Updated May 24, 2023
Introduction to MySQL CASE Statement
MySQL CASE is a MySQL Statement query keyword that defines the way to handle the loop concepts to execute the set of conditions and return the match case using IF ELSE. CASE in MySQL is a type of control statement which validates the set of conditional cases and displays the value when the first case is meeting otherwise else value and exits the loop. If no cases are found TRUE, and the statement does not have an ELSE part or value, then the CASE returns NULL. The CASE statement is similar to IF THEN ELSE logical loop statements. When run on MySQL server, it reads the conditional expressions, and when the expression case is matched, the nit shows the result. After that, it stops execution further.
Syntax of MySQL CASE Statement
The syntax below defines the CASE statement SQL query structure:
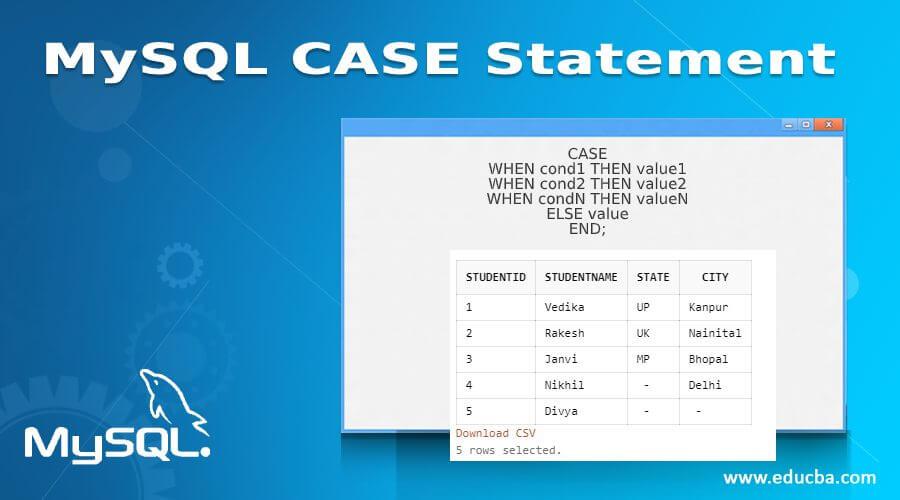
CASE
WHEN cond1 THEN value1
WHEN cond2 THEN value2
WHEN condN THEN valueN
ELSE value
END;Let us discuss these parameters given in the syntax above:
- Cond1,cond2,…..,condN: Denotes the required conditions to be evaluated in the list of CASE statements.
- Value1, value2, …..,valueN: Represents the values required to display when a condition is met.
- Value: Denotes the value to be displayed when the else part is meeting.
This part allows adding logical CASE statements in a query in MySQL. We use the CASE statement anywhere with the clauses such as WHERE SELECT and ORDER BY to make a valid statement. You can evaluate through the syntax shown below:
SELECT column1,column2,
CASE
WHEN cond1 THEN value1
WHEN cond2 THEN value2
WHEN condN THEN valueN
ELSE value
END
FROM TableName;How Does CASE Statement Work in MySQL?
The CASE Statement contains two procedures: one is Simple CASE, and the other one is Searched CASE. We use a CASE statement to provide the result values based on a matched condition using the logical control method to the SQL queries and the SQL clauses like SELECT, WHERE, and ORDER BY.
Suppose the following query explains the CASE logical part where we have mentioned a table like Students with fields StudentName, State, City; then the query will be written as:
SELECT StudentName, State, City FROM Students ORDER BY (
CASE
WHEN State IS NULL THEN City
ELSE State
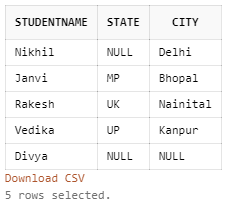
END);From here, we will come to know that when we have applied the CASE statement in the SELECT query to fetch the particular value that satisfies a specific case condition. In the above illustration, we have put the CASE statement on columns State and City, where if the State column contains a NULL value, then the query displays the City column value. If the case statement is not valid or the value is not found, then part value, i.e., State column value, is returned. Here, we have fetched the names of students, states, and cities where the CASE is applied with the ORDER BY clause to sort the result rows.
In the Simple CASE, the CASE the column value is matched with the conditional statement value in the WHEN clauses for equivalence and then produces the result value after that one in the syntax. But if no value is equal, it returns the ELSE part value if provided.
You should not use NULL in the WHEN clause value because if executed, the logical part will be NULL = NULL which is FALSE.
Now for Search CASE, it follows the same logical procedure as Simple CASE, but one part of the search case makes it different. Here, the CASE on satisfying results is the value whose MySQL Data Type is based on the context it is used for. For example, if a character string context is used in the statement, the result value will be in the same data type, string. Also, if the CASE conditional expression uses a numeric context, the value returned will be either in integer, decimal or real value data type.
Examples to Implement MySQL CASE Statement
Following are the CASE statement examples with outputs:
Example #1 – CASE Statement with SELECT & ORDER BY Clauses
Let us execute the above SQL query and show the result on the CASE part execution. For this, we must create a table for Students and insert some values.
1. Creating a Table
CREATE TABLE Students(StudentIDint, StudentNamevarchar(255), State varchar(255), City varchar(255) );2. Inserting a Few Fields
INSERT INTO Students (StudentID, StudentName, State, City) VALUES ('01', 'Vedika', 'UP', 'Kanpur');And so on.
3. SELECT Statement to Display the Table Data
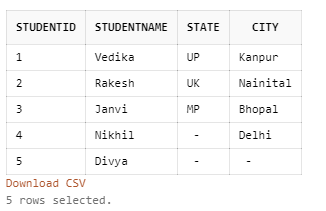
Query:
SELECT * FROM Students;Output:
4. CASE Statement with SELECT Query
Query:
SELECT StudentName, State, City FROM Students ORDER BY (
CASE
WHEN State IS NULL THEN City
ELSE State
END);Output:
Example #2 – CASE Statement with Aggregate Function
We will calculate the total sales count from the Orders table by order status using the CASE statement and the SUM() MySQL function.
1. Creating a Table
Query:
CREATE TABLE Orders (OrderIDint,SalesIDint, OrderStatusvarchar(255) );2. Inserting a Few Fields
Query:
INSERT INTO Orders (OrderID, SalesID,OrderStatus) VALUES ('10', '001', 'Shipped');And so on.
3. SELECT statement to display the Table Data
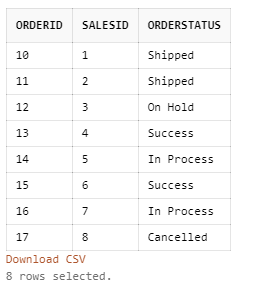
Query:
SELECT * FROM Orders;Output:
3. CASE Statement with SUM() and COUNT as Aggregate Functions in the SQL SELECT Query
Query:
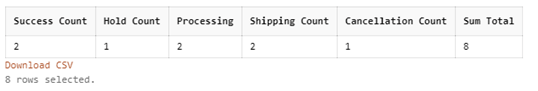
SELECT
SUM(CASE
WHEN OrderStatus = 'Success' THEN 1
ELSE 0
END) AS 'Success Count',
SUM(CASE
WHEN OrderStatus = 'On Hold' THEN 1
ELSE 0
END) AS 'Hold Count',
SUM(CASE
WHEN OrderStatus = 'In Process' THEN 1
ELSE 0
END) AS 'Processing',
SUM(CASE
WHEN OrderStatus = 'Shipped' THEN 1
ELSE 0
END) AS 'Shipping count',
SUM(CASE
WHEN OrderStatus = 'Cancelled' THEN 1
ELSE 0
END) AS 'Cancellation Count',
COUNT(*) AS Sum Total
FROM
Orders;Output:
Explanation: In the query above, firstly, the CASE statements execute and return 1 when the case matches the respective Order Status such as Success, In Progress, Shipped, Cancelled, On Hold, and otherwise zero. Secondly, after this, the Sum() function determines the total number of orders according to the order status.
Conclusion
- MySQL CASE statement permits executing the IF ELSE logic to the SQL queries to examine the conditional statements and fetch the required result sets or values from the database tables.
- We can only use the CASE statement with stored procedures, events, functions, and triggers. The conditional expression compares the range of distinct values and produces the corresponding result, which holds the data type depending on the context used in the query.
- Hence, we can say that the CASE statement in MySQL makes the query code more efficient and readable.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL CASE Statement” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.