Updated March 13, 2023

Introduction to Matlab Concatenate
Matlab Concatenate is used to combine 2 or more characters, strings, or elements of the array. It helps us in combining data present in different cells. Concatenation can also be used to combine 2 matrices and create a new matrix of larger size. It’s more like merging two data frames based on the need.
For example, at times we might need to combine ‘First Name’ and ‘Last Name’ present in different cells to get the complete name. In MATLAB we use ‘strcat’ and ‘cat’ function for concatenation.
In MATLAB, concatenation is of 2 types:
Horizontal concatenation: In this, 2 matrices are concatenated using commas.
Vertical concatenation: Here we concatenate our matrices using semicolons.
Syntax
Below is the syntax for Matlab Concatenate:
C = strcat (st1, st2, st3, … stN)
C = cat(dim, x, y)
Explanation: C = strcat (st1, st2, st3, … stN) is used to concatenate the input strings horizontally. C = cat (dim, x, y) is used to concatenate matrix ‘x’ and matrix ‘y’ along the dimension ‘dim’.
Examples to Implement Matlab Concatenate
Let us now understand the code of strcat function in MATLAB using different examples:
Example #1
In this example, we will learn how to concatenate character vectors. For our first example, we will follow the following steps:
1. Pass the required input character vectors
2. Input these character vectors in strcat function
Code:
St1 = 'let us learn'
St2 = ' concatenation'
St3 = ' in MATLAB'
C = strcat(St1, St2, St3)
Output:
Explanation: First, Declaring the first input character vector. Declaring the second input character vector. Declaring the third input character vector. Passing the input character vectors to the ‘strcat’ function. Please note that, in 2nd and 3rd input strings, we have passed an extra space in the beginning of the character. As we can see in the output, we have obtained a concatenated string of character vectors.
Example #2
In this example, we will take cell arrays of characters will see how the strcat functions works. For this example, we will follow steps:
1. Initialize the input cell arrays
2. Pass the input cell arrays to the strcat function
Code:
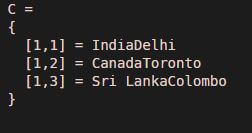
Country = {'India','Canada', 'Sri Lanka'};
Capital = {'Delhi','Toronto', 'Colombo'};
C = strcat(Country, Capital)
Output:
Explanation: First, Declaring the first input character array. Declaring the second input character array. Passing the input character arrays to the ‘strcat’ function. strcat will concatenate the corresponding elements of 2 arrays. So, the 1stelement of ‘Country’ array will get concatenated with the 1st element of ‘Capital’ array. As we can see in the output, we have obtained a concatenated string of cell arrays as expected by us. We can also pass the input strings in reverse order if we expect the output to be in that order.
Example #3
Code:
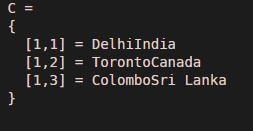
Country = {'India','Canada', 'Sri Lanka'};
Capital = {'Delhi','Toronto', 'Colombo'};
C = strcat(Capital, Country)
Output:
Explanation: First, Declaring the first input character array. Declaring the second input character array. Passing the input character arrays to the ‘strcat’ function. As we can see in the output, we have obtained a concatenated string of cell arrays as expected by us.
Example #4
In this example, we will take the same example used above. We will also add a string ‘, Capital-Country’ after each concatenated element. This helps us in providing any extra information that we might need to pass. For this example, we will follow the following steps:
1. Initialize the input cell arrays
2. Pass the input cell arrays to the strcat function
3. Pass the string ‘, Capital-Country’ as the 3rd argument
Code:
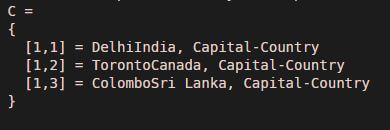
Country = {'India','Canada', 'Sri Lanka'};
Capital = {'Delhi','Toronto', 'Colombo'};
C = strcat(Capital, Country, ', Capital-Country')
Output:
Explanation: First, Declaring the first input character array. Declaring the second input character array. Passing the input character arrays to the ‘strcat’ function. strcat will concatenate the corresponding elements of 2 arrays. The string ‘, Capital-Country’ is added to every element of the concatenated array. As we can see in the output, we have obtained a concatenated string of cell arrays with an additional string in the end of each element.
Example #5
In this example, we will take two 3×3 matrices will see how the ‘cat’ functions works.
Code:
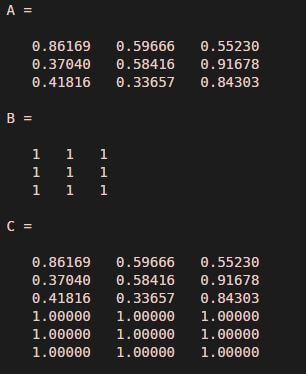
A = rand(3)
B = ones(3)
C = cat(1, A, B)
Output:
Explanation: First, Declaring the first input matrix. Declaring the second input matrix. Passing the input matrices to the ‘cat’ function. For concatenation, the first argument can take 2 values. For vertical concatenation, first argument will be ‘1’. For horizontal concatenation, the first argument will be ‘2’. As we can see in the output, we have obtained vertically concatenated matrices.
Conclusion
‘strcat’ function is used in MATLAB to concatenate strings or arrays. ‘cat’ function is used to concatenate 2 matrices. Both horizontal and vertical concatenation is possible in MATLAB.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Matlab Concatenate. Here we discuss an introduction to Matlab Concatenate, syntax, examples with code and output. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –