Updated March 17, 2023
Introduction to Math Functions in C
This article lists the different mathematical functions used in C programming languages with working code illustration. Computers do huge mathematical calculations and analyses of huge numbers, to do so we have used math features in C. Before Starting with, we need to know the C languages use header/library called Math.h for various mathematical functions. This helps in calculating trigonometric operations, logarithms, absolute values, square roots. So, let us explore the different types of functions used in this library. All these functions take double as a data type and return the same.
Various Math Functions in C
Let’s see various functions defined in math.h and the Math library is categorized into three main types: Trigonometric functions, math functions, Log/expo functions. To implement the below functions, it is mandatory to include<cmath.h> or <math.h> in the code.
1. floor (double a)
This function returns the largest integer value not greater than ‘a’ value. It rounds a value and returns a double as a result. It behaves differently for negative numbers, as they round to the next negative number.
Ex: floor (7.2) is 7.0
floor (-7.2) is -8.0
Example:
This program illustrates how to compute the floor for the declared value and rounds to the next value 10.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main()
{
double f= -9.33;
int final;
final = floor(f);
printf("Floor value of %.2f = %d", f, final);
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
2. ceil ()
Syntax:
double ceil (double b)This function returns the smallest integer value that is greater or equal to b and rounds the value upwards. For a negative value, it moves towards the left. Example 3.4 returns -3 has the output.
Example:
This program explains by taking input in the float argument and returns the ceil value.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main()
{
float n, ceilVal;
printf(" Enter any Numeric element : ");
scanf("%f", &n);
ceilVal = ceil(n);
printf("\n The Value of %.2f = %.4f ", n, ceilVal);
return 0;
}Output:
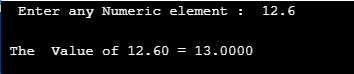
3. Sqrt ()
This function returns the square root of a specified number.
Syntax:
sqrt( arg)Example:
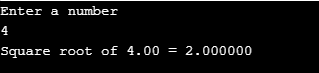
The below code explains the most known mathematical function sqrt() by taking ‘n’ values to compute the square root for the different ‘n’ values.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main()
{
double n,output;
printf("Enter a number\n");
scanf("%lf", &n);
output = sqrt(n);
printf("Square root of %.2lf = %f", n,output);
return 0;Output:
4. round ()
This function rounds the nearest value of a given input. It throws out the error if the value is too large. Other functions like lround (), llround () also rounds the nearest integer.
Syntax:
int round(arg)Example:
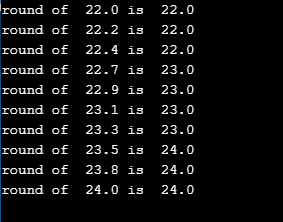
The below code is very simple which does round off to the nearest ‘r’ value in the for loop.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main ()
{
for(double r=110;r<=120;r+=1.1)
printf("round of %.1lf is %.1lf\n", r/5.0, round(r/5.0));
return 0;}Output:
5.pow ()
This function returns to power for the given number(ab). It returns a raised to the power of b, which has two parameters base and exponent.
Example:
In the Below source code, we are allowing a user to enter an input value to compute the power of the given two arguments.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main()
{
int r, ba, expr;
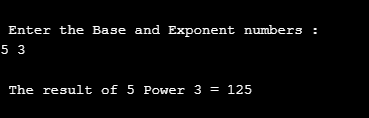
printf("\n Enter the Base and Exponent numbers : \n");
scanf("%d %d", &ba, &expr);
r = pow(ba, expr);
printf("\n The result of %d Power %d = %d ", ba, expr ,r);
return 0;
}Output:
6. trun()
This function helps in truncating the given value. It returns integer values. To truncate floating and double values truncf (), truncl () are used.
Syntax:
double trunc(a);Example:
Below source code takes two input values a, b to truncate the double values.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
void main() {
double m, n, a, b;
a = 56.16;
b = 85.74;
m = trunc(a);
n = trunc(b);
printf("The value of a: %lf\n",m);
printf("The value of a: %lf\n",n);
}Output:
![]()
7. fmod()
This function returns the remainder for the given two input values when m divided by n.
Syntax:
double fmod(double I, double j)Example:
In the below example it takes two values from the user to compute the remainder using fmod() function.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
int main(){
double fiN;
double secN;
double n;
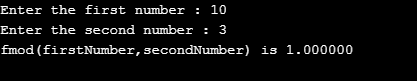
printf("Enter the first number : ");
scanf("%lf",&fiN);
printf("Enter the second number : ");
scanf("%lf",&secN);
printf("fmod(firstNumber,secondNumber) is %lf \n",fmod(fiN,secN));
}Output:
Trigonometric Functions
Below are the different functions of Trigonometric:
1. sin()
This built-in function gives sine value of the given number, calculates floating-point values. asin() computes arc, for hyperbolic it is sinh().
Syntax:
return type sin(y);y returns value in radians and return type takes double.
Example:
In the following source code, I have taken two different input values to calculate sin value and returns double.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main()
{
double a;
double z;
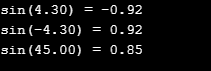
a = 4.3;
z = sin(a);
printf("sin(%.2lf) = %.2lf\n", a, z);
a = -4.3;
z = sin(a);
printf("sin(%.2lf) = %.2lf\n", a, z);
a = 45;
z = sin(a);
printf("sin(%.2lf) = %.2lf\n", a, z);
return 0;
}Output:
2. sinh()
This math function computes trigonometric tangent sine value for the given number.
Syntax:
double sinh(x);Example
In the below source code Sine hyperbolic is calculated by declaring an input value.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#define PI 3.141592654
int main()
{
double gt = 3.60, z;
z = sinh(gt);
printf("Sine hyperbolic of %.2lf is = %.2lf", gt, z);
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
3. cos()
This math function determines the trigonometric cosine value for the given element.
Syntax:
return type cos(argument);Example
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#define PI 3.14
int main()
{
double cVal, rVal, dVal;
for(int i=0;i<=2;i++)
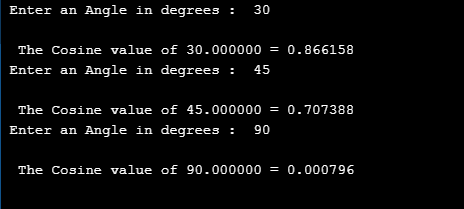
{
printf(" Enter an Angle in degrees : ");
scanf("%lf", &dVal);
rVal = dVal * (PI/180);
cVal = cos(rVal);
printf("\n The Cosine value of %f = %f ", dVal, cVal);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}Output:
4. cosh()
It returns hyberbolic cosine for a given value.
Syntax:
double cosh(y);Example
The below example shows it takes two different input values to compute hyperbolic.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main ()
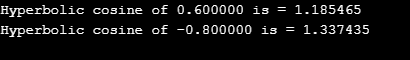
{
double k, r;
k = 0.6;
r = cosh(k);
printf("Hyperbolic cosine of %lf is = %lf\n", k, r);
k = -0.8;
r = cosh(k);
printf("Hyperbolic cosine of %lf is = %lf\n", k, r);
return 0;}Output:
5. tan()
This math library function calculates tangent values of the angle for the mathematical expression and measured in radians.
It can be declared as
double tan(arguments);Example
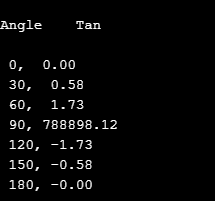
In the following source code, tan value is calculated for the following angles which is incremented using for loop.
# include <stdio.h>
# include <conio.h>
# include <math.h>
void main()
{
float z ;
int k ;
char ch ;
printf("\nAngle \t Tan \n") ;
for (k = 0; k <= 180; k = k + 30)
{
z = k * 3.14159 / 180 ;
printf("\n %d, %5.2f",k, tan(z));
}
getch() ;
}Output:
6. tanh()
tanh() function returns hyperbolic tangent of the given value. It takes a single parameter. In addition to find tangent for long double and float tanhl() and tanhf () are used for computation.
Syntax:
double tanh( val);Example:
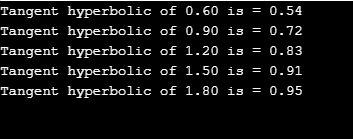
A tangent hyberbolic is calculated for ‘ j’ values using for loops. Let’s see how it works.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#define PI 3.141592654
int main()
{
double val, r;
for(double j=0.60; j<=2.0;j+=.30)
{
r = tanh(j);
printf("Tangent hyperbolic of %.2lf is = %.2lf",j, r);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}Output:
Log Arithmetic Functions
Below are the different functions of log arithmetic:
1. exp()
This function does computation on exponential for a given value(ex). There are also other subtypes like frexp(), Idexp() returning mantissa and multiplied to the power of x.
Syntax:
return type exp(value);Example:
The program takes numeric value from the user to compute the exponent for a given value and returns double.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main()
{
double numb, eVal;
printf(" Enter any Numeric Value : ");
scanf("%lf", &numb);
eVal = exp(numb);
printf("\n Exponential Value of e power %lf = %lf ", numb, eVal);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}Output:
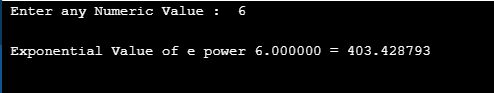
2. log()
This function returns the logarithm value of a given number. (to the base e. loge)
Syntax:
double log(arg);Example:
In the following example, log value for the given number is calculated using function. User-defined function lgm() does computation and function is called in the main function.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
float lgm ( float iv );
int main ()
{
float q, r ;
printf ( "\nEnter a number to find log value \n");
scanf ( "%f", &q ) ;
r = lgm ( q ) ;
printf ( "\nthe log value is %f is %f",q,r );
}
float lgm ( float iv ) // function definition
{
float exe ;
exe = log(iv);
return ( exe ) ;
}Output:

Conclusion
To conclude, we have seen different mathematical functions used in C programming and these are the direct library functions to use. C programs utilize these functions for various mathematical operations. To solve some complex versions of computations this built-in function benefits mathematically oriented programming language to return simple values.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Math Functions in C. Here we discuss different mathematical functions in C with examples. You can also go through our other suggested articles –


