Updated June 1, 2023
Introduction to MySQL FORMAT
The following article provides an outline for MySQL FORMAT. FORMAT function is used to format a numerical value in the table to any desired decimal points. Suppose the table columns have varying decimal points, one rounded off to 2 places and another to 4. And in the resulting output, we have to get a product of these two columns. In such cases, the output can have varying decimal places. Each row possessing different decimal points from each other can cause much ambiguity. So, When utilizing the FORMAT function with the SELECT query, you can specify the number of decimal points to round the output to. When the output variable hasn’t been defined beforehand is particularly useful.
Syntax of MySQL FORMAT
FORMAT function is used to format any numerical value in our output.
The syntax for this function will be as follow:
FORMAT (column_name, decimal_points)Here, the column_name is the field to be rounded off, and the decimal_points are how many places the value should be rounded to.
On a detailed note, the syntax can include one more optional field.
FORMAT (column_name, decimal_points, locale)Here, the field locale refers to the separators and groupings. This field uses the en_US locale by default, and it is not defined as optional. MySQL offers over 100 defined locales.
How does the FORMAT Function work in MySQL?
Given below shows how the FORMAT function works in MySQL:
Example #1
Let’s format a value with more decimal places to just two.
Code:
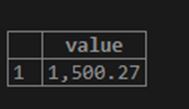
SELECT FORMAT(1500.26543,2) value;The query says to round off the value 1500.26543 to 2 places instead of 5 decimal places. I hope you are familiar with the principles of rounding off to consider values above 5 and below 5. So here, the expected output is 1500.27 (because the third digit after the decimal point is 5).
Output:
Example #2
Let’s see another example below.
Code:
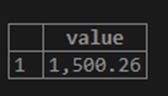
SELECT FORMAT(1500.26111,2) value;So here, the third digit after the decimal point is less than 5; thus, the expected output is 1500.26.
Output:
Example #3
The FORMAT function also adds extra zeros to extend the decimal places.
Code:
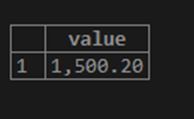
SELECT FORMAT(1500.2,2) value;The value is 1500.2 and has only one decimal place. But the result is to have 2 decimal places. So, an extra zero will be appended to this query.
Output:
Example #4
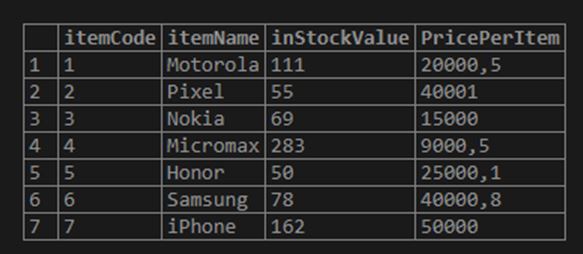
Let’s now consider a table inventory with data such as the number of items in stock and the rate per unit for each item. The resulting output in this scenario is the total stock value which will be a product of No. Of units and rate per unit for each item in stock.
Let’s consider the table below:
Code:
select * from inventory;Output:
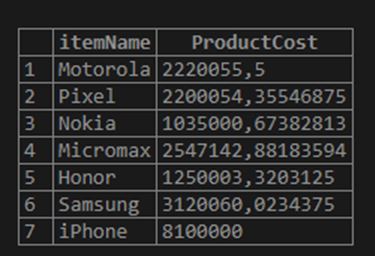
We will first see the result without using the FORMAT function.
Code:
SELECT itemName, instockValue * PricePerItem ProductCost FROM inventory;The resulting output displays itemName and ProductCost columns where the ProductCost column is a product of inStockValue and PricePerItem.
Output:
So, the output will look like this. It certainly looks clumsy and very inappropriate.
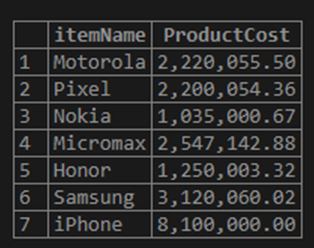
We can use the FORMAT function and retrieve a better-looking output now.
Code:
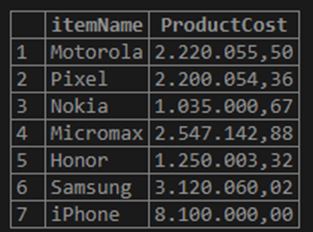
SELECT itemName, FORMAT (instockValue * PricePerItem, 2) ProductCost
FROM inventory;In this case, we have specified the decimal places to be rounded off to 2.
Output:
If we compare the outputs of this query and the previous query, we can understand that the latest output is of more clarity.
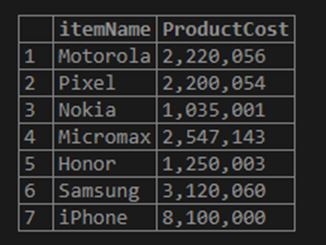
We can round off the decimal places to zero, also.
Code:
SELECT itemName, FORMAT (instockValue * PricePerItem, 0) ProductCost
FROM inventory;Output:
Here, the output is rounded off to zero decimal places. We can specify the decimal places to be 0; if we leave it blank, the default value is 0.
Example #5
We spoke about using locale in the FORMAT query. By default, the locale is en_US. Let’s try any other locale and identify the difference.
We will see two examples for locales.
a. This query is to update the output as Spanish in Spain.
Code:
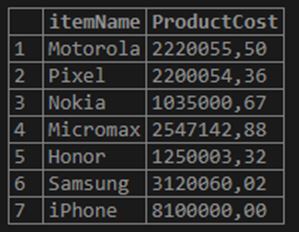
SELECT itemName, FORMAT (instockValue * PricePerItem, 2, 'es_ES') ProductCost
FROM inventory;Output:
b. The decimal point is replaced by comma ‘,’ instead of a dot.” in this locale. And there are no grouping thousands in this format.
Let’s try another locale.
Code:
SELECT itemName, FORMAT (instockValue * PricePerItem, 2, 'de_DE') ProductCost
FROM inventory;Output:
In this location, use a comma (,) to represent the decimal point and group thousands using a dot (.). This is the reverse of the default locale en_EN.
Conclusion
In this article, we saw the syntax and examples of the FORMAT function. FORMAT function displays output in the desired format with proper decimal places defined. The syntax for the SELECT query includes formatting the numerical value, specifying the desired number of decimal places, and optionally including the locale. An important point to be noted is that the data type of the values is to be decimal. Because in the INT data type, the decimal places already do not hold valid. The default locale value is en_EN.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL FORMAT” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.