Updated February 27, 2023

Introduction to MongoDB Relationships
In MongoDB, the representation of how the number of multiple documents is connected logically to each other is known as MongoDB Relationships. There are two ways to create such relationships, which are Embedded and Referenced methods, respectively. Embedded Relationships and Document Referenced Relationship, which have their ways to work with multiple types of relationships are implemented.
While Embed works great with One-to-One and One-to-Many relationships, the referenced is good for Many-to-Many relationships. These two types of relationships are also known as Denormalization, which is Embedded, while Reference relationships are known as Normalization. Establishing relationships between documents can help refine the database structure and work in favour to develop the performance and make execution time shorter.
Types of MongoDB Relationships
Here we have two basic types that determine the relationship, Embedded or Reference. These types are distinguished based on how they are connected.
1. Embedded Relationships
Simply Stating, when we attempt to embed a BSON document, it is known as Embedded Relationships in MongoDB with any other document. With Embedded Relationships, there are two sub relationships.
Given below are the sub relationships:
a. One-to-one relationship: This is the simplest of all relationship. Here, we have a one-parent document and one child document for the parent, that’s one to one.
Example:
Here, we will insert a document, which will key, with another sub-document, a child document.
Code:
db.fun.insert({"Name":"Sulaksh", "Age":25,"Add":{"City":"Pune","State":"MA"}})
Above query will insert a document in a fun collection, with details as mentioned and Add key will have a child document. Let’s retrieve our document and check. Upon executing find query, the return will be as shown in the screenshot below:
Output:
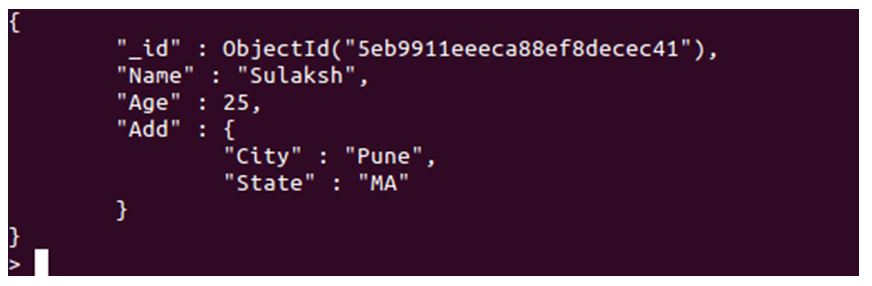
As you can see, we have a parent document which holds some data and a sub-document. The main document is the parent, and sub-document here is the child.
b. One-to-many relationship: To simply put it, One to Many relationships consist of one parent with multiple child documents. Similar to one to one but with many child documents. Establishing a relationship using the embedded method can reduce the number of reading operations performed to retrieve data.
Code:
db.fun.insert(
{"Name": "Ajay",
"Age": 25,
"Add":
[
{"City": "Pune"},
{"State": "MH"}
]
})
Above query will insert a new record with Name and Age, but with Add, it will insert two subdocuments. In this example, City and State will be our many relationships to the one.
Output:
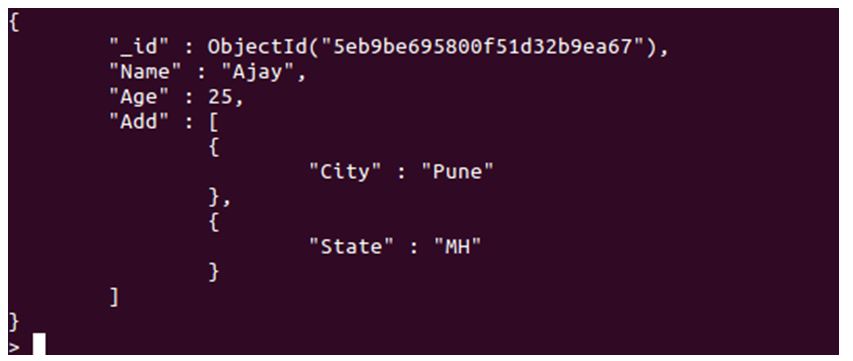
As you can see, we have subdocuments in the key of add, which is to state, One to Many relationships. The simplest example of one to many relationships can be an employee with multiple addresses or multiple phone numbers. Usually, an employee might have multiple addresses or phone numbers, and the mongodb relationship helps us save such complicated data in documents with ease.
One of the major advantages of creating Embedded Relationships in MongoDB is that it executes the queries faster than the referenced relationship. This relationship also boosts the performance, and the results are fetched quickly. This applies for large datasets too.
