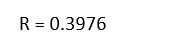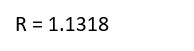Updated March 15, 2023
Introduction to MATLAB Random Numbers
MATLAB or Matrix Laboratory is a programming language that MathWorks developed. This powerful language finds its utility in technical computing. MATLAB provides us with a convenient environment that can be used to integrate tasks like manipulations on matrix, plotting data and functions, implementing algorithms, creating user interfaces, etc. MATLAB is also convenient as it gives the solutions in a form its user can easily understand. Furthermore, it uses mathematical notations to display the solutions.
Areas in Which MATLAB Can Be Used
Below are a few areas where we can use MATLAB:
- Computation
- Development of Algorithms
- Modeling
- Simulation
- Prototyping
- Analysis and Visualization of data
- Scientific graphs
- Engineering graphics
- Developing applications
MATLAB comprises several techniques to perform the uses mentioned above. The objective of this article is to have a thorough understanding of random functions in MATLAB. As the name suggests, the purpose of the random number function is to generate a random number’ per the arguments passed to the function.
Syntax of MATLAB Random Numbers
- R = rand
- R = rand(n)
- R= random(‘name’, X)
- R = random(‘name’, X, Y)
- R = random(‘name’, X, Y, Z)
- R = random(‘name’, A, B, C, D)
- R = random(pd)
- R = random(‘name,’ az1,…, azN)
Description of Random Number Functions in MATLAB
Now let us understand all these MATLAB random numbers one by one.
- R= rand
This function will return a single number that is uniformly distributed in the interval (0,1).
Below is a simple example to understand this:
R = rand
Output:
A little modification to this function can be done to get a complex number with an imaginary part.
Here is an example of generating a complex number:
R = rand + i*rand
Output:
2. R = rand(n)
This function can be used to get the desired dimension matrix of random numbers. In simpler words, this function will return a matrix of random numbers and dimensions n-by-n. The dimensions of the matrix are decided as per the argument passed to the function
Here is an example:
R = rand(3)
This will return a 3 * 3 matrix
Output:
3. R = rand(ab)
This function will return a matrix of random numbers where the argument ‘ab’ will decide the dimensions of the matrix. The main purpose of this function is to create a random number array, which will have the same dimensions as the array passed in the argument.
We have an array X = [2 3 : 1 0]. We will first get the size of this array using the ‘size’ function as Sz = size(X) and R = rand(Sz).
So, below is an example to understand this clearly:
X = [2 3 : 1 0]
Sz = size(X)
R = rand(Sz)
R = rand(size(X))
Output:
4. R= random(‘name’, X)
Here X defines the distribution parameter, and the name is the distribution family; this function will return a random number from the one-parameter name and X.
Now we will understand this function with the help of an example:
R = random(‘chi-square’, 10)
Chisquare is the randomly distributed family in this function, and 10 is the distribution parameter. The function will return:
Output:
If we run it one more time, it will return:
5. R = random(‘name’,X,Y)
Here X and Y are the two input distribution parameters; this function will return a random number from the two input parameters specified by the ‘name’ distribution family
Now we will understand this with the help of an example:
Here Beta is the random distribution family with two input parameters (1,2)
R = random('Beta', 1, 2)
Output:
Here Beta is the random distribution family with two input parameters (2,3)
R = random('Beta', 2, 3)
Output:
6. R = random(‘name’ , X, Y, Z)
Here, X, Y, and Z are the three input distribution parameters; this function will return a random number from the three parameters specified by the ‘name’ distribution family.
Let us understand this with an example:
Here Burr is the random distribution family with three input parameters (5,1,2). This function will return:
R = random('Burr', 5, 1, 2)
Output:
Similarly, if we pass the following three input parameters,
R = random('Burr', 1, 2, 3)
Output:
7. R = random(pd)
Here pd is the probability distribution object, and the function will return a random number from the probability distribution object.
Let us understand this with an example:
pd = makedist(‘beta’)
Here we have created ‘poisson’ probability distribution object
pd= beta distribution
Bata distribution
A=1
B=1
R = random(‘pd’)
This will return:
R=0.6839
R=random(‘name,’ az1,…, azN)
It will return an array of random numbers with az1 to azN from the mentioned probability distribution using input parameters from any of the above syntaxes.
Let us now understand this function with an example:
A= [5 2; -2 7];
sa = size(A);
R = random(‘Burr’, 2, 1, 1, sz)
This will return:
R= 2X2
1.9198 3.6547
1.6074 4.8815
Conclusion
With the help of MATLAB, we have access to a convenient environment that can be used to integrate tasks like matrix manipulation, data and function charting, algorithm implementation, user interface creation, etc. Another benefit of MATLAB is that it provides solutions in a simple way for the user to understand.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to MATLAB Random Numbers. Here we discuss the introduction, various syntaxes, and Description of Random Number Functions in MATLAB. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –