
Introduction to MariaDB JSON Functions
MariaDB provides one more important function to the user that is MariaDB JSON. Basically, the MariaDB JSON function is a standard text format, and it is used for data interchange as well as unstructured data. MariaDB JSON function supports almost all versions of MariaDB. The main advantage of the MariaDB JSON function is that some data are schema-less, and some data works strictly that is with schema in that case, how we can match the format of data. So using the MariaDB JSON function, we neat all unstructured data as per our requirement. In another way, we can explain MariaDB JSON function is like it builds a relation between structured and unstructured data.
Syntax:
create table table_name (colm name 1 data types (size), colm name 2 data types (size), …… colm name N data types (size), check( JSON_VALID(colm Name is or null) );Explanation:
- In the above syntax, we use a create table statement to implement the MariaDB JSON function.
- In which we created a table with different attributes as shown in the above statement.
- After that, we use the JSON function here we check the function of JSON. It is used to check the field of a specified column name.
How do JSON Functions work in MariaDB?
- Normally JSON functions work on unstructured data as well as works for data interchange.
- In structural data means we created table names as companies with different attributes and all attributes are in a well-structured format that means all content of the table is in well suited to relational format.
- On the other hand, we need to add different attributes into the table that have a different meaning this attribute we consider non – relational attributes. So MariaDB JSON works on data interpretation.
- In which that JSON function interchanges data to match the data type means all attributes in a single form.
- This is the working of the JSON function in MariaDB.
Examples of MariaDB JSON Functions
Given below are the examples of MariaDB JSON Functions:
Example #1
Structured Data.
Code:
create table computer(comuter_id int not null primary key auto_increment,
computer_name varchar(255) not null,
computer_price decimal(9,2) not null,
stock int not null,
attr varchar(1000));Explanation:
In the above table, we have a different attribute that looks like column names in relational database tables, and we have a column name as attr that can store any relevant information about the computer as a JSON string. Notice here we don’t use JSON as a data type because that is not available in MariaDB, but we can use it as a function, and it acts as a text string with JSON format. See here we have attr attribute that can store any kind of data, even non-valid JSON. The good thing in MariaDB is that we have a check constraint to check if an inserted value is valid or not valid after every insert or update operation in MariaDB. For that reason, we can use check constraint at the time of table creation as follows.
Code:
create table computer1(comuter_id int not null primary key auto_increment,
computer_name varchar(255) not null,
computer_price decimal(9,2) not null,
stock int not null,
attr varchar(1000),
check (json_valid (attr)));Explanation:
In the above example, we created the same table as the previous computer table; in this table, we just add a JSON function with a check constraint as shown in the above example.
The computer1 table has a different attribute as follows.
- computer_id is an integer column with auto_increment property, so MariaDB will automatically increment a sequential number when we insert a new row into the specified table. In addition, the computer_id column is a primary key constraint, as shown in the above statement.
- computer_name a variable-length character with a maximum size of the character. The computer_name has a not-null constraint that means we cannot insert null values into this column.
- computer_price is a decimal data type, and it also has not null constraint.
- stock int is an integer column, and it also has not null constraint.
- attr a variable-length character with a maximum size of the character.
Finally, we add a check constraint into the computer1 table by using the JSON function.
The result of the above statement we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
Output:
![]()
Now try to insert some records into the computer1 table by using the following statement.
Code:
insert into computer1 (computer_name, computer_price, stock, attr) values ("HP",20.1, 150, null);Explanation:
By using the above statement, we insert some records into the computer1 table. See here null value is not accepted by JSON function, so we need to change the table definition as follows.
Code:
create table computer1(comuter_id int not null primary key auto_increment,
computer_name varchar(255) not null,
computer_price decimal(9,2) not null,
stock int not null,
attr varchar(1000),
check (attr is null or json_valid (attr)));Explanation:
Here in this example, we add one more constraint as shown in the above statement to avoid the null constraint problem. Now try to insert records by using the following statement.
Code:
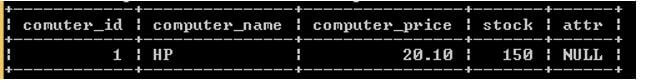
insert into computer1 (computer_name, computer_price, stock, attr) values ("HP",20.1, 150, null);
select * from computer1;Explanation:
Now everything is ok. We are able to insert data into the computer1 table because we already changed the table definition. The result of the above statement we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
Output:
Example #2
Indexing on JSON values.
Basically, MariaDB does not support functional indexes but virtual columns that can be indexed, but see here we use plain text column with data type name as attr, but we cannot create an index on an individual column JSON string due MariaDB does not support the functional indexing.
Example #3
Virtual Column.
Let’s see a simple example attribute attr with color. A virtual column that contains color extracted from the attr column and index on that. In this situation, we can use the JSON_VALUE function that accesses a JSON value and path.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MariaDB JSON Functions” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