2. Document Referenced Relationships
Instead of inserting a child document inside a parent document, we create two separate documents with parent and child relationship. So we have a parent document with some data. We have child documents, inserted separately in the different collection but with a single connection with a key from the parent document. Implementing this method of creating relationships helps reduce errors in data and is useful in maintaining consistency with the data.
3. Many to Many Relationships
Many to Many relationships are a mongodb relationship, where any two entities inside a document can have multiple relations. A basic example of many to many relationships can be Companies and Clients. A Company can or might have multiple clients for various projects and tasks, while an individual client can have business relations with multiple companies.
Example:
Here we will implement an example with many to many relationships. For this, we will have two separate collections with names as Authors and Books respectively.
Code:
db.authors.insert( { _id : 4, authorname : "R Tagore" } )
Above query will insert a single document, inside authors collection, which is our parent collection. We have used “_id” here, which we will use as a foreign key for child collection.
Code:
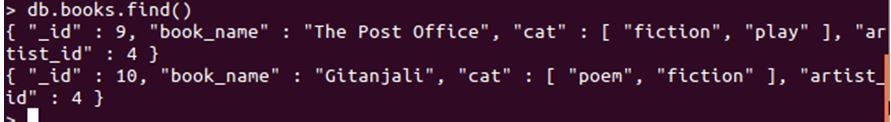
db.books.insert( {
_id : 9,
book_name : "The Post Office",
cat : [ "fiction", "play"],
artist_id : 4
})
Above query will insert a new document into our child collection, which artist_id, in connection with parent collection’s _id. Insert multiple such documents, and then we will execute an aggregation pipeline to fetch these records from two separate collections.
After inserting multiple documents, our collection will look like:
Output:
db.books.find()
4. Aggregation Pipeline
It is simply a collection of commands to be executed one by one in a sequence. We will create a pipeline to return documents from books collection, where id will be local, and artist_id will be foreign fields. Finally, we will add a $match operator, which will only return documents with an author name as R Tagore in the authors’ collections.
Code:
db.authors.aggregate( [
{ $lookup:
{ from: "books",
localField: "_id",
foreignField: "artist_id",
as: "All Books" } },
{ $match : { authorname : "R Tagore" }
}]).pretty()
Output for the above query will be the list of all the documents with the author name R Tagore in books collection.
Output:
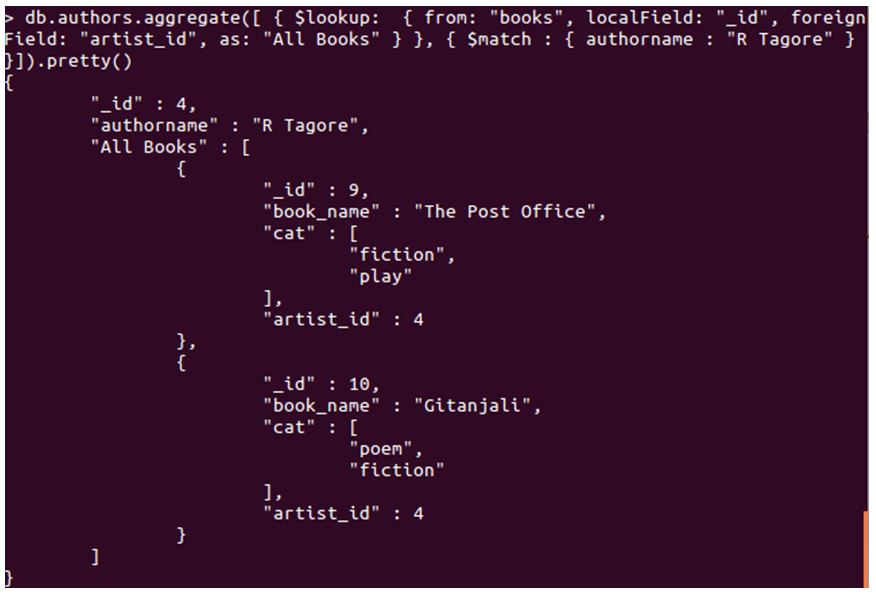
As you can see, our pipeline has returned results as expected. We have implemented many to many relationships, among books and authors.
Conclusion
MongoDB has two types of relationships. Embedded and Reference made. Every relationship has its advantages and usages. These relationships help in improving performance. Based on the situation, it implements any of the relationships as One to One, One to Many or Many to Many. Implementing this relationship has resulted in betterment with data consistency.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to MongoDB Relationships. Here we discuss the introduction and different types of MongoDB relationships, respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

