
Introduction to Matlab fopen
Matlab fopen statement is used for an open a file or obtains information about open files. The file handling operations like reading from file or writing on a file for these operations we need to first open a file for that fopen statement is used. We open a file in binary mode or text mode and we specify the access type like r, w, r+, a, etc. and the default access type is read. The fopen statement returns data stored in fileID1, fileID1 is a file identifier on open file.
Syntax:
The syntax for Matlab open is as shown below:
fileID1 = fopen(filename)
fileID1 = fopen(filename,permission)
fileID1 = fopen(filename,permission,machinefmt,encodingIn)
[fileID1,errmsg] = fopen(___)
fIDs = fopen('all')
filename = fopen(fileID)
[filename,permission,machinefmt,encodingOut] = fopen(fileID)
How to Use Matlab fopen?
We use fopen statement for only open the file for these we don’t need to specify anything simply we take a fopen statement and that file name which we want to open. But in another case, if we want to write or read from file we must specify the access type in fopen statement. For these we want to specify the permission, the permission is as followed:
- ‘r’: The file is open for reading. And it’s a default condition.
- ‘r+’: The file is open for both reading as well as writing.
- ‘w’: It will delete the contents of an existing file or simply it creates a new file and opens it for writing.
- ‘w+’: It will delete the contents of an existing file or simply it creates a new file, and open it for both readings as well as writing.
- ‘a’: It will create and open a new file or open an existing file for writing, appending to the end of the file.
- ‘a+’: It will create and open a new file or open an existing file for reading and writing, appending to the end of the file.
- ‘A’: It will append without automatic flushing; used with tape drives
Examples to Implement Matlab fopen
Below are the examples of Matlab fopen:
Example #1
Let us see one example, in this example, we open the text file using fopen and read the data from that file. For these first we take a fopen statement, in this fopen we specify that which file we want to open that file name and the access type mode of that file, for those we take fopen in parenthesis text file name with .txt extension textfile1.txt and the access type mode is read ‘r’ and these two arguments are separated by a comma. And this fopen statement we take in a file identifier that is fileID1. And then we simply read that file using a fscanf statement. And lastly, we need to close that file using a file identifier and close statement; the file close statement is fclose and files identifier of open file that is fileID1.
Code:
clc;
clear all;
close all;
fileID1 = fopen('textfile1.txt','r');formatSpec = '%s';A1 = fscanf(fileID1,formatSpec)fclose(fileID1);
Output:

Example #2
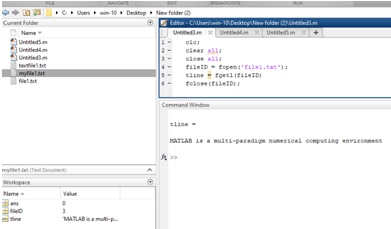
Let us see an example related to the fopen statement, we already created one text file with extension .txt ‘file1.txt’ in that text file we write something information. For reading or displaying one line from that text file, we write a Matlab code, in Matlab code, we use a fopen statement fopen statement is used for an open a file or obtain information about an open file. In this example, we used fopen statement for an open a text file which we earlier created with the name ‘file1’. Then we assign a file identifier to that fopen statement. Then we use an ‘fgetl’ function it is an inbuilt function available on Matlab it used for reading one line from a file. This readied line stored in line variable and we displaying that data and then we close the file, for closing a file we take fclose in that file identifier.
Code:
clc;
clear all;
close all;
fileID = fopen('file1.txt');
tline = fgetl(fileID)fclose(fileID);
Output:
Example #3
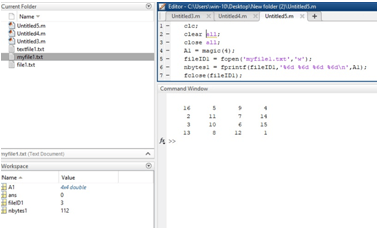
Let us see one example related to fopen statement, in this example, we create a matrix using a magic function, the magic function is nothing but it creates a matrix of n-n number in our example it creates 4- by-4 matrix. The matrix is stored in variable A1. This matrix we want to write in a file for that we need to open that file. To open a file we use a fopen statement, fopen in parenthesis the file name in which we want to write a matrix and a type of access mode that is written ‘w’ and these we assign to the fileID1, fileID1 is a file identifier of an open file. Then we use a fprintf statement to write that matrix on a text file. Then we simply close that open file by using a file close statement and a file identifier of an open file. And for verification that the matrix is written on that text file or not we use a type function, type in parenthesis that file name in which we write a matrix.
Code:
Clc;
clear all;
close all;
A1 = magic(4);fileID1 = fopen ('myfile1.txt','w');nbytes1 = fprintf(fileID1,'%6d %6d %6d %6d\n',A1)fclose(fileID1);type('myfile1.txt')
Output:
Conclusion
In this article we saw the basic concept of fopen statement, basically fopen is nothing but an open a file or obtain information about open files. We also saw the different syntax for fopen statement used in Matlab code. Also, we saw the different some examples related to fopen.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Matlab fopen. Here we discuss the Introduction to Matlab fopen and its Syntax along with different Examples and its Code Implementation. You can also go through our suggested articles to learn more –

