Updated June 28, 2023
Introduction to Modulus Operator in C
The % (percentile) operator denotes the modulus operator in C. This modulus operator is added to arithmetic operators. This modulus operator works between 2 operands. The modulus operator finds the division with numerator by denominator, resulting in the remainder of the number. Remainder always integer numbers only. If no remainder is there, then it gives you 0(zero) as the remainder.
Syntax:
Let’s consider a and b are 2 integers; then the modulus expression becomes
a%bReturn value possibilities:
- If a is not completely divisible by b, it produces some non-zero integer value.
- If a is completely divisible by b, then the remainder becomes 0(zero).
- If a is some number and b is 0, then we get a compile-time error.
How does Modulus Operator work in C?
The modulus operator works based on the value received by the end user. It always finds the remainder of 2 numbers with respect to the numerator.
The below example will illustrate the exact functionality.
- Example: 7 % 3 gives us remainder as 1 because when we divide 7 by 3, then we get 2 as quotient and 1 as remainder.
- Same way: 8%3 gives us the remainder as 2 because when we divide 8 by 3, then we get 2 as quotient and 2 as remainder.
Calculation of ‘%’ Operator in C
Let’s see the internal calculation of the ‘%’ operator in C:
a%b will be resolved as a-(a/b)*b
Example:
Let a=8 and b=3, then
- a%b >> a-(a/b)*b
- 8%3 >> 8-(8/3)*3
- 8-(2)*3
- 8-6
- 2
Therefore 8%3 is 2.
Examples to Implement Modulus Operator in C
Below are the examples mentioned:
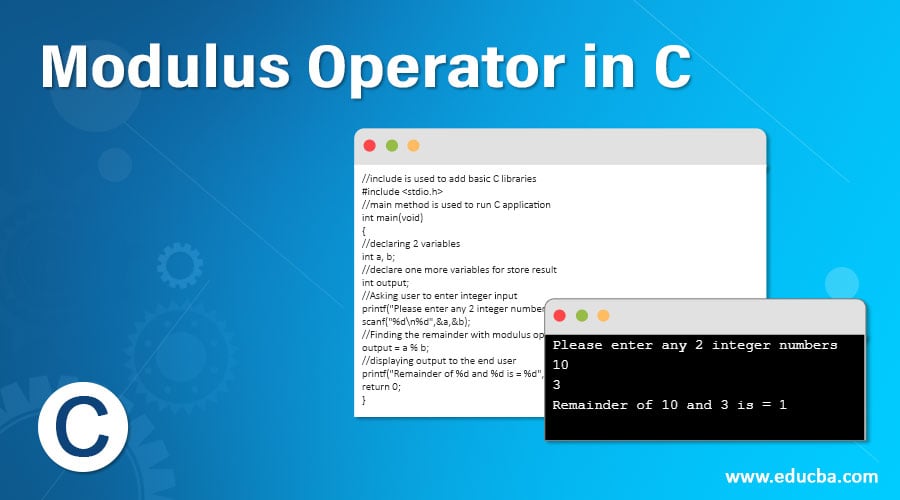
Example #1
Remainder for integer numbers
Code:
//include is used to add basic C libraries
#include <stdio.h>
//main method is used to run C application
int main(void)
{
//declaring 2 variables
int a, b;
//declare one more variables for store result
int output;
//Asking user to enter integer input
printf("Please enter any 2 integer numbers \n");
scanf("%d\n%d",&a,&b);
//Finding the remainder with modulus operator
output = a % b;
//displaying output to the end user
printf("Remainder of %d and %d is = %d", a,b,output);
return 0;
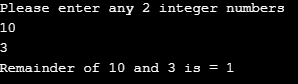
}Output:
Example #2
The remainder with float numbers
Code:
//include is used to add basic C libraries
#include <stdio.h>
//main method is used to run C application
int main(void)
{
//declaring 2 variables
float a, b;
//declare one more variables for store result
float output;
//Asking user to enter integer input
printf("Please enter any 2 integer numbers \n");
scanf("%f\n%f",&a,&b);
//Finding the remainder with modulus operator
output = a % b;
//displaying output to the end user
printf("Remainder of %f and %f is = %f", a,b,output);
return 0;
}Output:
Explanation: As discussed in this example, we are trying to find out the remainder for 2 float numbers, resulting in a compile-time error.
Example #3
Remainder for numerator float and denominator int
Code:
//include is used to add basic C libraries
#include <stdio.h>
//main method is used to run C application
int main(void)
{
//declaring 2 variables
float a;
int b;
//declare one more variables for store result
int output;
//Asking user to enter integer input
printf("Please enter any 2 integer numbers \n");
scanf("%f\n%d",&a,&b);
//Finding the remainder with modulus operator
output = a % b;
//displaying output to the end user
printf("Remainder of %f and %d is = %d", a,b,output);
return 0;
}Output:
Explanation: In this example, float numerator with integer denominator will also result in a compile-time error.
Example #4
Remainder for numerator int and denominator float
Code:
//include is used to add basic C libraries
#include <stdio.h>
//main method is used to run C application
int main(void)
{
//declaring 2 variables
int a;
float b;
//declare one more variables for store result
int output;
//Asking user to enter integer input
printf("Please enter any 2 integer numbers \n");
scanf("%d\n%f",&a,&b);
//Finding the remainder with modulus operator
output = a % b;
//displaying output to the end user
printf("Remainder of %d and %f is = %d", a,b,output);
return 0;
}Output:
Explanation: In this example, an int numerator with a float denominator will also result in a compile-time error. This concludes both values must be integer type only.
Example #5
The remainder with zero denominators
Code:
//include is used to add basic C libraries
#include <stdio.h>
//main method is used to run C application
int main(void)
{
//declaring 2 variables
int a;
int b=0;
//declare one more variables for store result
int output;
//Asking user to enter integer input
printf("Please enter any 1 integer number \n");
scanf("%d",&a);
//Finding the remainder with modulus operator
//denominator 0 will result into undefined so we got exception in the output
output = a % b;
//displaying output to the end user
printf("Remainder of %d and %d is = %d", a,b,output);
return 0;
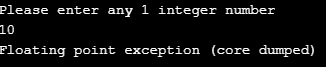
}Output:
Conclusion
The c modulus operator finds the remainder of the 2 numbers. This is always an integer only. An important conclusion from the above example is modulus operator is applicable only to integer numbers.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Modulus Operator in C. Here we discuss an introduction to Modulus Operator, working, calculation, and examples. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –