What is Model Distillation?
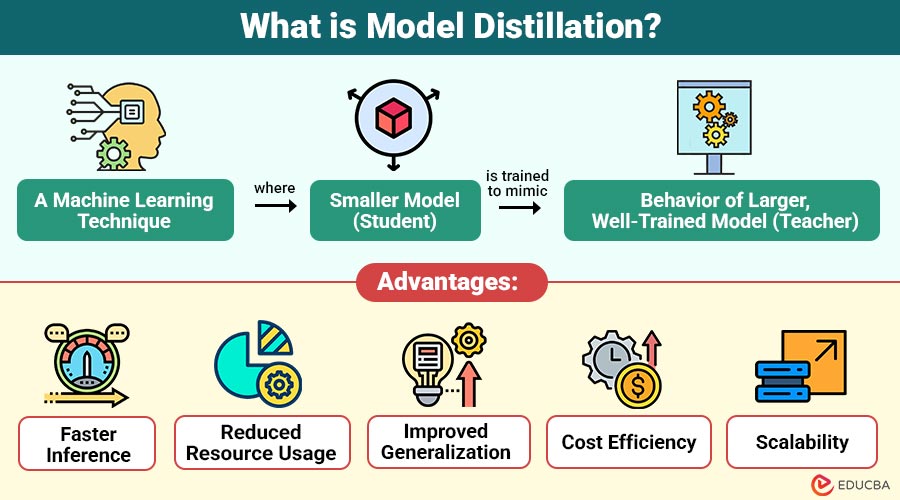
Model distillation is machine learning technique where a smaller model (student) is trained to mimic behavior of larger, well-trained model (teacher). Instead of learning only from ground-truth labels, the student model learns from the teacher’s predictions, which contain richer information about data relationships.
The teacher model is usually highly accurate but computationally expensive, while the student model is lightweight and optimized for efficiency. Through distillation, the student achieves performance close to the teacher with significantly fewer parameters.
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Importance
- Working
- Key Components
- Types
- Difference
- Advantages
- Limitations
- Real-World Use Cases
Key Takeaways:
- Model distillation transfers knowledge from large models to smaller ones without significantly sacrificing accuracy.
- Distilled models enable faster inference, lower memory usage, and efficient deployment on edge devices.
- Soft labels from teacher models help student models generalize better across tasks and datasets.
- Model distillation reduces operational costs while maintaining scalable, high-performance AI systems in production.
Why is Model Distillation Important?
Here are the reasons that explain the importance of model distillation in modern machine learning systems:
1. Lower Compute & Memory
Model distillation minimizes model size and complexity, reducing memory usage and computational demands during training and inference.
2. Improving Inference Speed
Smaller distilled models perform faster predictions, enabling real-time responses and significantly reducing latency across production systems.
3. Edge & Mobile Deployment
Distilled models run efficiently on mobile, edge, and IoT devices with limited processing power.
4. Reduced Cost & Energy
Reduced model size lowers hardware requirements, energy consumption, and overall operational costs for large-scale deployments.
How Does Model Distillation Work?
The model distillation process typically involves following steps:
1. Train the Teacher Model
A large, high-capacity model is trained on a dataset using traditional supervised learning techniques. This model achieves high accuracy but may be computationally expensive.
2. Generate Soft Targets
Instead of using only hard class labels, the teacher model outputs probability distributions over classes. These probabilities capture inter-class similarities.
3. Train the Student Model
The student model is trained using the original dataset, teacher’s soft outputs and a combined loss function that balances teacher guidance and ground truth labels
4. Optimize and Deploy
The resulting student model is lightweight, faster, and suitable for deployment while retaining much of the teacher’s performance.
Key Components of Model Distillation
Here are the core components that work together to transfer knowledge from large model to a smaller, efficient one:
1. Teacher Model
A large, complex, highly accurate model trained on extensive data, typically a deep neural network or ensemble, serving as the knowledge source.
2. Student Model
A smaller, simpler model architecture optimized for efficiency, faster inference, and reduced resource usage while learning to mimic the teacher model.
3. Temperature Scaling
A technique that softens output probability distributions, revealing hidden class relationships and providing richer learning signals for the student during training.
4. Distillation Loss
A specialized loss function combining teacher predictions and true labels to guide the student toward closely matching the teacher’s behavior.
Types of Model Distillation
Below are the major types of model distillation, each focusing on a different way of transferring knowledge from teacher models to student models:
1. Response-Based Distillation
Students learn from teacher output probabilities, transferring soft labels to smaller models, commonly used in image classification and speech recognition systems tasks and applications.
2. Feature-Based Distillation
Students learn intermediate feature representations from teacher networks, not only final predictions, benefiting deep neural networks and complex computer vision tasks, applications, and scenarios.
3. Relation-Based Distillation
Preserves relationships between data samples learned by teacher models, helping students capture structural knowledge, often applied in metric learning and similarity tasks domains.
4. Self-Distillation
A single model learns through multiple layers or training stages, improving generalization and performance without significantly increasing parameters or overall model size.
Difference Between Model Distillation and Model Compression
Here is a clear comparison highlighting how model distillation differs from model compression:
| Aspect | Model Distillation | Model Compression |
| Primary Goal | Knowledge transfer | Reduce model size |
| Technique | Teacher-student learning | Pruning, quantization |
| Accuracy Impact | Minimal loss | Can degrade performance |
| Training Required | Yes | Sometimes |
| Deployment Efficiency | High | High |
Advantages of Model Distillation
Here are the advantages that make model distillation a valuable technique for modern AI deployment:
1. Faster Inference
Smaller models process inputs faster, enabling real-time decision-making for latency-sensitive applications and production systems worldwide at scale.
2. Reduced Resource Usage
Lower memory and computational requirements make deployment feasible on edge devices and in resource-constrained environments worldwide today.
3. Improved Generalization
Soft labels convey richer information, helping student models learn better decision boundaries across diverse tasks and domains.
4. Cost Efficiency
Reduced infrastructure costs for storage, computation, and energy consumption significantly lower overall operational expenses for organizations globally.
5. Scalability
Enables large-scale deployment across distributed systems and consumer devices without compromising performance or efficiency.
Limitations of Model Distillation
Despite its benefits, model distillation has certain limitations:
1. Requires a Well-Trained Teacher Model
Model distillation depends on an accurate, well-trained teacher model, which may in turn require large datasets, extensive training time, and significant computational resources.
2. Student Performance Depends on Teacher Quality
If the teacher model is biased or poorly generalized, the student will inherit these weaknesses, limiting performance gains and potentially amplifying existing prediction errors.
3. Training Can Be Complex and Time-Consuming
Distillation introduces additional training stages, hyperparameter tuning, and alignment challenges, increasing overall complexity and significantly extending development and experimentation timelines.
4. Not All Tasks Benefit Equally from Distillation
Some tasks, especially those that require high interpretability or symbolic reasoning, may show little improvement when knowledge distillation techniques are applied.
Real-World Use Cases
Here are some use cases where model distillation is widely used to improve effectiveness and performance:
1. Mobile and Edge AI
Large cloud models are distilled into lightweight versions for smartphones, IoT devices, and embedded systems with limited computing resources.
2. Natural Language Processing
Developers distill large language models into compact versions for chatbots, search engines, and recommendation systems that require faster responses.
3. Computer Vision
High-accuracy vision models are distilled efficiently for real-time object detection in autonomous vehicles and surveillance systems.
4. Healthcare Applications
Efficient distilled models enable faster diagnosis and medical image analysis on limited hardware in clinical environments.
5. Recommendation Systems
Distilled models deliver personalized content with lower latency and reduced computational costs across large-scale platforms.
Final Thoughts
Model distillation is a powerful and practical technique that enables organizations to deploy efficient, high-performing AI systems without sacrificing accuracy. It guarantees scalability, performance, and cost-effectiveness across real-world applications by transferring knowledge from sophisticated models to simpler ones. As AI continues to evolve, model distillation will remain a key strategy for making advanced intelligence accessible, deployable, and sustainable.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is model distillation the same as pruning?
Answer: No. Distillation transfers knowledge between models, while pruning removes unnecessary parameters.
Q2. Does distillation always reduce accuracy?
Answer: Typically, the accuracy loss is minimal and often acceptable given efficiency gains.
Q3. Can distillation be used with non-neural models?
Answer: Yes, though it is most effective with neural networks.
Q4. Is model distillation suitable for small datasets?
Answer: Yes, as soft labels help improve learning when labeled data is limited.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Model Distillation” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.