Updated June 2, 2023

Definition of MariaDB Select Database
MariaDB provides different clauses to the user to perform a different operation as per requirement, so select one type of clause. Basically select is used to retrieve the data from the database server. When we use the select database command it retrieves the current database name that is in use, which means it is useful to check the current database name. Selecting a database is another concept when we need to select a database at that time, we use the USE keyword to select a specific database. So selecting and using a database is totally different, but it performs similar functions related to the database. We can perform different operations on databases by using select clauses.
Syntax:
select database();Explanation:
In the above syntax, we use the select clause with a database function, as shown in the above statement, here select clause retrieves the current database name from the MariaDB server and the database function is used to indicate the name of the database.
How to Select Database in MariaDB?
Let’s see how the select database works in MariaDB as follows.
The select clause is used to retrieve data, or we can say records, table, and database from the MariaDB server means that we can use a select clause as per user requirement. Each select expression shows what type of data we need to retrieve from the database or server.
After execution of the select database command, it returns the current database name that is the default database name otherwise, it returns the null.
We can also use SCHEMA () as a synonym for the DATABASE () both commands perform the same function.
Examples
Let’s see the different examples of select databases as follows.
First, connect to the MariaDB server using the client program, so we required a password. Then use the following statement to see the current database.
select database();Explanation:
In the above example, we use a select clause followed by a database function, as shown in the above statement. Suppose users need to see the current database name so that time we can use the above statement and return the current database name. The final output of the show databases queries we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
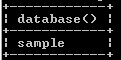
Example: If we don’t use any database.
select database();Explanation:
In the above example, we use a select clause followed by a database function, as shown in the above statement. Suppose the user wants to see the name of the current database so that times we can use the above statement but return the null value because we can’t use any database. The final output of the show databases queries we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
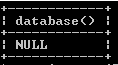
Example
Suppose users need to switch to another database and then need to check the current database name at that time, we use the following statement.
First, we need to use the different database as follows
First, we need to check all available databases from the server as follows.
show databases;Explanation:
By using the above statement, we list all databases from the MariaDB server and then use any of them. The final output of the show databases queries we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
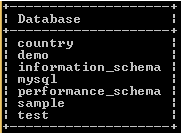
Syntax:
use database name;Explanation:
In the above syntax, the use database command is used to select a specific database from the MariaDB server, here, the database name is used to specify the database name we need to use as the current database.
Example
use demo;Explanation:
With the help of the above statement, we switch the database, which means one database to another database; here demo is the database name that we need to use for our workspace. The final output of the show databases queries we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
![]()
After switching databases, we again perform a select database command as follows.
select database();Explanation:
See hereafter switching the database name, we execute the select database () command to check the current database name, here, we changed the database sample to demo. The final output of the show databases queries we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
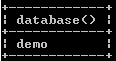
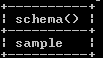
Now see how the schema works as follows.
select schema();Explanation:
In the above example, we use a select clause to fetch our workspace’s default database or current database. Here select clause followed by the schema keyword works similarly to a select database of our current workspace. The final output of the show databases queries we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
Now let’s see a different example of a select database as follows.
Suppose we created a new database name office, and we need to use it for the current workspace, so first, we need to create the database by using the following statement as follows.
create database office;Explanation:
In the above example, we used to create a database statement to create a new database here, we created a new database name, office. The final output of the show databases query we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
![]()
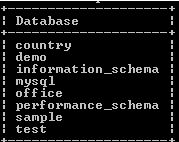
Now see the created database by using the following statement as follows.
show databases;Explanation:
In this example, we use the show databases command to list all databases from the MariaDB server. The final output of the show databases queries we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
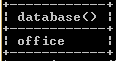
Now use the created database for our current workspace by using the following statement as follows.
use office;Explanation:
When executing the above statement, it shows the database is changed because of the use command. The final output of the show databases queries we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
![]()
Finally, we can now see the current database name by using the following statement.
select database();Explanation:
When we execute the above statement, which contains the select clause followed by the database keyword, it is used to see the current database of our workspace. The final output of the show databases queries we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
Conclusion
We hope from this article you have understood about the MariaDB select database. This article taught us the basic syntax of special databases and see different examples of select databases. This article taught us how and when to use MariaDB select database.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on the “MariaDB Select Database” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

