Updated March 6, 2023
Definition of MongoDB Triggers
Mongodb trigger allows us to execute the logic as per schedule; MongoDB provides the three types of triggers, i.e., database triggers, authentication triggers, and schedules triggers. Database triggers are used to automatically respond to any document updation, insertion, and deletion; authentication triggers are used to execute when new user creation, deletion, and authentication, and Scheduled triggers will execute at the time of pre-defined schedule. MongoDB database triggers are used to listen to the changes from the documents collection, and also it will pass the events of database triggers to the function of the trigger.
Syntax:
Below is the parameter which was used at the time of trigger creation.
{
“Trigger_type”: Name of type of trigger,
“Trigger_name”: Name of trigger,
“Name_of_function”: function name,
“Config”: {
“Name_of_service”: service name,
“database_name”: name of database,
“collection_name”: name of collection,
“database_operations_types”: types of database operations,
“full_document” : <Type is Boolean>,
“Unordered” : <optional>,
“Match expression” : <optional>,
}
Parameter description of MongoDB triggers.
1) Trigger type – This is defined as a type of trigger which was we have used at the time of trigger creation.
2) Trigger name – This parameter is mandatory while creating triggers. It is defined as the name of the trigger.
3) Function name – This is defined as the name of the stitch function in MongoDB. This is a required parameter while creating a new trigger.
4) Database name – This is the database name from which we have selected the collection of creating triggers.
5) Collection name – This is the name of the collection which was used to create a new trigger in MongoDB. The collection name is a mandatory parameter while creating triggers.
6) Service name – This parameter is defined as the name of service which was we have used at the time of creating the trigger in MongoDB.
7) Operation types – This is defined as the name of operations which was we have used at the time of creating a new trigger. Name of database operations like insert, update, and delete.
8) Full document – This is also a required parameter at the time of creating a trigger in MongoDB.
9) Unordered – This is an optional parameter in the MongoDB trigger. The default value of this parameter is false. To enable the value of this parameter, we need to set it true.
10) Match expression – This is also an optional parameter while using a trigger in MongoDB. Match expression is used to configure the trigger to execute when a specified event occurs.
How do triggers work in Mongodb?
MongoDB database triggers is allows us to execute the logic of server-side when any documents will add, deleted, or updated from the database collection.
The main use of MongoDB database triggers is to implement complex data interaction and to update the information.
MongoDB database triggers basically used the change steams to listen to changes from database collection.
Basically, there are three types of triggers available in MongoDB. We can create triggers by using the MongoDB Atlas cluster.
MongoDB Atlas is used to replace command instead of update command while executing update using data explorer.
Scheduled triggers in MongoDB will allow us to execute server-side logic on a regular schedule of intervals or by using the cron expressions.
We can use a schedule trigger to run the report, update the documents at certain intervals of time, or sending an automated email.
While creating a new trigger using MongoDB atlas, we can see a function editor where we can write javascript code that was executed by trigger.
We can restart or resume our trigger after creating on MongoDB atlas cluster.
MongoDB triggers are only available on the MongoDB Atlas cluster, which was running on version 3.6 or later.
MongoDB triggers are used to execute the database and application logic automatically. It is executing automatically either by creating an event or a pre-defined schedule.
MongoDB trigger uses the following operation type at the time of creating a new trigger in MongoDB.
1) Insert
2) Update
3) Delete
4) Replace
- Insert operation type is defined as adding new documents in the collection when an event occurs.
- The update operation is defined as update or change existing documents from the collection.
- Delete operation is defined as delete existing documents from the collection when a specified event occurs.
- Replace operation is defined as replacing documents from the collection.
Example
The below example shows that create triggers in MongoDB are as follows. In the below example, we have to create the database trigger name as MongoDB_Trigger.
1) Create a trigger in MongoDB
First, we have to define the trigger type, trigger name, enabled event order, and link data source.
Trigger type – Database
Trigger name - MongoDB_Trigger
Enables – ON
Event ordering – ON
Link data source – Cluster
Figure – defining the trigger type, trigger name, enabled event order, and link data source.
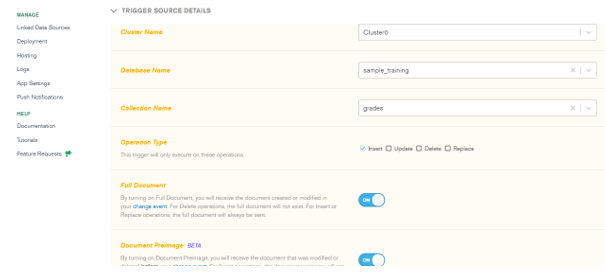
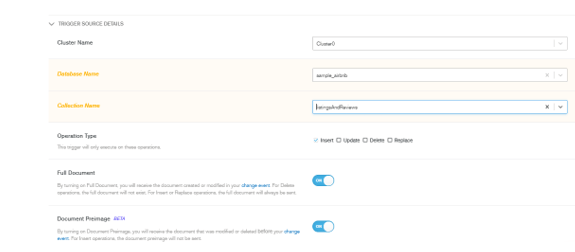
Second, we have to define the cluster name, operation type, full document, and document preimage.
Cluster name – Cluster0
Database name – sample_training
Collection name – grades
Operation type – Insert
Full document – ON
Document preimage – ON
Figure – defining the cluster name, operation type, full document, and document preimage.
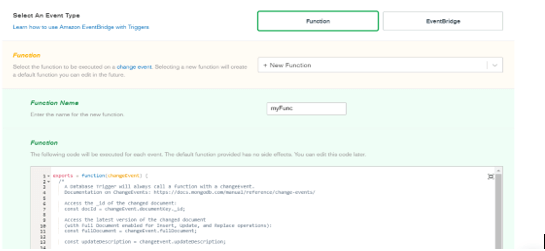
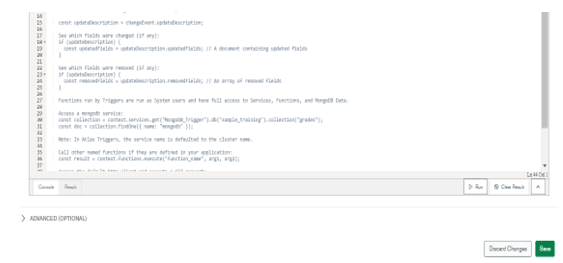
In the below image, we have to define the event type and function name.
Code:
Function name – myFunc
Function –
exports = function (changeEvent) {
db.grades.insert ({name: “MongoDB", grades: "A"})
}
Figure – defining the event type and function name.
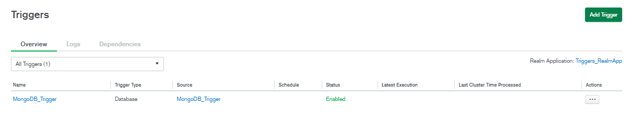
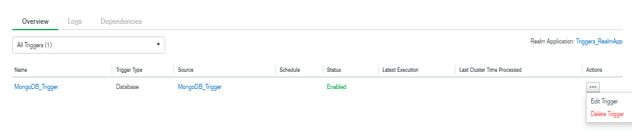
In the below example, we can see that MongoDB_Trigger is created in the MongoDB Atlas cluster.
Figure – Trigger is created in MongoDB Atlas cluster.
2) Edit trigger in MongoDB
If suppose we want to edit the already created trigger, we can edit using the following steps. We have to edit the trigger name as MongoDB_Trigger.
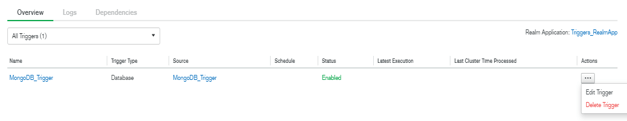
First, select the trigger which was we want to edit, then click on the edit trigger button.
Figure – Edit the trigger which was already created in MongoDB.
We have to edit the database name from sample_training to sample_airbnb and collection name from grades to listings and reviews.
Figure – Edit the database and collection name from MongoDB trigger.
Save all the changes by clicking the save button.
Figure – Save all edited changes of triggers.
3) Delete trigger in MongoDB
We can delete the unused trigger in MongoDB. We have to delete the MongoDB_Trigger. First, select the trigger which was we want to delete, then click on the delete trigger button.
Figure – Delete the trigger in MongoDB.
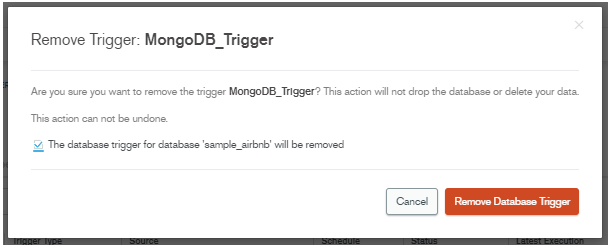
Click on confirm button, then click on the remove database trigger button.
Figure – Delete trigger in MongoDB.
Conclusion
MongoDB trigger is used to execute the logic of server-side when the collection document is added, deleted, or removed from the database collection. Database triggers, authentication triggers, and scheduled triggers are the types of triggers in MongoDB. Triggers are very useful and important in MongoDB.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to MongoDB Triggers. Here we discuss the definition, syntax, How triggers work in Mongodb? Examples and code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –