements the MySQL Hour() function to find the hour component using the time value provided. Here, the result value will be 0 to 23 for a time of day worth. However, this range of values for time is much larger. Therefore the Hour may result in values that are greater than 23.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL Hour()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

