What is Multimedia?
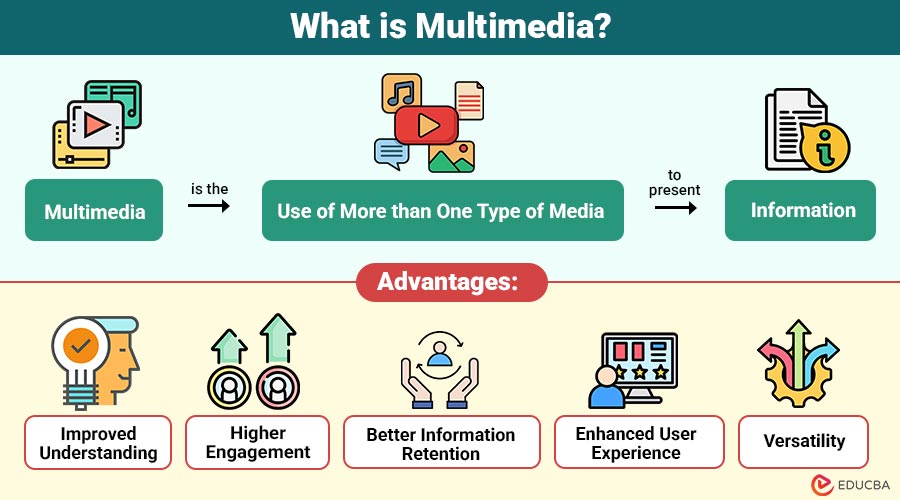
Multimedia is the use of more than one type of media to present information. These media elements work together to deliver content dynamically and interactively. A typical multimedia application may include written text, visual graphics, sound effects, video clips, and animations, often enhanced with user interaction.
In simple terms, when information is communicated using a combination of visuals, sound, and text rather than plain text alone, it is considered multimedia.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Multimedia combines text, visuals, audio, video, animation, and interactivity to communicate information more effectively globally.
- It enhances engagement, understanding, and retention by addressing diverse learning styles and user preferences worldwide.
- Multimedia is widely applied across education, business, marketing, healthcare, entertainment, and digital communication platforms today.
- Interactive multimedia empowers users to control the flow of content, significantly improving personalization and the overall user experience.
Core Elements of Multimedia
Multimedia systems are built using several key components. Every component contributes uniquely to improving comprehension and communication.
1. Text
Text is most basic form of media and provides structure and clarity. It includes titles, paragraphs, captions, menus, and navigation instructions.
2. Images and Graphics
Images, photographs, charts, and illustrations help visualize information, making it easier to understand and remember.
3. Audio
Audio includes music, speech, sound effects, and narration. It adds emotional depth and improves engagement, especially in storytelling and learning environments.
4. Video
A video combines visuals and audio to deliver information in a realistic and impactful way. It is widely used for tutorials, advertisements, entertainment, and presentations.
5. Animation
Animation uses motion to explain processes, concepts, or stories. It is particularly useful for explaining abstract or complex ideas.
6. Interactivity
Interactivity allows users to control or influence the content. Examples include clickable buttons, quizzes, games, simulations, and navigation menus.
Types of Multimedia
It can be categorized based on how users interact with it and how content is delivered.
1. Linear Multimedia
Linear multimedia delivers content in a fixed sequence without user navigation, progressing automatically from start to finish.
2. Non-Linear Multimedia
Non-linear multimedia lets users freely control navigation, choose paths, and access content in any order based on their preferences.
3. Interactive Multimedia
Interactive multimedia requires active user input, providing real-time feedback and dynamic responses to actions performed by the system.
4. Hypermedia
Hypermedia links multimedia elements via hyperlinks, enabling seamless, nonlinear navigation across related text, images, audio, and video.
Applications of Multimedia
It is widely used across industries for its versatility and effectiveness.
1. Education and E-Learning
Enhances learning by combining visuals, audio explanations, videos, and interactive exercises. It supports different learning styles and improves knowledge retention.
2. Entertainment
Movies, music videos, video games, streaming platforms, and digital art heavily rely on multimedia to deliver immersive experiences.
3. Business and Corporate Communication
Businesses use multimedia in presentations, training programs, product demonstrations, and internal communication to convey information clearly and professionally.
4. Marketing and Advertising
Multimedia advertisements attract attention through videos, animations, graphics, and sound. Social media campaigns and digital ads heavily depend on multimedia content.
5. Healthcare
In healthcare, multimedia is used for medical training, patient education, diagnostic visualization, and telemedicine solutions.
6. Journalism and Media
Digital journalism uses multimedia storytelling by combining text articles with images, videos, infographics, and interactive data visualizations.
Advantages of Multimedia
Offers numerous advantages across learning, communication, and engagement.
1. Improved Understanding
Combining text, visuals, audio, and animations simplifies complex concepts, making information clearer and easier to understand.
2. Higher Engagement
Audio-visual elements capture user attention effectively, increasing interest, focus, and involvement for longer durations.
3. Better Information Retention
Visual and interactive content enhances memory recall, helping users retain information more effectively over time.
4. Enhanced User Experience
Rich media and interactivity create intuitive, enjoyable experiences that improve usability and user satisfaction.
5. Versatility
Adapts easily across platforms like websites, mobile applications, presentations, and social media channels.
Disadvantages of Multimedia
Despite its benefits, it also has certain disadvantages:
1. High Development Cost
Developing quality multimedia requires skilled professionals, advanced tools, and significant time investment, increasing overall production costs.
2. Technical Requirements
Systems demand high processing power, sufficient storage capacity, and reliable internet connectivity for smooth performance.
3. Accessibility Challenges
Improperly designed multimedia may exclude users with disabilities without captions, screen reader support, or alternative content.
4. Maintenance and Updates
Regular updates, content revisions, and technical maintenance make multimedia systems resource-intensive and time-consuming to manage.
Real-World Examples of Multimedia Use
Below are some common real-world examples that demonstrate how multimedia is effectively used across different digital platforms and applications.
1. Online Courses
Online courses integrate videos, animations, quizzes, and audio explanations to enhance learning effectiveness and engagement.
2. Interactive Websites
Interactive websites combine images, text, audio, videos, and navigation menus to deliver engaging user experiences.
3. Digital Advertisements
Digital advertisements use motion graphics, sound effects, visuals, and text to attract attention and promote products.
4. Video Conferencing Platforms
Video conferencing platforms support live video, audio, screen sharing, chat features, and real-time collaboration tools.
Final Thoughts
Multimedia has transformed the way information is created, shared, and experienced. By combining multiple forms of media, it enhances communication, improves understanding, and delivers richer user experiences. From education and business to entertainment and healthcare, multimedia continues to shape the digital world. It will become an increasingly important component of contemporary communication and creativity as technology advances.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Why is multimedia important?
Answer: It makes information more engaging, easier to understand, and more memorable.
Q2. How does multimedia improve learning outcomes?
Answer: Multimedia improves learning by presenting information visually and interactively, helping learners understand concepts faster and retain knowledge longer.
Q3. Where is multimedia used the most?
Answer: Education, entertainment, marketing, business communication, and digital media.
Q4. Is multimedia only digital?
Answer: No, multimedia is not only digital. While it existed earlier in non-digital forms like live presentations and teaching aids, today it is mainly used in digital platforms due to better interactivity and accessibility.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Multimedia” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
