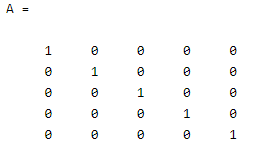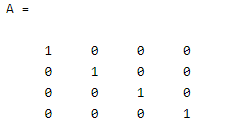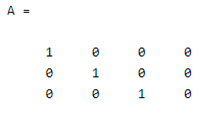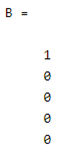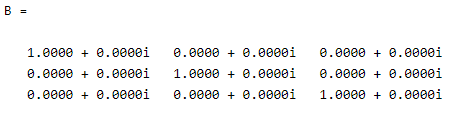Updated March 4, 2023
Introduction to Matlab eye
Matlab provides different types of functions to the user, the eye is one of the functions provided by Matlab. Basically, Matlab eye () is used to identify the n by n matrix whose main diagonal is ones and zeros, otherwise, Matlab eye () function returns the n by m matrix whose main diagonal is ones and zeros. If we specify the size with Matlab eye () function then I return the array diagonal with ones and zeros. Normally Matlab eye () function is used to identify the matrix as per the user requirement for different purposes.
Syntax
There are multiple syntaxes available for Matlab eye () as follows.
Variable name = eye
Variable name = eye (n by n matrix)
Variable name = eye (n by m matrix)
Variable name = eye (array size)
Explanation
In the first syntax, we use different parameters such as variable name means an actual variable name that depends on the user and after that, we use the eye () function. In this syntax eye () is used to return scalar 1.
In the second we pass the size of a matrix with eye () function as shown in the above syntax. That means it is used to identify the n by n matrix whose main diagonal is ones and zero.
In the third syntax we define n by m size of matrix it is also used to return whose main diagonal is ones and zeros elsewhere.
In the fourth syntax, we define the array size as shown in the above syntax, which means it returns the ones on the main diagonal and zeros elsewhere.
How does the eye work in Matlab?
Now let’s see how the eye () function works in Matlab as follows. Now let’s see the different input arguments that are required for the eye () function as follows.
Dimension Size of the first variable (n):
Normally dimension size of the first variable is always an integer and it has the following properties as follows.
Here we consider n and I variables for an explanation.
- If the value of n is only an integer input argument then matrix (I) is a square that we can consider as n – by- n matrix.
- If the value of n is zero then we can consider the matrix as empty.
- If the value of n is negative then we can consider it as 0 or we can treat it as a 0.
It uses different data types such as double, single, int8, int16…Up to int64.
Dimension Size of the second variable (m):
Normally dimension size of the second variable is always an integer and it has the following properties as follows.
- If the value of m is 0 then the matrix is 0.
- If the value of m is negative then we consider it as 0 or we can treat it as a 0.
It also uses the same data types that mean double, single, int8, int16…Up to int64.
Size of the array (sa):
It is used to specify the row vector that does not have more than two integer values and it also has the following properties as follows.
- If the size is 0 then we can consider the matrix as empty.
- If the size is negative then we can consider it as 0.
It also uses the same data types such as double, single, int8, int16…Up to int64.
Examples
Now let’s see different examples of Matlab eye () function for better understanding as follows.
Now let’s see a very simple example of eye () function
A = eye(5)
Explanation
In the above example, we try to create an n – by – n matrix by using the Matlab eye () function; here the value of n is 5 so we created a 5 by 5 matrix and A is the variable name that we assign for the matrix. Notice here all diagonals are ones and other elements are zero. The final output of the above statement we illustrated by using the following screenshot as follows.
Similarly, we can create a square matrix by using the eye () function as follows.
A = eye(4)
Explanation
By using the above statement we try to create the 4 by 4 square identity matrix. In which all diagonals are ones and other elements are zeros. The final output of the above statement we illustrated by using the following screenshot as follows.
Now let’s see another example of eye () function as follows.
A = eye(3,4)
Explanation
By using the above statement we try to implement the rectangular matrix. Here the size of the matrix is 3 by 4 as shown in the above statement. The final output of the above statement we illustrated by using the following screenshot as follows.
Now let’s see how we can create the identity vector as follows.
A = [5,1]
B = eye(A)
Explanation
By using the above statement we try to create the 5 by 1 identity vector. Here first we specify the size of the vector and after that, we call that vector by using the eye () function as shown. The final output of the above statement we illustrated by using the following screenshot as follows.
Now let’s see the example of non-default data type as follows.
A = eye (4, "uint16")
Explanation
In the above example, we use uint16 data type as shown, here we created a 4 by 4 matrix. The final output of the above statement we illustrated by using the following screenshot as follows.
Now let’s see some complex examples as follows.
A = [2+3i, 4i]
B =eye(3,'like',A)
Explanation
By using the above example we try to implement the complex example. In this example, we use a complex value like an array, or we can say that it is not a real value. The final output of the above statement we illustrated by using the following screenshot as follows.
So in this, we can implement the Matlab eye () function as per our requirement.
Conclusion
We hope from this article you learn Matlab eye. From the above article, we have learned the basic syntax of the eye and we also see different examples of the eye. From this article, we learned how and when we use Matlab eye.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Matlab eye. Here we discuss the basic syntax of the eye and we also see different examples of the eye. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –