Updated April 17, 2023
Introduction to MariaDB Join
MariaDB provides join functionality to the user. Basically, join is used to retrieve data from multiple tables. When we have more than one table, and we need to display a combined attribute at that time, we can use join constraint, or we can say join functionality. Join operation is based on a matching column that we call keys; MariaDB provides different types of join constraint such as simple join, left join and right join. When we need to implement join constraint at that time, we must know basic about key constraint then and then we can use join constraint as per our requirement.
Types of Join in MariaDB
Given below are the three different types of MariaDB join:
1. MariaDB Inner Join
MariaDB inner join is also called simple join. In which we can show all records from either table or multiple tables when conditions are satisfied.
Syntax:
select colm name 1, colm name 2,…… colm name N
from table name 1
inner join table name 2
on table name 1.colm name = table name 2. Colm name;Explanation:
- In the above syntax, we use a select clause with an attribute of table name 1; after that, we use inner join with table name 2; the inner join keyword is used to retrieve data from both tables.
- Then we use another keyword that is on with the colm name of table 1 and colm name of table 2. This syntax is executed when the condition is matched.
Example:
We need two different tables for implementation purposes, so first, create two tables by using the following statement.
Code:
create table stud(
stud_id int auto_increment,
stud_name varchar(255) not null,
address varchar(255) not null,
primary key (stud_id));So first, we created a stud table with different attributes then insert some records by using insert into a statement as follows.
Code:
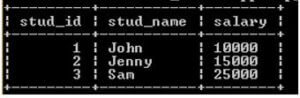
insert into stud(stud_name, address) values ("John", "Mumbai"), ("Jenny", "Goa"), ("Sam", "Mumbai");
select * from stud;Now the first table is ready, to create another table and insert some records by using the same process.
Code:
create table empp(
emp_id int auto_increment,
emp_dept varchar(255) not null,
salary varchar(255) not null,
primary key (emp_id));Now insert some records by using insert into the statement as follows.
Code:
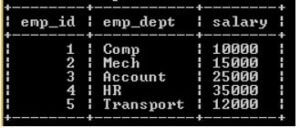
insert into empp(emp_dept, salary) values ("Comp", 10000), ("Mech", 15000), ("Account", 25000), ("HR", 35000), ("Transport",12000);
select * from empp;Now both tables are ready. The result of the above statement we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
Output:
stud table:
empp table:
Now we can implement inner join with the help of the above two tables and syntax as follows.
Code:
select stud_id, stud_name, salary from stud
inner join empp
on stud.stud_id = empp.emp_id;Explanation:
- Sometimes users want to see records from multiple tables. At that time, we use join here; we use an inner join to show a combined view of both tables.
- In this example, we use a select clause with column name from the first table as well as the second table as shown in the table; after that, we use inner join and on a keyword with conditions as shown in the above statement.
- The result of the above statement we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
Output:
Now we can compare the above screenshot for more details.
2. MariaDB Left Join
MariaDB Left Join is also called a left outer join. In which we return all rows from the left side table specified in the on condition and only those rows from the right table that match the condition.
Syntax:
select colm name 1, colm name 2,…… colm name N
from table name 1
left [outer] join table name 2
on table name 1.colm name = table name 2. Colm name;Explanation:
- In the above syntax, we use a select clause with join keywords such as left join and on; it works the same as an inner join.
- In the left join, it returns all rows from the left side table if condition is met.
Example:
We have two table stud and empp that were previously created; here, we assume stud is the left side table, and empp is the right side table.
Code:
select stud_id, stud_name, emp_dept from stud
left join empp
on stud.stud_id = empp.emp_id;Explanation:
- In the above example, we use a select clause with different attributes, as shown in the statement.
- Here we use the left join type of MariaDB join in which that left join returns all rows from the left side table, and the only condition matches rows from the right side table; in this example, our left side table is a stud.
- The result of the above statement we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
Output:
3. MariaDB Right Join
This is another type of MariaDB join; it is also called MariaDB Right Outer Join. Right works the same as left join. In the right join, it returns all rows from the right-hand side table and only matching rows from the left side table.
Syntax:
select colm name 1, colm name 2,…… colm name N
from table name 1
right [outer] join table name 2
on table name 1.colm name = table name 2. Colm name;Explanation:
- In the above syntax, we use the select clause the same as previous types. The only difference is that we use the right join keyword with the left side table and right side table.
Example:
Code:
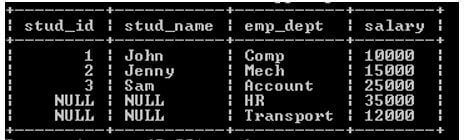
select stud_id, stud_name, emp_dept, salary from stud
right join empp
on stud.stud_id = empp.emp_id;Explanation:
- In the above example, we use a select clause with a combined attribute from both tables that we need to show; after that, we use the right join keyword with the right side table, and for condition purpose, we use on keyword as shown in the above statement.
- See here in the left side table there are 3 rows, and on the right side table, five rows are present; when we execute the above query, it returns all rows from the right-hand side and only matching rows from the left-hand side.
- The result of the above statement we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
Output:
Conclusion
From the above article, we saw types of Join with their basic syntax of each type, and we also see different examples of MariaDB Join. From this article, we saw how and when we use MariaDB Join.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MariaDB Join” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.