Updated March 13, 2023
Introduction to Matlab readtable
Read table function in MATLAB is used to create a new table by reading data present in the form of columns in a file. The file from where the read table function can read the data can be a text file, a comma-separated or csv file, or some other excel workbook. The functionality of creating a table by reading from a text file can also be achieved in MATLAB using the in-built Import tool. Please note that we will be utilizing in-built MATLAB files for this article. You can use the same code to create tables from files stored in your local machine. In this topic, we are going to learn about Matlab readtable.
Syntax of read table function:
R = readtable (file)
R = readtable (file, x, y)
Description of the syntax:
- R = readtable (file) is used to create a table in MATLAB by reading the data in the file called ‘file’. Here ‘file’ can be a text, csv, or any other excel file with column-oriented fields.
- R = readtable (file, x, y) is used to create a table in MATLAB by reading the data in the file called ‘file’. Here the extra arguments passed are to control the type of table we create from the input data file. We can control parameters like formats of the columns, number of rows or columns we need
Examples of Matlab readtable
Let us now understand the code to create a user-defined function in MATLAB
Example #1
In this example, we will create a table in MATLAB by reading the data from an in-built text file using the readtable function. Below are the steps to be followed:
- Initialize the function readtable with the file to be read as an input argument
- For this example, we will use the in-built text file called ‘grades.txt.’
Code:
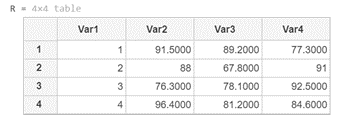
R = readtable (‘grades.txt’)
[Initializing the readtable function and passing the in-built file ‘grades.txt’ as the argument]
[readtable function will read this text file and will give a table as an output]
This is how our input and output will look like in MATLAB:
Input:
Output:
As we can see in the output, the readtable function has read the grades.txt text file and given us a table as the output.
In the above example, the text file has only 4 rows and 4 columns; our output table is very small. However, there might be cases where we have a very large file, and we need to view only a small portion of it as a table.
Example #2
In this example, we will create a table in MATLAB by reading the data from an in-built text file using the readtable function. The file we will be using in this example has 123523 rows and 29 columns. Therefore, we will first create a table for this entire file, and in the next example, we will see how to get a sub-set of this table. Below are the steps to be followed:
- Initialize the function readtable with the file to be read as an input argument
- For this example, we will use the in-built csv file called ‘airlinesmall.csv
Code:
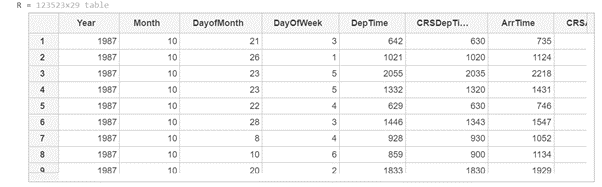
R = readtable (‘airlinesmall.csv)
[Initializing the readtable function and passing the in-built file ‘airlinesmall.csv’ as the argument]
[readtable function will read this csv file and will give a table as an output]
This is how our input and output will look like in MATLAB:
Input:
Output:
As we can see in the output, the readtable function has read the airlinesmall.csv file and given us a table as the output. Since the output table is too large to fit in one screen, we have the scroll option in the output.
Next, we will learn how to get a sub-set of this table as the output.
Example #3
In this example, we will use the same ‘airlinesmall.csv’ file to create a table in MATLAB but will create a sub-set of the entire table. As we noticed in the output in the previous example, the number of rows and columns in the ‘airlinesmall’ data were 123523 and 29, respectively. Therefore, we will now create a sub-table with 5 rows and 4 columns. Below are the steps to be followed:
- Initialize the function readtable with the file to be read as an input argument
- Here also we will use the in-built csv file called ‘airlinesmall.csv
- Pass the range which we need as the argument
Code:
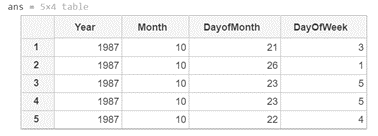
R = readtable (‘airlinesmall.csv)
[Initializing the readtable function and passing the in-built file ‘airlinesmall.csv’ as the argument]
R (1:5, 1:4)
[Passing the range, we need as argument]
This is how our input and output will look like in MATLAB:
Input:
Output:
As we can see in the output, the readtable function with the range passed as an argument has read the airlinesmall.csv file and given us a sub-table as the output.
Conclusion
- By using the readtable function, we can create a table in MATLAB by reading data from a file.
- The different file extensions like .txt, .csv can be passed as an argument to the readtable function
- We can use the readtbale function to get a sub-set of the entire table if required.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Matlab readable. Here we discuss the Examples of Matlab readable along with the inputs and outputs. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –