Updated June 6, 2023
Introduction to MySQL Clustered Index
Normally, indexes in MySQL are a distinct data structure implemented to swiftly find table rows with particular table column values. An index is a B-Tree structure that stores the key values applied for quicker lookups in the MySQL databases. In MySQL, a clustered index is an index that physically manages the ordering of the table rows. The InnoDB tables in MySQL handle the management of clustered indexes. When creating a clustered index, the system stores all table rows based on the key columns specified during the index creation. This is because the clustered index organizes the table rows in a specific order. It’s important to note that each table can have only one clustered index.
Syntax
To create a clustered index, follow the basic syntax structure. However, it’s important to note that the previous one must be removed before defining a column as a clustered index. When a column is designated as the primary key, it automatically becomes the clustered index for that particular table. Delete the previous one first to set another column as a clustered index.
//Dropping index
DROP INDEX TableName.IndexName
//Creating Clustered Index
CREATE Clustered Index IndexName_TableName_ColumnName
ON TableName(ColumnName ASC)How does Clustered Index work in MySQL?
- Each database InnoDB table needs a clustered index. It represents the Primary key that supports data handling like INSERT, UPDATE, SELECT, and DELETE. Therefore, whenever a user states a PRIMARY Key in the InnoDBtable database, MySQL practices the Primary key as MySQL clustered index.
- Suppose, in case, the table does not contain any primary key for a specific table. Then, MySQL will examine for the initial UNIQUE index, which defines all the key columns specifies the NOT NULL attribute, and applies this UNIQUE index as MySQL Clustered index.
- Also, if the InnoDB table contains no Primary Key or any UNIQUE key index, MySQL will internally produce a concealed clustered index as GEN_CLUST_INDEX on a fake column that consists of the row ID values. Therefore, we can say that each database InnoDB table contains only a single clustered index always.
- Now, all the remaining indexes besides clustered indexes are defined as secondary or non-clustered indexes. Each record in an InnoDB table in the secondary index consists of the Primary key columns for the columns and rows stated in the non-clustered index. Hence, MySQL will use this primary key value in the clustered index for the row lookups.
- Thus, a short primary key must be present; otherwise, when MySQL implements the secondary indexes, it will take more space. In MySQL, defining a table column with the auto-increment integer attribute for the primary key column is common.
- A clustered index table helps store indexes and data simultaneously based on key values sorted in one direction. It can use one or multiple columns to create an index in a database table.
Benefits:
- By utilizing MySQL Clustered Index, cache hits can be maximized, and page transfers can be minimized.
- It is the ultimate option for a group or range with min, max, and count queries.
- At the beginning of the range, it implements a location mechanism to find an index entry.
- Also, clustered index supports fragmentation and other operations.
Drawbacks:
- It includes several insert records present in a non-sequential direction.
- Creates various constant page separations like index pages or data pages.
- It constantly takes a lengthy time to update the table records.
- It requires additional work for query statements such as updates, inserts, and deletes.
Examples of MySQL Clustered Index
Here are some MySQL Clustered Index examples:
Suppose we are creating a table named Training using the CREATE command as follows:
Code:
CREATE TABLE Training(TID INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, Label VARCHAR(255), Information TEXT) ENGINE = INNODB;Here, you can see that after mentioning the columns and data types with related attributes, we have added an engine, i.e., InnoDB, to ensure that the table creates in MySQL in InnoDB apart from other engines like MyISAM and others.
Again, we have added here FULLTEXT indexes to Label and Information columns in the table Training created above using the query below:
Code:
CREATE FULLTEXT INDEX Information ON Training(Infromation);
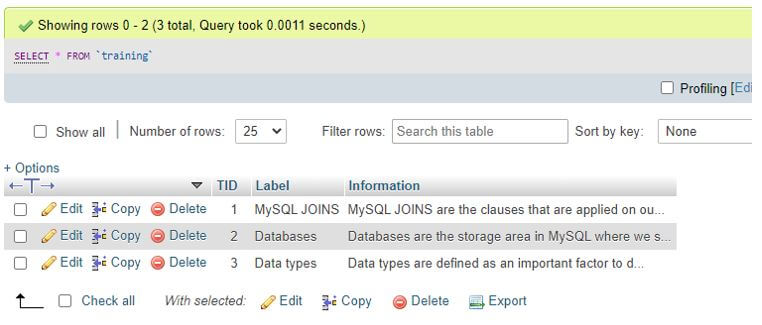
CREATE FULLTEXT INDEX Label ON Training(Label); Now, let us also insert some sample record data into the table Training by the following query: Code:INSERT INTO Training (TID,Label, Information) VALUES(‘1’,’MySQL JOINS’,‘MySQL JOINS are the clauses that are applied on our database tables to combine two or more tables to provide the result set.’);Let us display the contents and structure of the table Training as follows:
Code:
SELECT * FROM Training;Output:
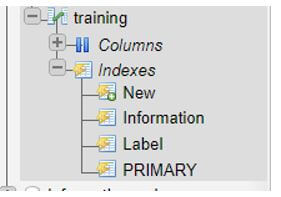
Again, let us view the indexes created on this table that make a clustered index for InnoDB table Training as follows:
It shows that in an InnoDB table, the Primary key column index represents the MySQL clustered index for storing the table data with associated key values in a sorted way.
We can even create a table like this to have a clustered index where we have defined two integer columns as primary keys in the InnoDB table:
Code:
CREATE TABLE Students( Stud_Id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, User_Id INT NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (User_Id, Stud_ID) //clustered index ) ENGINE = InnoDB ;Output:
Conclusion
MySQL Clustered Index defines the direction of each table data in a database according to the key values which can be physically stored uniquely. Suppose a Unique or Primary key exists in a relational database table column. In that case, MySQL will permit creating a clustered index based on that definite column, named PRIMARY. It helps in key lookups, index scanning, and other index-related data operations in the table.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL Clustered Index” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.