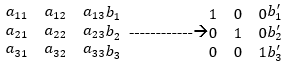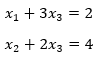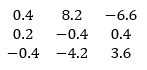Updated February 27, 2023
Introduction to Matlab rref
MATLAB inbuilt method rref is designed to form Reduced Row Echelon Form applying the ‘Gauss-Jordan elimination method’ and partial pivoting. This is used to remove the dependencies of successive rows of a matrix from each other, performing a set of operation on the rows. This functionality is useful to solve system linear equations easily. The resultant matrix from rref() function consists of zero at non-diagonal positions whereas diagonal positions gets occupied with Ones as shown below:
Syntax:
The rref function in MATLAB can exhibit different behavior by dealing with different parameters of pivoting and each follows different syntax as explained below:
| Syntax | Description |
Rm = rref(M) |
This syntax can be used to create reduced row echelon form for the input matrix ‘M’by adopting the method of Gauss-Jordan elimination through partial pivoting. |
Rm= rref(M,tol) |
This syntax can be used to create reduced row echelon form for the input matrix ‘M’witha pivot tolerance being specified, which is used by the algorithm to determine negligible columns. |
[Rm,p] = rref(M) |
This syntax can be used to create reduced row echelon form for the input matrix ‘M’and results nonzero pivots p as return values. |
Examples of Matlab rref
Following are the examples:
Example #1
The below example is written to create a reduced row echelon form for a nXn matrix.
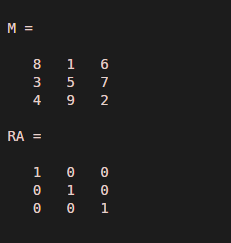
M = magic(3)
RA = rref(M)
Output:
As the input matrix is a full rank matrix, rref results in an identity matrix.
Example #2
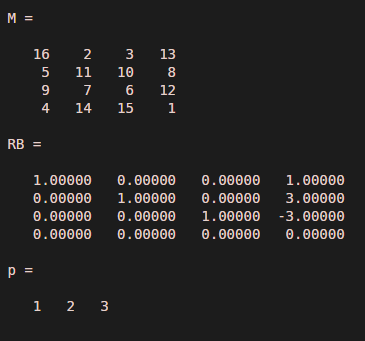
The below code snippet is developed to find out the reduced row echelon form and non-zero pivot column for a nXn matrix.
M = magic(4)[RB,p] = rref(M)
Output:
Attributes
| Attribute | Description |
| Input matrix (M) |
|
| Pivot tolerance (tol) |
|
| Reduced row echelon form of M (R) |
|
| Nonzero pivot columns (p) |
|
Example #3
An augmented matrix can be defined as an equivalent representation with respect to a system of linear equations. In the derived set of equation, when an equation is multiplied by a constant and is added to another equation, then the resultant solution consisting set of a new system is the same as the previous one.
Example:
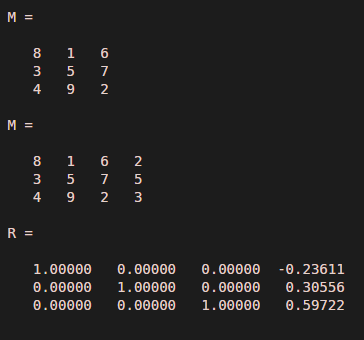
The below code generates reduced row echelon form for the augmented matrix M(:,4) using rref() method.
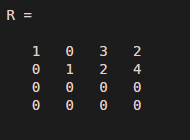
M = magic(3)M(:,4) = [2; 5; 3]R = rref(M)
Output:
Example #4
1. Solving system equation: Rref() is usefull in order to solve set of linear equations.
Example:
The input matrix M for the system is derived from the coefficients of the variables as:
M = [2 2 10;
6 3 24;
2 4 14;
-3 3 -3];
b = [12 24 20 6]';
M = [M b];
R = rref(M)
Output:
The resultant equation is:
As there is not pivot element for third column, it shows that this system has multiple solutions.
2. Finding Matrix Inverse by reducing an Augmented Matrix
Rref() is used to find reverse of a matrix by following the algorithm as:
The Augmented matrix I: [A I] can be reduced to
[I X];Then X = .
Example:
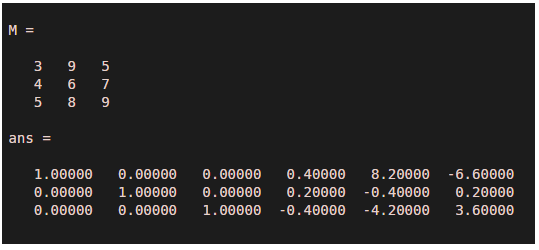
M=[3 9 5;4 6 7;5 8 9]rref([M eye(size(M))])
Output:
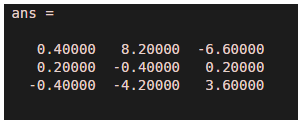
Hence the answer is:
The output can be validated by comparing the result from inv() method :
inv(M)
Limitations
- In the computation of rank and basis vectors of a matrix, using orth, rank, and null is comparatively faster and accurate as compared to that of computing by means of rref non zero pivot column.
- In case of an input matrix being badly scaled or having a deficient rank or close to singular, mldivide function is recommended to use.
Additional Point:
- In the calculation carried out in the operation of rref method, the application of partial pivoting in Gaussian elimination reduces round off errors, but it does not eliminate completely.
- It can be said that matrix M is in row echelon form when the below conditions are satisfied:
-
- All rows with nonzerovalues are above rows with all zeros.
- For each row, the leading coefficient is exactly to the right of the element in the row, above it.
It qualifies to be reduced row echelon form when it satisfied the additional condition of having each leading coefficient as 1, and must be having only nonzero in the respective column.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Matlab rref. Here we also discuss the Introduction and syntax of Matlab rref along with different examples and its code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –