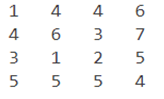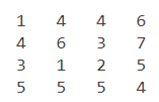Updated March 6, 2023
Introduction to Matlab Write to File
In Matlab, fprintf function is used to write data to a text file. This function will first apply firstspec to all the elements of the input arrays in the column order and then will write the data into a text file. We need to use fopen function in conjunction with the fprintf function, so that we can open the file first and then write the required data to it.
Syntax to write data to a file:
fprintf(formatSpec, X1, X2, ..., Xn)
fprintf(file_ID, formatSpec, X1, X2, ..., Xn)
Description:
- fprintf(formatSpec, X1, X2, …, Xn)will write the data to our file by applying the formatSpec to all the elements of the input arrays X1, X2, …Xn in the column order
- fprintf(file_ID, formatSpec, X1, X2, …, Xn) will write the data to our file ‘file_ID’ by applying the formatSpec to all the elements of the input arrays X1, X2, …Xn in the column order
Examples of Matlab Write to File
Let us now understand the code to use the above 2 functions to write to a file
Example #1
In this example, we will use the fprintf function to write data to our file. The data to be written will be output of a mod function. Below are the steps to be followed:
- Initialize the input array
- Pass this input arrayand mod function as an argument to the fprintf function
- Use ‘%d’ inside fomatspec to print each value of the array
Code:
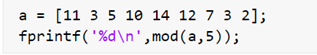
a = [11 3 5 10 14 12 7 3 2];
fprintf('%d\n',mod(a,5));
This is how our input and output will look like in MATLAB:
Input:
Output:
As we can see in the output, the fprintf function has the written output of the mod function.
In the next example, we will create a test file and will write data to it.
Example #2
In this example, we will use the fprintf function to write data to a test file. The data to be written will be an array of integers. Below are the steps to be followed:
- Initialize the input data to be written in the file
- Use fopen function to open the file called testfile. Pass the second argument ‘w’ to the fopen function, which signifies that we will be writing to this file
- Use the fprintf function to write the input data to this file
- Use ‘%3d’ inside fomatspec to print each value of the array at the required distance
- Close the file
- Use the type function to confirm if the data is written in the file
Code:
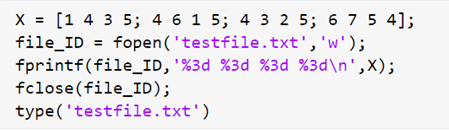
X = [1 4 3 5; 4 6 1 5; 4 3 2 5; 6 7 5 4];
file_ID = fopen('testfile.txt','w');
fprintf(file_ID,'%3d %3d %3d %3d\n',X);
fclose(file_ID);
type('testfile.txt')
This is how our input and output will look like in MATLAB:
Input:
Output:
As we can see in the output, the fprintf function has written our data to the file created. Please note that, we must pass ‘w’ as an argument to the fopen function, else we will only have the read-only permission to the file and would not be able to write to it or make any changes.
Let us understand this with an example.
Example #3
In this example, we will use the fprintf function to write data to a test file. We will try to edit the same file created in the above example. However, in this case, we will not pass ‘w’ as an argument to the fopen function. Below are the steps to be followed:
- Initialize the input data to be written in the file
- Use fopen function to open a file called testfile.
- Use the fprintf function to write the input data to this file
- Use ‘%3d’ inside fomatspec to print each value of the array at the required distance
- Close the file
- Use the type function to confirm if the data is written in the file
Code:
X = [11 412 5; 14 0 1 15; 1 3 1 5; 3 7 15 4];
file_ID = fopen('testfile.txt');
fprintf(file_ID,'%3d %3d %3d %3d\n',X);
fclose(file_ID);
type('testfile.txt')
This is how our input and output will look like in MATLAB:
Input:
Output:
As we can see in the output, the fprintf function is not able to write the new data to our file. This is because we only had read-only permission for this file and were not able to edit it.
Conclusion
- We use fprintf function in MATLAB to write our data to a text file
- This function is used in conjunction with the fopen function
- An argument ‘w’ must be passed to the fopen function so that we have the edit permission
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Matlab Write to File. Here we also discuss the introduction and syntax of matlab write to file along with different examples and its code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –