What are Microlearning Strategies?
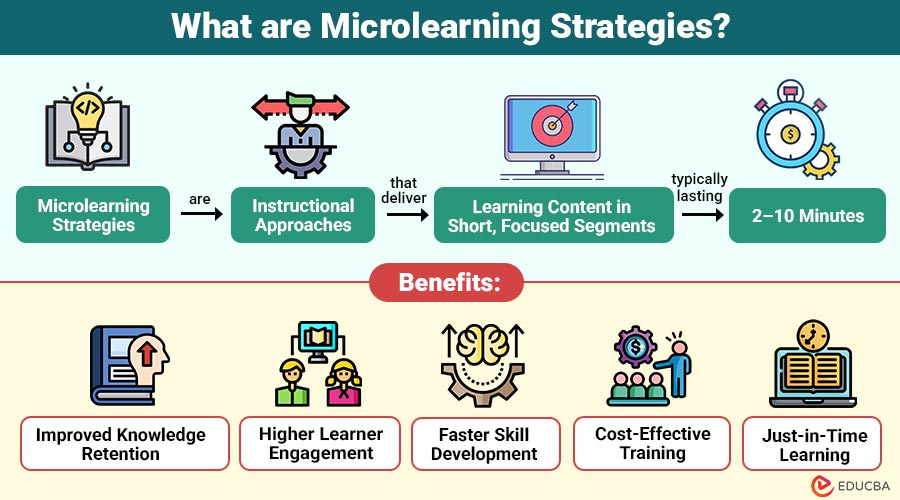
Microlearning strategies are instructional approaches that deliver learning content in short, focused segments, typically lasting 2–10 minutes. Each microlearning unit targets a single learning objective, making it easier for learners to understand, remember, and apply information.
Instead of lengthy courses or manuals, microlearning uses formats such as short videos, quizzes, infographics, flashcards, podcasts, or scenario-based exercises. These strategies are especially effective in corporate training, digital education, and skill-based learning environments. For example, learners often enhance retention by using an AI flashcard maker, which structures complex content into repeatable review prompts tailored to their needs.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Microlearning strategies deliver short, focused content that improves learner engagement, retention, and the application of practical knowledge.
- These strategies support continuous upskilling by enabling flexible, on-demand learning without interrupting daily work responsibilities.
- Using diverse formats like videos, quizzes, and scenarios personalizes learning and accommodates different learner preferences.
- Microlearning is most effective when it is well-structured, goal-driven, and integrated with deeper training on complex subjects.
Why Microlearning Strategies are Important?
Here are the key reasons why microlearning has become essential in modern learning and development environments:
1. Increasing Digital Distractions
Microlearning provides short, focused lessons that align with attention spans amid constant digital notifications and multitasking habits.
2. Remote and Hybrid Work Environments
Microlearning enables flexible, on-demand learning accessible anytime, supporting geographically distributed remote and hybrid teams.
3. Rapid Skill Obsolescence
Short learning modules enable rapid updates and refresher courses to keep skills current in rapidly changing industries.
4. Demand for Continuous Upskilling
Microlearning supports ongoing skill development through small, frequent lessons without disrupting daily work schedules.
5. Preference for Personalized Learning
Microlearning enables the delivery of content tailored to individual roles, goals, and learning pace preferences.
Types of Microlearning Strategies
Organizations can implement microlearning using various strategies depending on learning goals and audience needs.
1. Video-Based Microlearning
Video-based microlearning uses short, focused videos to explain a single concept quickly, thereby improving engagement, retention, and understanding through visual and auditory modalities.
2. Scenario-Based Learning
Scenario-based learning presents realistic, short situations where learners make decisions, helping them practice problem-solving skills and apply knowledge effectively in real-world contexts.
3. Quiz and Assessment Modules
Quiz and assessment modules use brief evaluations to reinforce key concepts, measure understanding in real time, and provide immediate feedback that strengthens knowledge retention.
4. Infographics and Visual Learning
Infographics and visual learning summarize information using visuals such as charts, icons, and diagrams, enabling faster comprehension and easier recall of complex concepts.
