Updated June 6, 2023
Introduction of MySQL ENUM
ENUM is a datatype in MySQL. The column which is mentioned as ENUM datatype is a String object that can have only one value, which are chosen from the list of mentioned values. We can list up to 65535 values. A blank value will be inserted if a value is not present in the list.
In this session, we will learn about the ENUM data type with syntax along with the syntax: –
Syntax:
Let us see the syntax of how we create the column of ENUM datatype: –
create table<table_name>
(
Column_name1 ENUM(value1, value2,..),/ * - - - ENUM Data type column - - - * /
Column_name2 ENUM(value1, value2,..),/ * - - - ENUM Data type column - - - * /
.
.
.
);Here the values for the “column_name1” and “column_name2” are one among the list specified.
Advantage:
- MySQL ENUM uses numeric indexes (1, 2, 3, . .), which represent the string values because of which it has compact data storage.
- It has readable queries, which makes it a readable query and output.
How Does MySQL ENUM Works?
Let us see where the ENUM is usually defined in MySQL. If we check the list of all users, the columns specified in the user table are mostly defined as an ENUM data type. Below are a few columns for the same.
| Field | Type | NULL | KEY | DEFAULT |
| Select_priv | enum(‘N’,’ Y’) | NO | N | |
| Insert_priv | enum(‘N’,’ Y’) | NO | N | |
| Update_priv | enum(‘N’,’ Y’) | NO | N | |
| Delete_priv | enum(‘N’,’ Y’) | NO | N | |
| Create_priv | enum(‘N’,’ Y’) | NO | N | |
| Drop_priv | enum(‘N’,’ Y’) | NO | N | |
| Reload_priv | enum(‘N’,’ Y’) | NO | N | |
| Shutdown_priv | enum(‘N’,’ Y’) | NO | N | |
| Process_priv | enum(‘N’,’ Y’) | NO | N | |
| File_priv | enum(‘N’,’ Y’) | NO | N | |
| Grant_priv | enum(‘N’,’ Y’) | NO | N | |
| References_priv | enum(‘N’,’ Y’) | NO | N | |
| Index_priv | enum(‘N’,’ Y’) | NO | N | |
| Alter_priv | enum(‘N’,’ Y’) | NO | N | |
| Show_db_priv | enum(‘N’,’ Y’) | NO | N | |
| Super_priv | enum(‘N’,’ Y’) | NO | N | |
| Create_tmp_table_priv | enum(‘N’,’ Y’) | NO | N | |
| Lock_tables_priv | enum(‘N’,’ Y’) | NO | N | |
| Execute_priv | enum(‘N’,’ Y’) | NO | N | |
| Repl_slave_priv | enum(‘N’,’ Y’) | NO | N | |
| Repl_client_priv | enum(‘N’,’ Y’) | NO | N | |
| Create_view_priv | enum(‘N’,’ Y’) | NO | N | |
| Show_view_priv | enum(‘N’,’ Y’) | NO | N | |
| Create_routine_priv | enum(‘N’,’ Y’) | NO | N | |
| Alter_routine_priv | enum(‘N’,’ Y’) | NO | N | |
| Create_user_priv | enum(‘N’,’ Y’) | NO | N | |
| Event_priv | enum(‘N’,’ Y’) | NO | N | |
| Trigger_priv | enum(‘N’,’ Y’) | NO | N | |
| Create_tablespace_priv | enum(‘N’,’ Y’) | NO | N | |
| ssl_type | enum(”,’ANY’, ‘X509’, ‘SPECIFIED’) | NO |
Let us consider a simple example of the same: –
Table creation: –
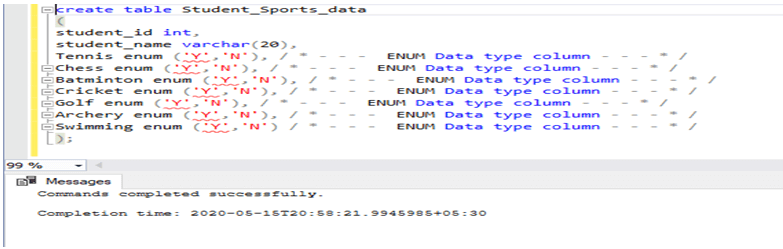
create table Student_Sports_data
(
student_id int,
student_name varchar(20),
Tennis enum('Y','N'),/*--- ENUM Datatypecolumn---*/
Chess enum('Y','N'), /*--- ENUM Datatypecolumn---*/
Batminton enum('Y','N'),/*--- ENUM Datatypecolumn---*/
Cricket enum('Y','N'),/*--- ENUM Datatypecolumn---*/
Golf enum('Y','N'),/*--- ENUM Datatypecolumn---*/
Archery enum('Y','N'),/*--- ENUM Datatypecolumn---*/
Swimming enum('Y','N')/*--- ENUM Datatypecolumn---*/
);Screenshot for the same: –
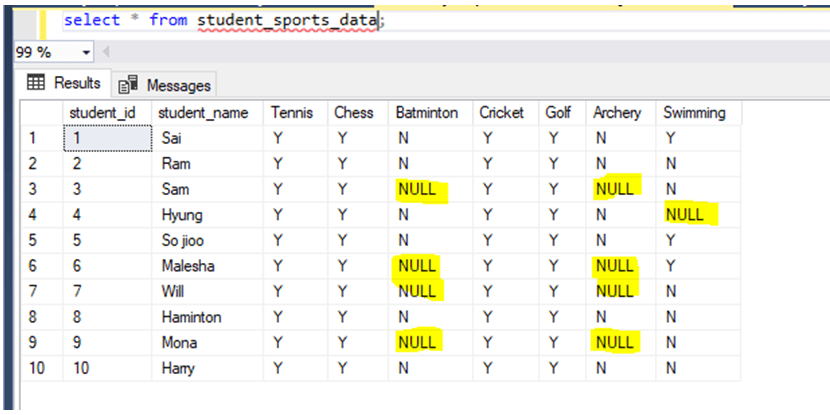
Let us insert data into the table: –
insert into student_sports_data values(1,'Sai','Y','Y','N','Y','Y','N','Y');
insert into student_sports_data values(2,'Ram','Y','Y','N','Y','Y','N','N');
insert into student_sports_data values(3,'Sam','Y','Y','NO','Y','Y','NO','N');
insert into student_sports_data values(4,'Hyung','Y','Y','N','Y','Y','N','NO');
insert into student_sports_data values(5,'So jioo','Y','Y','N','Y','Y','N','Y');
insert into student_sports_data values(6,'Malesha','Y','Y','No','Y','Y','NO','Y');
insert into student_sports_data values(7,'Will','Y','Y','NO','Y','Y','NO','N');
insert into student_sports_data values(8,'Haminton','Y','Y','N','Y','Y','N','N');
insert into student_sports_data values(9,'Mona','Y','Y','NO','Y','Y','YES','N');
insert into student_sports_data values(10,'Harry','Y','Y','N','Y','Y','N','N');Select the items from the table: – Here, the values inserted that are other than ‘Y’ and ‘N’ are represented as NULL.
select * from student_sports_data;Output:
Example of MySQL ENUM
Let us consider another example below and check the working of the ENUM.
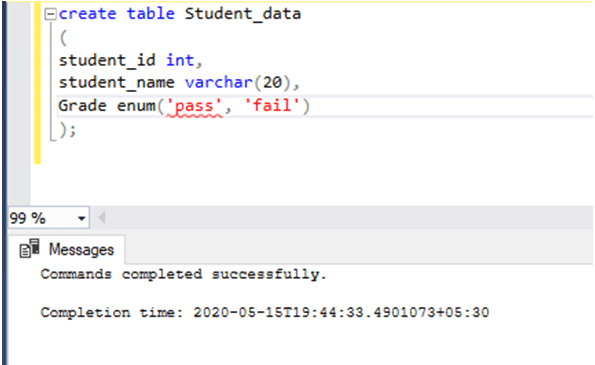
Table creation:
create table Student_data
(
student_id int,
student_name varchar(20),
Grade enum('pass','fail') / * - - - ENUM Data type column - - - * /
); Screenshot for the same: –
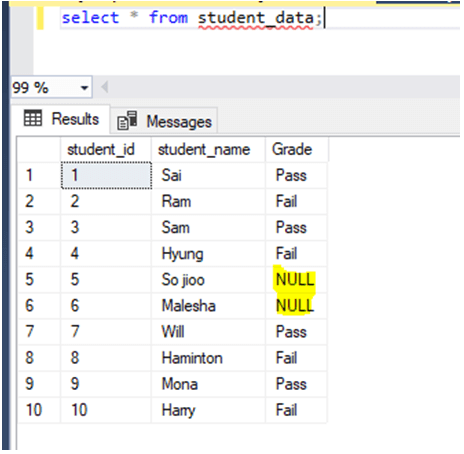
Let us insert data into the table: –
insert into student_data values(1,'Sai','Pass');
insert into student_data values(2,'Ram','Fail');
insert into student_data values(3,'Sam','Pass');
insert into student_data values(4,'Hyung','Fail');
insert into student_data values(5,'So jioo','No');
insert into student_data values(6,'Malesha','No');
insert into student_data values(7,'Will','Pass');
insert into student_data values(8,'Haminton','Fail');
insert into student_data values(9,'Mona','Pass');
insert into student_data values(10,'Harry','Fail');In the above insert, we could see that there are two rows the values which we inserted into the table for the column “Grade” are other than “Pass” and “Fail”. So the value will be NULL.
select * from student_data;Output:
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL ENUM” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.