Updated April 12, 2023

Introduction to MariaDB SHOW TABLES
MariaDB provides show table commands to the user, in which we are able to know all details about the database table. With the help of the show tables command, we can list all non-temporary tables and view tables and sequences of tables from the database. We can perform different operations on the database table by using the show table command. The select clause is used to access that from the database as per our requirement; similarly, the show tables command is used to view tables from the database server. We can use clauses with the show tables command as a user requirement to see specific tables or records from the MariaDB server.
Syntax
show tables from specified database name;Explanation
In the above syntax, we use the show tables command with the specified database name as shown in the above syntax. Here we can also use the like clauses for specific results, and this is depending on user requirement.
How SHOW TABLES works in MariaDB?
Let’s see how the Show tables command works in the MariaDB server as follows:
Normally show tables command is used to list non-temporary tables from the database but shows lots of information about each non-temporary table; we can view table and sequence of tables from the specified database.
We can use the Like clause with the show tables command; the Like clause is used to indicate which specific table names to match from the database. The Like and where normally used to returns rows from the database table. The full modifier option is supported by the show full table command, and it displays second output column values. The information_schema.TABLES we can also use to show tables, which means it works the same as the show tables statement.
Examples
Let’s see the different examples of MariaDB show tables command as follows.
show tables;Explanation
If we already selected the database, then the show tables command returns tables, view, and sequence from the current database. In this example, we already connected to the sample database. The final output of the above query we illustrate by using the following snapshot.

In some cases, if we are not connected to any specified database, at that time, we can use from clause to specify the database name from which we need to show the tables, views, and sequences. So let’s see the example of that type as follows.
show tables from demo;Explanation
In the above example, we used the show tables command with from clause as shown in the above statement, here we specified a particular database name from which we need to show tables, views, and sequence. The final output of the above query we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
![]()
We can also use the full option in the show tables command; it includes an additional column field that is table_type into the final result. The table_type we can refer to as base table, view, and sequence.
Syntax
show full tables from specified database name;Explanation
In the above syntax, we used the show full tables command with the specified database name. We can also use clauses to specify a search condition and find the tables, views, and sequence, but we cannot use both clauses at the same time.
Example
show full tables;Explanation
In this example, we already connected to the sample database; here, we use the full option with the show tables command. So it returns all the detailed structures of the specified table. The final output of the above query we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
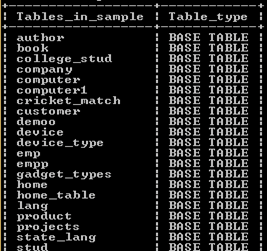
Now let’s see how we can use like clause with show tables as follows
Syntax
show tables like 'specified value%';Explanation
In the above syntax, we used the show tables command with like clause as shown in the above syntax, here specified value means the actual value that we need to find, such as table, views, and sequence.
Example
show tables like 'b%';Explanation
In the above example, we used the show tables command with the like clause; here, like clause is used to show tables, views, and sequence whose name starts with b character. The final output of the above query we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
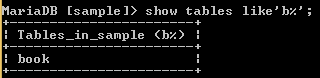
The same example we can execute with the full option as follows.
show full tables like 'demo%';Explanation
In the above example, we used the show tables command with full option, and like clause Here, the clause is used to show tables, views, and sequence whose name starts with a demo word. As shown in the above example. The final output of the above query we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
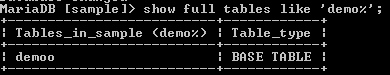
Let’s see one more example of this type as follows.
Example
show full tables like 'emp1%';Explanation
In the above example, we use the full tables statement with the like clause; here, we need to list all tables whose name starts with an emp1 word as shown in the above statement. The final output of the above query we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
![]()
Now let’s see MariaDB show tables command with where clause as follows.
Syntax
show full tables where specified table name = 'base table name';Explanation
In the above syntax, we used a where clause with the show tables command as shown. Here where clauses list all tables from specified database names.
Example
show full tables where table_type = 'base_type';Explanation
In the above example, we use the show tables command with where clause; in this example, we already connected with the database name as a sample, and with the help of the above statement, we list all base tables from the sample database. The final output of the above query we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
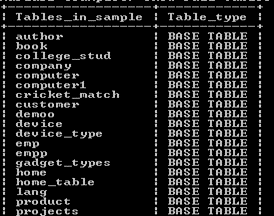
Now let’s see how we can combine use like and where clauses as follows.
The answer to this point is that we cannot combine both clauses at the same time; we can say this is a limitation of MariaDB show tables.
Conclusion
We hope from this article you have understood about the MariaDB show tables. From this article, we have learned the basic syntax of MariaDB show tables, and we also see different examples of MariaDB show tables. From this article, we learned how and when we use MariaDB show tables.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MariaDB SHOW TABLES” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

