Updated May 24, 2023
Introduction to MySQL Average
To find the average of a field in various records, we use MySQL Average. We can find the average of the records of a column by using the “Group by” clause.MySQL AVG() function is an aggregate function that allows you to calculate the average value of column values. To calculate the average of the distinct values from a column, we can use the “DISTINCT” operator. AVG function will ignore “NULL” values.
AVG function can be used in the subqueries. It can be used along with the control flow functions like IF, IFNULL, NULLIF, and CASE.
Syntax:
SELECT AVG(EXPRESSION) FROM <TABLE_NAME>;Here above is the syntax of the Average function. The average function returns the data of the INT datatype.
How Does MySQL Average Work?
Now let us create a table, perform the average function on the column, and retrieve the data.
Query:
create table Freelancer_data
(
Freelancer_id INT,
Freelancer_Name VARCHAR(20),
Type_of_work VARCHAR(30),
No_of_submission INT,
No_of_pages_submitted INT,
EMAIL varchar(30)
);1. Insert data Into the Table
Query:
insert into freelancer_data values (1278,'Jack','Typist', 2, 300,'[email protected]');
insert into freelancer_data values (2278,'Will','Artical Writer', 3, 450,'[email protected]');
insert into freelancer_data values (3278,'Rose','Artical Writer', 3, 540,'[email protected]');
insert into freelancer_data values (4278,'Ben','Typist', 3, 860,'[email protected]');
insert into freelancer_data values (5278,'Stuart','Typist', 5, 600,'[email protected]');
insert into freelancer_data values (6278,'Rample','Artical Writer', 6, 900,'[email protected]');
insert into freelancer_data values (7278,'Jackern','Typist', 3, 700,'[email protected]');
insert into freelancer_data values (8278,'fred','Artical Writer', 2, 300,'[email protected]');
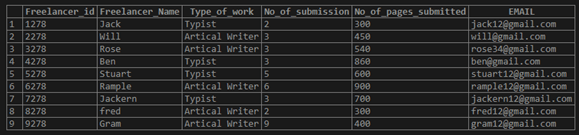
insert into freelancer_data values (9278,'Gram','Artical Writer', 9, 400,'[email protected]');2. Select the Data from the Table
Query:
select * from freelancer_data;Output:
3. Now let us find the average Pages Submitted by the Freelancer
Query:
select AVG(No_of_pages_submitted) as "Average papers submitted" from freelancer_data;Output:
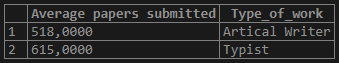
Now let us find the average pages submitted by the freelancer based on the Type_of_work using the “GROUP BY” clause:
Query:
select AVG(No_of_pages_submitted) as "Average papers submitted", Type_of_work from freelancer_data group by 2;Output:
or
Query:
select AVG(No_of_pages_submitted) as "Average papers submitted", Type_of_work from freelancer_data group by Type_of_work;Output:
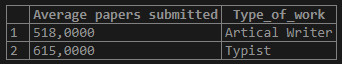
4. Using AVG() With “HAVING” Clause
To set conditions for the output of the average values, we use the “HAVING” clause.
Query:
select AVG(No_of_pages_submitted) as "Average papers submitted", Type_of_work
from freelancer_data
group by 2
having AVG(No_of_pages_submitted) > 600;or
Query:
select AVG(No_of_pages_submitted) as "Average papers submitted", Type_of_work
from freelancer_data
group by Type_of_work
having AVG(No_of_pages_submitted) > 600;Output:
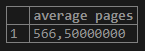
5. Using AVG() with sub-query
In the sub-query, we find the average based on “type_of_work”. The outer query gets the average for the output of the inner query.
