Updated May 19, 2023
Introduction to Mat2cell in Matlab
The ‘mat2cell’ function in Matlab converts arrays, vectors, or multidimensional matrices into smaller cell arrays, vectors, or multifaceted matrices. The basic principle behind this concept is to convert a matrix into cells. It converts only the dimensions and formats of the matrix without changing elements, which means there is no data loss in this function. This function can be performed in two ways one way is by providing rows distribution, and another way is by giving rows as well as columns distribution. By using this function, we are changing the dimensions of the matrix, but we can again restore our original data or elements by using the mat2cell process.
Syntax
Below is the syntax for Mat2cell Matlab:
Op = mat2cell (in, [ 4 3 ] )
Output variable name = mat2cell (input variable name, [ rows of first matrix rows of second matrix ]
OR
Op = mat2cell (in , [ 3 2 ] , [ 2 3 ] )
Output variable name = mat2cell ( input variable name , [ first sub - matrix dimensions second sub - matrix dimensions ]
How does Mat2cell Matlab work?
Mat2cell function needs some parameters to operate on input .in the first way we need to provide row distribution of matrix to the function. Suppose there are 4 rows in input then row distribution for output will be [ 1 3 ] or [ 2 2 ] or [ 3 1 ] or [40] or [04]. In the second approach, we need to provide cell array dimensions. Suppose there are 3 rows and 4 columns in the input matrix, so dimensions of the input matrix will be 3 by 4. Then distributions are such that [ 2 1 ] [ 2 2 ]. Distribution should be the addition of dimensions of submatrices. There are other distributions also processed for this example like [ 3 1 ][ 1 2 ] or [ 1 2 ] [ 3 1 ].
Examples to Implement Mat2cell Matlab
Below are examples mentioned:
Example #1
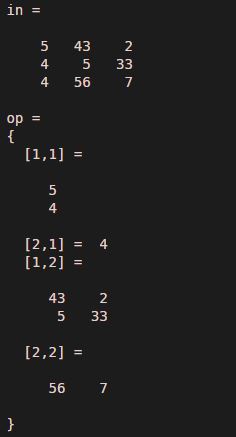
Let us assume one input matrix with three rows and three columns, here the input matrix is assigned to variable ‘in’, and the output matrix is assigned to variable ‘op’. In this example, we have used the multi-dimensions approach. The first matrix dimensions are [ 2 1 ], and the second dimensions are [ 1 2 ].
Code:
clc ;
clear all ;
in = [ 5 43 2 ; 4 5 33 ; 4 56 7 ]
op = mat2cell( in ,[ 2 1 ],[ 1 2 ] )
Output:
Example #2
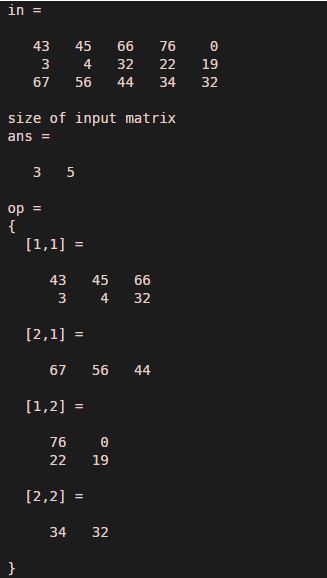
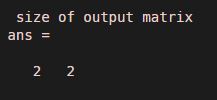
In this example, we assume a matrix of three rows and five columns which means the size of the input matrix is three by five. Here input matrix is assigned to variable ‘in’, and the output matrix is assigned to variable ‘op’. We have used a sub-matrix dimensions approach to convert the input matrix into a cell matrix. Dimensions of the submatrix are [ 2 1 ] and [ 3 2 ], so that satisfies the criteria of the addition of rows and columns; that is, two plus three is five, and one plus two is three. We also observe the result by using a size function. The size of the input matrix is [ 3 5 ], and the size of the output matrix is [ 2 2 ]
Code:
clc ;
clear all ;
in = [ 43 45 66 76 0 ; 3 4 32 22 19 ; 67 56 44 34 32 ]
display ( 'size of input matrix ' )
size ( in )
op = mat2cell ( in , [ 2 1 ] , [ 3 2 ] )
display ( ' size of output matrix ' )
size( op )
Output:
Example #3
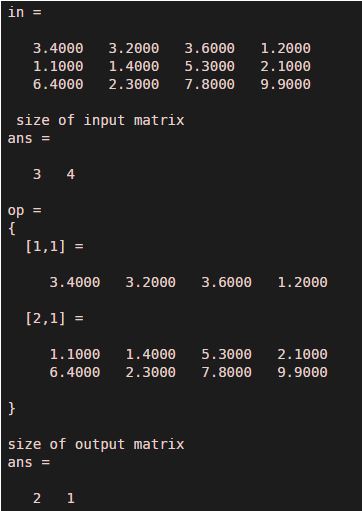
In this example, we can see another approach of distribution that is only row distribution; here, the input matrix is assigned to variable ‘in,’ and the output matrix is set to variable ‘op.’ Let us assume an input matrix of four rows and three columns, meaning the input matrix size is three by four. We have applied the mat2 cell function with row distribution [ 1 2 ]. Row distribution [ 1 2 ] means there will be two cell-matrix first matrix will have one row with four columns, and the second matrix will have two rows with four columns. This approach changes only rows of dimensions, and columns’ dimensions remain.
Code:
clc ;
clear all ;
in = [ 3.4 3.2 3.6 1.2 ; 1.1 1.4 5.3 2.1 ; 6.4 2.3 7.8 9.9 ]
display ( ' size of input matrix ' )
size ( in )
op = mat2cell ( in , [ 1 2 ])
display ( 'size of output matrix' )
size ( op )
Output:
Conclusion
‘mat2cell’ function is a very effective command to adjust the dimensions of a multidimensional matrix. It converts the multidimensional matrix into a cell matrix without affecting data or elements of the input matrix. We can use any type of input to use this function, such as arrays, vectors, or multidimensional matrices. Similarly, we can convert cell-matrix or arrays into a matrix by using a function cell2 mat. Cell2mat function acts exactly the opposite of the mat2cell function.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Mat2cell Matlab” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.