Updated February 28, 2023

Introduction to MongoDB Delete
MongoDB Delete method is an essential method, used to delete or remove a collection or a document existing in a MongoDB Collection. Upon creating a document or updating an existing document, we might encounter a situation where we might have to delete some records, which is where the Delete method can be implemented. MongoDB’s Delete methods are shell commands, which allow a user to delete or remove the records or documents upon insertion and if not needed. Multiple programming languages support these methods to delete records with APIs.
Syntax:
There are two basic ways to implement Delete Method, which are deleteOne method and deleteMany method. Every method has its functions and applicability, based on which it can be used.
1. Syntax for deleteOne method
db.collection.deleteOne( < filter > )
Explanation:
- Simply removes a single document from a collection, which matches the mentioned filter. Here, collection specifies the name of the collection from which we intend to delete the record.
- Then, deleteOne specifies that only one record must be deleted and the filter, is the criteria based on which, the records to be deleted must be selected.
2. Syntax for deleteMany method
db.collection.deleteMany( < filter > )
Explanation:
- Removes a total number of documents that match with the filter mentioned. Like deleteOne, the collection holds the same place, but the deleteMany specifies that the number of records to be deleted can be more than one.
- Filter helps in selecting the documents, which matches the criteria mentioned and then it selects the number of records that matches, which can be more than one. It deletes the total number of records selected.
Refer the below screenshot of help docs on MongoDB Shell:
Output:

As you can see in the above help, both methods take optional parameters. Followed by the working of the method, respectively.
The syntax for Delete without filter or parameters:
We have seen delete document, with single or multiple documents and how to add filters to make sure specific documents are deleted. If we want to delete every single document inside a collection, we will pass simply empty filter, which is, {}.
db.locs.deleteMany( {} )
How does Delete Command work in MongoDB?
- Specifically, the deleteOne method will delete the very first document, which matches with the mentioned filter. Using the field with a unique index like “_id” could work in a better way for precious deletion.
- With the Delete Command working, there is an execution, which occurs only in case of capped collections, which are collections with fixed size and will overwrite its oldest records when it reaches a maximum set limit. To remove such capped collections and proceed with normal working, it is recommended to implement the db.collection.drop() method.
- Working on the remove method is similar to delete(), but it differs only with the return values. When deleted with the delete method, the return will be the acknowledgement of the deletion and number of records deleted, while with remove method, write result is returned with several records removed.
Examples of MongoDB Delete
Given below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1 – deleteOne
Code:
db.code.deleteOne({"name":"malti"})
Output:
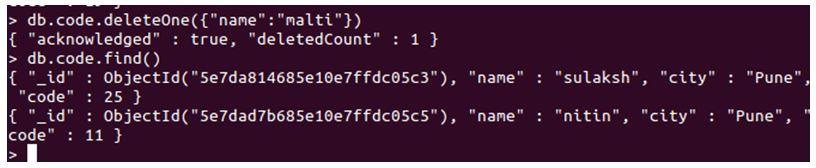
Explanation:
- Here we attempt to delete a single record, which matches with mentioned key-value pair. To start with, code is our collection in which the document might or might not exist. Then we have our method which is deleteOne, and then we have the filter mentioned inside. Here, our filter should look for a document that has the key as “name” and the value must match to “malti”.
- Upon finding a document which matches the filter, the method will delete the document. As you can see, we implemented the deleteOne method and then when we listed the whole collection, we now don’t have any record or a document with the name as malti.
Example #2 – deleteMany
Code:
db.code.find()
db.code.deleteMany({"city":"Pune"})
Output:
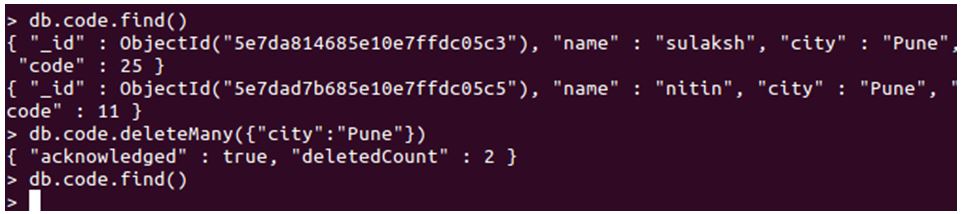
Explanation:
- Started with db, with collection name, we have our deleteMany method, which will delete multiple documents in the code collection. It will rely on the filter mentioned to delete these documents. Our filter is “{“city”: “Pune”}”, meaning it will delete every document that has the city key, matching with the value of Pune.
- Executing this query, every document present in the collection “code” will be deleted at once with the Pune as a city. As you can see, we implemented the deleteMany method with filter and then returned the whole collection, which is now empty. Initially, we had two documents with the city like Pune, but there are no documents with the city as Pune after executing our query. This is how deleteMany deletes every record that matches the filter.
Example #3 – Complete Deletion
A delete method which deletes every single record available in the collection, at once. By simply not specifying any filter, we attempt to delete every single record stored in the collection.
Code:
db.locs.deleteMany( {} )
db.code.find().count()
Output:
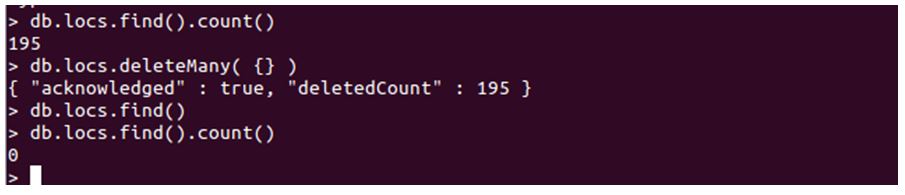
Explanation:
- As you can see in the above screenshot, we firstly checked the total count of records in the collection, which was 195. Then we executed the deleteMany query with a blank filter, which deleted every single record available.
- Which resulted in emptying the whole collection. Later upon checking for the count, we get 0; as a result, meaning no record. That’s how deleteMany with no filter works.
Conclusion
To wrap it up, delete is an important function for MongoDB and can be used in two ways. It simply removes the document that matches the filter. It can be used to delete one document at once or many documents altogether. We understood the working of each method followed by the examples and screenshot. Delete methods are used to remove records from the collection, deleteOne deletes the first record that matches the filter and deleteMany removes every record that matches the filter.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to MongoDB Delete. Here we discuss the introduction, how to delete command works in MongoDB and examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