Query:
SELECT
AVG(AVG_PAGES) as "average pages"/* Outer query*/
FROM
(select
AVG(NO_OF_PAGES_SUBMITTED) AS "AVG_PAGES" /* -- inner query --*/
from
freelancer_data
GROUP BY TYPE_OF_WORK) AVG;Output:
6. Using AVG() with Control functions
Let us find the average of the pages submitted if the “no_of_submission” is 3. Else, consider it as “null”. As AVG ignores the NULL values, the below output is average for only the submission count is =3.
Query:
SELECT
AVG(IF(No_of_submission= 3,
No_of_pages_submitted,
NULL))/No_of_submission 'Avg pages'
FROM
freelancer_data;Output:
Example to Implement MySQL Average
Now let us consider other simple examples below:
Query:
create table sample_AVG
(
ID INT,
NAME VARCHAR(30),
DEPT_NO INT,
SALARY FLOAT(10,2)
);1. Insert data Into the Table
Query:
insert into SAMPLE_AVG values (1278,'Jack', 2, 90000);
insert into SAMPLE_AVG values (2278,'Will', 2, 80000);
insert into SAMPLE_AVG values (3278,'Rose', 3, 78000);
insert into SAMPLE_AVG values (4278,'Ben', 3, 45000);
insert into SAMPLE_AVG values (5278,'Stuart', 3, 67000);
insert into SAMPLE_AVG values (6278,'Rample', 4, 57000);
insert into SAMPLE_AVG values (7278,'Jackern', 4, 47000);
insert into SAMPLE_AVG values (8278,'fred', 4, 68000);
insert into SAMPLE_AVG values (9278,'Gram', 4,86000);Query:
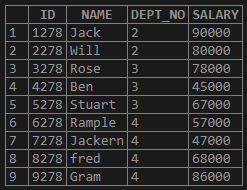
select * from SAMPLE_AVG;Output:
2. Now let us find the average of salary from the Table
Query:
select AVG(salary) as "Average salary" from sample_avg;Output:
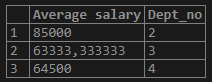
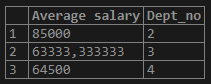
3. Now let us find the average SALARY based on the DEPT_NO using the “GROUP BY” Clause
Query:
select AVG(salary) as "Average salary", Dept_no from sample_avg group by 2; /* - - Position of the column - -*/Output:
or
Query:
select AVG(salary) as "Average salary", Dept_no from sample_avg group by dept_no;Output:
4. Using AVG() With “HAVING” Clause
To set conditions for the output of the average values, we use the “HAVING” clause.
Query:
select
AVG(salary) as "Average salary",
Dept_no from sample_avg
group by 2
having AVG(salary) > '65000'or
Output:
Query:
select
AVG(salary) as "Average salary",
Dept_no from sample_avg
group by dept_no
having AVG(salary) > '65000'Output:
5. Using AVG() with sub-query
In the sub-query, we find the average based on “dept_no”. The outer query gets the average for the output of the inner query.
Query:
SELECT
AVG(AVG_SAL) as "average salary"
FROM
(select
AVG(salary) as "Avg_sal",
Dept_no from sample_avg
group by 2
)AVG;Output:
6. Using AVG() with Control Functions
Here let us find the SALARY average if the “DEPT_NO” is in 3, 4 else, consider it “null”. As AVG ignores the NULL values, the below output is average for only the submission count is 3 and 4.
Query:
SELECT
AVG(IF(DEPT_NO IN (3,4),
SALARY,
NULL))/COUNT(DEPT_NO) 'AVGSALARY'
FROM
SAMPLE_AVG;Output:
Conclusion
- To find the average of a field in various records, we use MySQL Average. We can find the average of the records of a column by using the “Group by” clause.
- MySQL AVG() function is an aggregate function that allows you to calculate the average value of column values.
- To calculate the average of the distinct values from a column, we can use the “DISTINCT” operator. AVG function will ignore “NULL” values.
- AVG function can be used in the subqueries. It can be used along with the control flow functions like IF, IFNULL, NULLIF, and CASE.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL Average” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.