5. Flashcards and Spaced Repetition
Flashcards and spaced repetition deliver small learning units repeatedly over time, reinforcing memory, improving recall, and supporting long-term retention of important information.
6. Micro-Podcasts and Audio Clips
Micro-podcasts and audio clips provide short, focused lessons, enabling learners to acquire knowledge conveniently while commuting, exercising, or multitasking during daily activities.
Benefits of Microlearning Strategies
Here are the key benefits that make microlearning an effective and modern learning approach:
1. Improved Knowledge Retention
Short, focused lessons minimize cognitive overload, helping learners retain information more effectively over time.
2. Higher Learner Engagement
Interactive, multimedia-based microlearning captures attention, increases motivation, and keeps learners actively engaged.
3. Faster Skill Development
Learners quickly gain practical skills and apply knowledge immediately without lengthy or time-consuming training sessions.
4. Cost-Effective Training
Microlearning content requires less development time, is easier to update, and can be reused efficiently.
5. Just-in-Time Learning
Employees access relevant learning materials precisely when needed, supporting immediate problem-solving and performance improvement.
Difference Between Microlearning and Traditional Learning
Here are the key differences between microlearning and traditional learning approaches:
| Factor | Microlearning | Traditional Learning |
| Content Length | Short (2–10 minutes) | Long (hours or days) |
| Learning Focus | Single objective | Multiple objectives |
| Engagement | High | Moderate to low |
| Flexibility | On-demand | Scheduled |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Knowledge Retention | High | Lower over time |
Use Cases of Microlearning Strategies
Here are the common use cases where microlearning strategies are effectively applied:
1. Skill Development and Upskilling
- Technical skills
- Soft skills like communication and leadership
- Digital tool training
2. Education and E-Learning
- Exam preparation
- Language learning
- Concept revision
3. Customer Education
- Product tutorials
- Feature updates
- User guides
4. Performance Support
- Job aids
- How-to guides
- Process reminders
Best Practices for Implementing Microlearning Strategies
Here are the key best practices to ensure the successful and effective implementation of microlearning strategies:
1. Define Clear Learning Objectives
Each microlearning module should focus on one clear, measurable outcome to ensure effective learning.
2. Keep Content Simple and Focused
Eliminate unnecessary details and deliver only essential information learners need for immediate understanding.
3. Use Multiple Content Formats
Combine videos, quizzes, visuals, and audio formats to sustain interest and improve learning engagement.
4. Design for Mobile Learning
Create responsive content optimized for mobile devices, enabling easy access and learning anywhere.
5. Incorporate Gamification
Use badges, points, and progress tracking to motivate learners and encourage consistent participation.
Challenges of Microlearning Strategies
Despite its advantages, microlearning has some challenges:
1. Limited Depth
Microlearning cannot fully address complex subjects without complementary in-depth training or extended learning programs.
2. Design-intensive
Effective microlearning demands careful planning to ensure clarity, relevance, and meaningful learning outcomes.
3. Fragmentation Risk
Poorly organized microlearning can lead to disconnected knowledge and a lack of coherent understanding.
4. Low Reflection Time
Short modules may not allow sufficient time for deep reflection, critical thinking, or concept exploration.
5. Content Overload
Managing, updating, and organizing numerous microlearning assets can become challenging without proper systems.
Final Thoughts
Microlearning strategies offer a powerful, flexible, and learner-centric approach to modern education and training. By delivering short, focused, and engaging content, organizations can enhance knowledge retention, improve performance, and support continuous learning in an increasingly dynamic environment. When implemented thoughtfully and aligned with learning objectives, microlearning strategies can transform how individuals learn and how organizations grow.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is microlearning effective for all topics?
Answer: It works best for skill-based, practical, or reinforcement learning topics.
Q2. Can microlearning replace traditional training?
Answer: It complements traditional training rather than fully replacing it.
Q3. Is microlearning suitable for corporate training?
Answer: Yes, it is widely used in corporate onboarding, compliance, and skill training.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Microlearning Strategies” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

